motan系列3——服务注册
1、回顾motan注册BeanDefinition
motan的整个注册、启动就是通过介入spring容器的启动来实现的,所以我们在这一节继续根据spring的启动顺序来看一下motan的服务注册。
在motan系列1——与spring集成中,我们介绍了motan是通过 AnnotationBean 实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,将添加了@MotanService注解的类的 BeanDefinition 注册到 BeanDefinitionRegistry 的。这里再说下 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,这个接口只提供了一个方法 ,用来修改类的 BeanDefinition 信息或是向 BeanDefinitionRegistry 注册一些自定义的类。
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory var1) throws BeansException;
2、motan解析@MotanService的spring链路
AnnotationBean 还实现了BeanPostProcessor ,其中的 postProcessAfterInitialization() 就是motan用来解析@MotanService注册服务的。motan在postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法中解析@MotanRefer,这个在后面分析。来看下这两个方法在spring启动过程中的调用:
BeanFactory.getBean()——>createBean()——>populateBean()(属性注入)——>initializeBean()(初始化bean),前置和后置处理器就是在initializeBean()方法中调用的。
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { //省略。。。 /** * 调用BeanPostProcessor后置处理器的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法 */ if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } /** * 先调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet,在调用我们定义的init方法 */ try { invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } /** * 调用BeanPostProcessor后置处理器的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法 */ if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
这就非常清晰地看到motan的调用时机了。
3、@MotanService的具体解析
代码如下,我们省略配置解析部分,这一步主要是解析service、basicService、protocol、registry中的信息(不清楚的可以参考motan的简单使用),将所有配置封装到com.weibo.api.motan.config.springsupport.ServiceConfigBean中。
@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Class<?> clazz = bean.getClass(); MotanService service = clazz.getAnnotation(MotanService.class); if (service != null) { ServiceConfigBean<Object> serviceConfig = new ServiceConfigBean<Object>(); /** * 缺省。。。 */ try { serviceConfig.afterPropertiesSet(); } catch (RuntimeException e) { throw (RuntimeException) e; } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } } serviceConfig.setRef(bean); serviceConfigs.add(serviceConfig); serviceConfig.export(); } return bean; }
来看下 ServiceConfigBean。
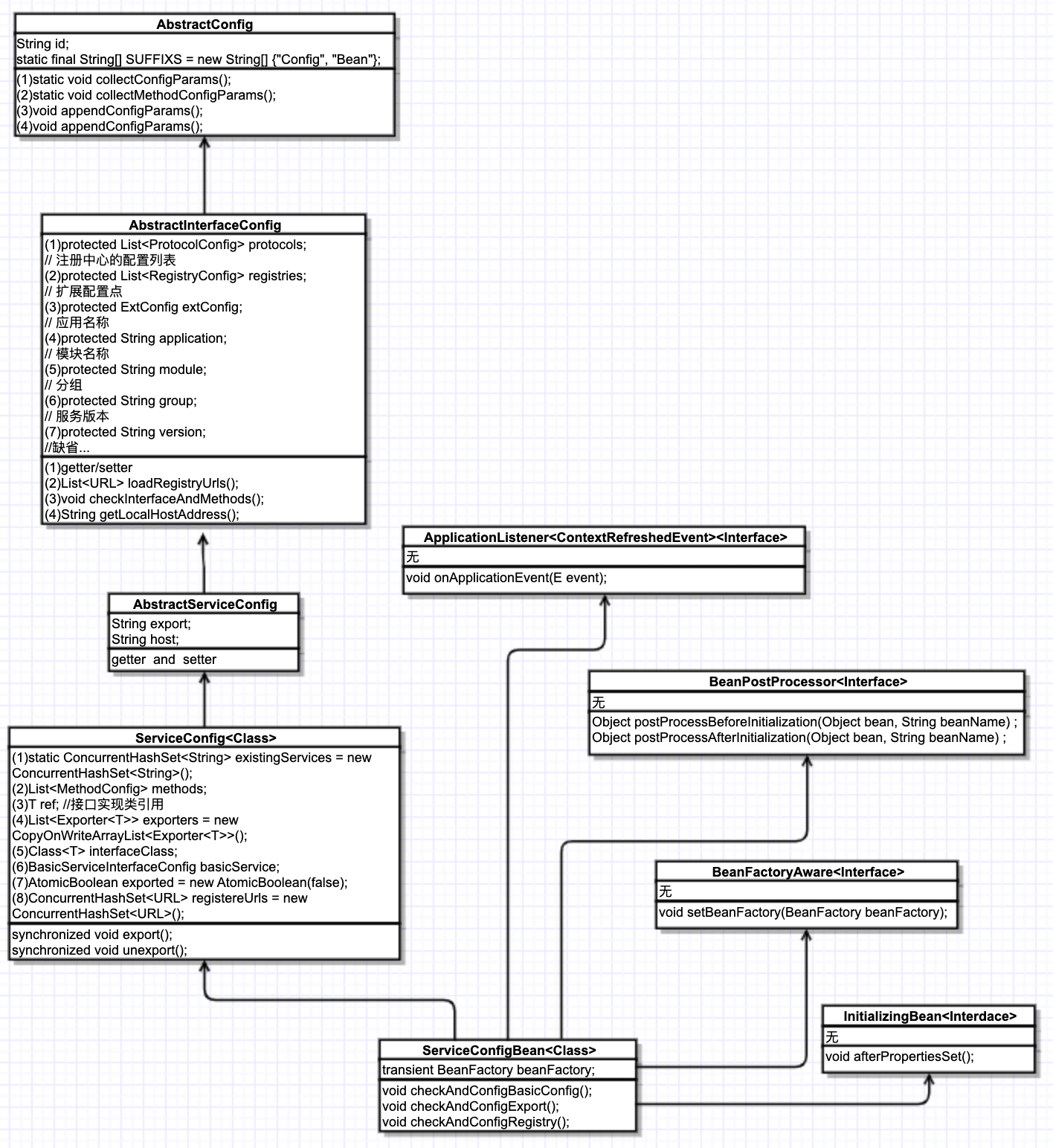
Motan将配置信息封装到 ServiceConfigBean 后,调用了 afterPropertiesSet() 方法,由上图可知,这个方法是 InitializingBean 接口中抽象方法的实现。
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // 注意:basicConfig需要首先配置,因为其他可能会依赖于basicConfig的配置 checkAndConfigBasicConfig(); // 检查是否已经装配export,如果没有则到basicConfig查找 checkAndConfigExport(); // 检查并配置registry checkAndConfigRegistry(); }
- 检查配置解析过程后,ServiceConfigBean的
basicService属性是否为空,如果是空,需要重新解析并设置他的值。
