Spring容器启动前传——web应用
spring是通过实现ServletContext的监听器来创建和初始化整个容器的,那ServletContext又是什么呢?
可以把它理解为Web应用的一个共享内存,一个Web应用对应一个ServletContext,项目启动时就会创建ServletContext(关于ServletContext可以看一下这篇文章https://www.jianshu.com/p/31d27181d542,这不是本文的重点)
spring也根据容器生命周期提供了各种事件,许多中间件集成spring也是基于这些事件来做的,这也是框架提供可扩展的一种方式,如下图:
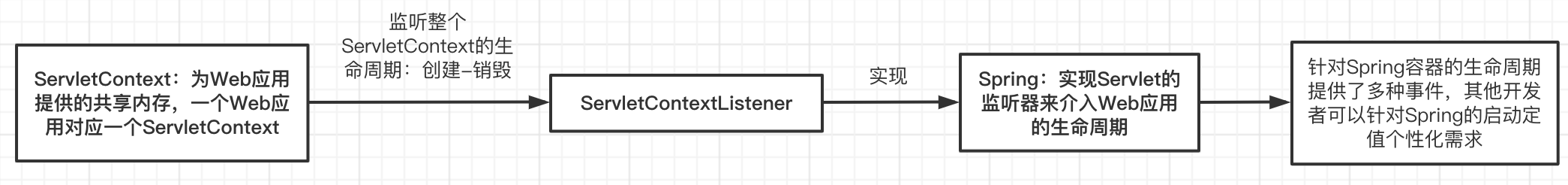
当创建ContextLoaderListener时,由于监听器实现了ServletContextListener接口,而ServletContextListener提供了监听web容器启动时,初始化ServletContext后的事件监听及销毁ServletContext前的事件监听;因此,contextLoaderListener默认实现contextInitialized和contextDestroyed这两个方法;容器的初始化就是从contextInitialized开始的;
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
* 初始化容器
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
* 销毁容器
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
initWebApplicationContext(servletContext)方法,其中又两个重要的方法。
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) { if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " + "check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!"); } Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class); servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that // it is available on ServletContext shutdown. if (this.context == null) {
/**
* 创建上下文
*/ this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); } if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> // determine parent for root web application context, if any. ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext); cwac.setParent(parent); }
/**
* 加载配置和刷新上下文
*/ configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext); } }
/**
* 将上下文设置到ServletContext中
*/ servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) { currentContext = this.context; } else if (ccl != null) { currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" + WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]"); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } return this.context; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex); throw ex; } catch (Error err) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", err); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err); throw err; } }
先看下 createWebApplicationContext(servletContext) 方法:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) { Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc); if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]"); } return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }
determineContextClass(sc) 方法是确定要创建的上下文类型,可以定义自己的实现类,如下:在web.xml中配置
<context-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>My ContextClass</param-value>
</context-param>
如果没有定义,就用默认的 WebApplicationContext。
再来看下 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext) 方法。
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) { if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) { // The application context id is still set to its original default value // -> assign a more useful id based on available information String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM); if (idParam != null) { wac.setId(idParam); } else { // Generate default id... wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath())); } } wac.setServletContext(sc); /** * 设置配置文件加载路径 */ String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM); if (configLocationParam != null) { wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam); } // The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context // is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for // use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh /** * 创建系统环境 */ ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment(); if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { /** * 获取系统参数和属性配置 */ ((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null); } /**
* 设置自定义的全局初始化器和上下文初始化器
*/ customizeContext(sc, wac); wac.refresh(); }
获取配置文件路径,可以自己设置,如下:
<servlet>
<!-- 通过初始化参数,指定xml文件的位置 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:my-spring.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
如果没有设置,默认的是在/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml。
getEnvironment() 方法,会创建 StandardServletEnvironment 类,在创建其父类 AbstractEnvironment 创建时会读取系统环境参数和属性配置。
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initialized " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " with PropertySources " + this.propertySources);
}
}
看下 customizePropertySources(this.propertySources) 方法
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
获取属性配置 getSystemProperties() 其实就是调用的 System.getProperties() ,获取环境参数 getSystemEnvironment() 调用的 System.getenv()。
customizeContext(sc, wac) 方法就是实例化自己定义的初始化器,并只执行。关于 AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer spring中并没有任何实现,是其提供的一个扩展点,springBoot中有很多实现。具体的逻辑可以参考这篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/f641385712/article/details/92709404
最后,看到refresh是不是就比较亲切了。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号