如何重新设置他的值呢?从UML图中我们可以找到 basicService 的位置,在 ServiceConfig 类中的第7个Field。字段类型是 BasicServiceInterfaceConfig。这个检查其实就是找到当前Spring容器中所有 BasicServiceInterfaceConfig 类型的bean,如果只找到一个,就把这个赋值到 basicService 上,如果有多个,需要找到 BasicServiceInterfaceConfig 的 isDefault 属性为true的那个,并赋值。
- 检查
export的值是否已经设置,如果没有设置,到basicService中查找。
这一步其实是检查 protocol,也就是 motan、motan2这些协议是否已经设置好,export字段的格式为:protocol1:port1,protocol2:port2。对应到UML中,export字段在 AbstractServiceConfig 类中。 这里同时会将 export 的值解析到 AbstractInterfaceConfig 的 protocols 字段中。
- 检查注册中心的配置
例如 zookeeper、consul 这些是否已经配置好。如果是空的话,还是从 basicService 中查找,并将结果配置到 AbstractInterfaceConfig 的 registries 属性中。
这些都检查好以后,basicService、export、protocols、registries这些字段就初始化好了。然后会将新创建出来的这个 ServiceConfigBean 实例添加到 AnnotationBean 的 serviceConfigs 属性中。
至此 @MotanService 解析完成,可以准备发布并注册服务了。
4、服务的发布与注册
在上面的步骤中完成了 motan 几个关键属性(protocol、registry)的封装。然后调用 serviceConfig.export() 的发布。
public synchronized void export() { // 这里加了个并发的控制,锁使用的是 this // 如果已经发布过了,直接返回 if (exported.get()) { LoggerUtil.warn(String.format("%s has already been expoted, so ignore the export request!", interfaceClass.getName())); return; } // 检查暴露服务的类是否是某个接口的实现,如果不是则抛出异常 // 检查暴露的方法是否在接口中存在,如果没有则抛出异常 checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods); // 解析注册中心地址,并将host、port等参数封装到URL类中 List<URL> registryUrls = loadRegistryUrls(); if (registryUrls == null || registryUrls.size() == 0) { throw new IllegalStateException("Should set registry config for service:" + interfaceClass.getName()); } // 解析协议和服务暴露的端口,默认为 `motan` 协议。Map的结构为:<协议, 端口> Map<String, Integer> protocolPorts = getProtocolAndPort(); for (ProtocolConfig protocolConfig : protocols) { Integer port = protocolPorts.get(protocolConfig.getId()); if (port == null) { throw new MotanServiceException(String.format("Unknow port in service:%s, protocol:%s", interfaceClass.getName(), protocolConfig.getId())); } // 注册并暴露服务 doExport(protocolConfig, port, registryUrls); } afterExport(); }
上述代码先初始化了暴露服务之前需要的一些数据:注册中心地址、服务协议、暴露端口等,真正执行服务注册的是 doExport 方法。这个方法较长,这里只贴出关键部分。
private void doExport(ProtocolConfig protocolConfig, int port, List<URL> registryURLs) { // ... 省略 ... // 省略部分代码主要作用是处理下面这行URL中的参数,例如:protocolName -> motan,hostAddress -> 本机IP,port -> 暴露端口 等 // map是解析出来的配置,以及一些默认配置,例如: /* "haStrategy" -> "failover" "module" -> "ad-common" "check" -> "false" "nodeType" -> "service" "version" -> "1.1.0" "filter" -> "cafTracing,pepperProfiler,sentinelProfiler" "minWorkerThread" -> "20" "retries" -> "1" "protocol" -> "motan" "application" -> "ad-common" "maxWorkerThread" -> "200" "shareChannel" -> "true" "refreshTimestamp" -> "1571821305290" "id" -> "ad-commonBasicServiceConfigBean" "export" -> "ad-commonProtocolConfigBean:8022" "requestTimeout" -> "30000" "group" -> "ad-common" */ URL serviceUrl = new URL(protocolName, hostAddress, port, interfaceClass.getName(), map); // 校验服务是否已经存在 // 注册完成的服务会添加到一个set中,serviceExists方法就是检查这个set中是否已经包含了这个服务的描述符(描述符的格式大概是host、port、protocol、version、nodeType组合的字符串) // serviceUrl就是这个东西:motan://192.168.100.14:8022/com.coohua.ad.common.remote.api.AdCommonRPC?group=ad-common if (serviceExists(serviceUrl)) { LoggerUtil.warn(String.format("%s configService is malformed, for same service (%s) already exists ", interfaceClass.getName(), serviceUrl.getIdentity())); throw new MotanFrameworkException(String.format("%s configService is malformed, for same service (%s) already exists ", interfaceClass.getName(), serviceUrl.getIdentity()), MotanErrorMsgConstant.FRAMEWORK_INIT_ERROR); } List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>(); // injvm 协议只支持注册到本地,其他协议可以注册到local、remote if (MotanConstants.PROTOCOL_INJVM.equals(protocolConfig.getId())) { // ... 省略,主要关注下面的注册中心暴露服务 } else { for (URL ru : registryURLs) { urls.add(ru.createCopy()); // 这里是一个浅拷贝,只是new了一个URL,具体字段用的还是之前的引用。 } } // registereUrls 是注册中心的URL for (URL u : urls) { u.addParameter(URLParamType.embed.getName(), StringTools.urlEncode(serviceUrl.toFullStr())); registereUrls.add(u.createCopy()); } ConfigHandler configHandler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ConfigHandler.class).getExtension(MotanConstants.DEFAULT_VALUE); // 到注册中心注册服务,urls是注册中心的地址 exporters.add(configHandler.export(interfaceClass, ref, urls)); }
最后调用 configHandler.export 注册时,经过上面的解析过程,url的parameters参数中已经包含了注册需要用到的信息,例如:
"path" -> "com.weibo.api.motan.registry.RegistryService"
"address" -> "192.168.103.254:2181"
"application" -> null
"name" -> "direct"
"connectTimeout" -> "3000"
"id" -> "ad-commonRegistryConfigBean"
"refreshTimestamp" -> "1571821250310"
"embed" -> "motan%3A%2F%2F192.168.100.14%3A8022%2Fcom.coohua.ad.common.remote.api.AdCommonRPC%3FhaStrategy%3Dfailover%26module%3Dad-common%26check%3Dfalse%26nodeType%3Dservice%26version%3D1.1.0%26filter%3DcafTracing%2CpepperProfiler%2CsentinelProfiler%26minWorkerThread%3D20%26retries%3D1%26protocol%3Dmotan%26application%3Dad-common%26maxWorkerThread%3D200%26shareChannel%3Dtrue%26refreshTimestamp%3D1571821305290%26id%3Dad-commonBasicServiceConfigBean%26export%3Dad-commonProtocolConfigBean%3A8022%26requestTimeout%3D30000%26group%3Dad-common%26"
"requestTimeout" -> "1000"
接下来看一下 configHandler.export 做了什么事情。
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Class<T> interfaceClass, T ref, List<URL> registryUrls) { // 解码url -> motan://192.168.100.14:8022/com.coohua.ad.common.remote.api.AdCommonRPC?group=ad-common String serviceStr = StringTools.urlDecode(registryUrls.get(0).getParameter(URLParamType.embed.getName())); URL serviceUrl = URL.valueOf(serviceStr); // export service String protocolName = serviceUrl.getParameter(URLParamType.protocol.getName(), URLParamType.protocol.getValue()); // SPI的方式拿到具体的Protocol实现,默认情况下拿到 motan 的 Protocol Protocol orgProtocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getExtension(protocolName); Provider<T> provider = getProvider(orgProtocol, ref, serviceUrl, interfaceClass); Protocol protocol = new ProtocolFilterDecorator(orgProtocol); // 在这里走Motan的filter chain,并启动服务,filter chain通过调用 ProtocolFilterDecorator 的 decorateWithFilter 方法实现 // 走完filter chain后,会调用 orgProtocol 的 export 方法来暴露服务,这个方法的实现在 AbstractProtocol 类中 Exporter<T> exporter = protocol.export(provider, serviceUrl); // 在注册中心中注册服务 register(registryUrls, serviceUrl); return exporter; }
在 AbstractProtocol 的 export 方法中会调用 createExporter 方法创建一个 Exporter 类的实例(具体来说是 DefaultRpcExporter),在这个创建过程中会调用 NettyEndpointFactory 的 createServer 方法创建一个Server出来,并存放在exporter的server变量中。
然后调用 exporter 的 init 方法,在 init 方法中又调用了 doInit 方法,这个方法调用了 server.open(),至此,服务启动,并监听在本机指定的端口上。
@Override protected boolean doInit() { boolean result = server.open(); return result; }
server.open()中,就是netty启动监听端口了。
@Override public boolean open() { if (isAvailable()) { LoggerUtil.warn("NettyServer ServerChannel already Open: url=" + url); return state.isAliveState(); } if (bossGroup == null) { bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); } LoggerUtil.info("NettyServer ServerChannel start Open: url=" + url); boolean shareChannel = url.getBooleanParameter(URLParamType.shareChannel.getName(), URLParamType.shareChannel.getBooleanValue()); final int maxContentLength = url.getIntParameter(URLParamType.maxContentLength.getName(), URLParamType.maxContentLength.getIntValue()); int maxServerConnection = url.getIntParameter(URLParamType.maxServerConnection.getName(), URLParamType.maxServerConnection.getIntValue()); int workerQueueSize = url.getIntParameter(URLParamType.workerQueueSize.getName(), URLParamType.workerQueueSize.getIntValue()); int minWorkerThread, maxWorkerThread; if (shareChannel) { minWorkerThread = url.getIntParameter(URLParamType.minWorkerThread.getName(), MotanConstants.NETTY_SHARECHANNEL_MIN_WORKDER); maxWorkerThread = url.getIntParameter(URLParamType.maxWorkerThread.getName(), MotanConstants.NETTY_SHARECHANNEL_MAX_WORKDER); } else { minWorkerThread = url.getIntParameter(URLParamType.minWorkerThread.getName(), MotanConstants.NETTY_NOT_SHARECHANNEL_MIN_WORKDER); maxWorkerThread = url.getIntParameter(URLParamType.maxWorkerThread.getName(), MotanConstants.NETTY_NOT_SHARECHANNEL_MAX_WORKDER); } standardThreadExecutor = (standardThreadExecutor != null && !standardThreadExecutor.isShutdown()) ? standardThreadExecutor : new StandardThreadExecutor(minWorkerThread, maxWorkerThread, workerQueueSize, new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyServer-" + url.getServerPortStr(), true)); standardThreadExecutor.prestartAllCoreThreads(); channelManage = new NettyServerChannelManage(maxServerConnection); ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast("channel_manage", channelManage); pipeline.addLast("decoder", new NettyDecoder(codec, NettyServer.this, maxContentLength)); pipeline.addLast("encoder", new NettyEncoder()); pipeline.addLast("handler", new NettyChannelHandler(NettyServer.this, messageHandler, standardThreadExecutor)); } }); serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true); serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(url.getPort())); channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly(); serverChannel = channelFuture.channel(); state = ChannelState.ALIVE; StatsUtil.registryStatisticCallback(this); LoggerUtil.info("NettyServer ServerChannel finish Open: url=" + url); return state.isAliveState(); }
此时服务已经成功启动了,但还没注册到注册中心,所以还不能被发现。接下来,继续上面的代码,看一下 register(registryUrls, serviceUrl); 这行代码干了啥。
此时两个参数的值分别是:
- registryUrls:zookeeper://192.168.103.254:2181/com.weibo.api.motan.registry.RegistryService?group=default_rpc
- serviceUrl:motan://192.168.100.14:8022/com.coohua.ad.common.remote.api.AdCommonRPC?group=ad-common
这个方法的实现如下:
private void register(List<URL> registryUrls, URL serviceUrl) { for (URL url : registryUrls) { // 根据protocol的名称获取具体的 RegistryFactory ,这里以 zookeeper 为例 RegistryFactory registryFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RegistryFactory.class).getExtension(url.getProtocol()); if (registryFactory == null) { throw new MotanFrameworkException(new MotanErrorMsg(500, MotanErrorMsgConstant.FRAMEWORK_REGISTER_ERROR_CODE, "register error! Could not find extension for registry protocol:" + url.getProtocol() + ", make sure registry module for " + url.getProtocol() + " is in classpath!")); } // 尝试获取url对应registry已有的实例,如果没有,就创建一个 // 这里zookeeper是用ZkClient管理的 Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url); // 在zk中创建Node,完成服务的注册 registry.register(serviceUrl); } }
ZK中的注册结果:
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 0] ls /motan/ad-common/com.coohua.ad.common.remote.api.AdCommonRPC/server
[192.168.100.14:8022]
至此,服务就可以被调用方发现了。


