Spring容器启动流程——源码阅读分析
上文讲了Web应用Spring是通过监听器来启动的,容器的初始化就是从refresh( ) 方法开始的,接下来我们就从refresh( ) 方法来看看Spring启动都做了什么。
Tips:一定要结合源码自己好好梳理一遍,这样才能印象更加深刻,理解了Spring整个容器的生命周期,对于理解其他很多框架也是很有帮助的。
这篇文章分析了整个IOC容器启动流程的细节,篇幅较长,可以先看大概流程,然后再深入看细节。
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. //1、调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识 prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. //2、告诉子类启动refreshBeanFactory()方法,Bean定义资源文件的载入 // 创建bean工厂供后面方法使用——DefaultListableBeanFactory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. //3、为BeanFactory配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. //4、为容器的某些子类指定特殊的BeanPost事件处理器 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. //5、调用所有注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的Bean invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. //6、为BeanFactory注册BeanPost事件处理器. //BeanPostProcessor是Bean后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. //7、初始化信息源,和国际化相关. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. //8、初始化容器事件传播器. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. //9、调用子类的某些特殊Bean初始化方法 onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. //10、为事件传播器注册事件监听器. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. //11、初始化所有剩余的单例Bean,这一步执行了Bean属性注入、Bean初始化(执行后置处理器、init-method方法等) finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. //12、初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. //13、销毁已创建的Bean destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. //14、取消refresh操作,重置容器的同步标识。 cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... //15、重设公共缓存 resetCommonCaches(); } } }
大概了解了整个流程之后我们具体看下各个部分具体逻辑,spring提供很多能够介入容器启动过程的机会,可以基于此来定制化实现自己的逻辑。
1、prepareRefresh() 方法
protected void prepareRefresh() { /** * 设置启动时间、启动标识 */ this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); this.closed.set(false); this.active.set(true); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Refreshing " + this); } /** * 获取servletContext中的参数 */ // Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment initPropertySources(); /** * 这个过程分为两步 * (1)getEnvironment() 读取系统配置,设置环境变量 * (2)validateRequiredProperties() 验证所必须的系统参数是否为空,有为空的就会收集到一起统一抛出异常 */ // Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable // see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); /** * 创建早期的事件集合 */ // Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents, // to be published once the multicaster is available... this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>(); }
这个方法主要做一些准备工作,包括ServletContext参数、系统(JVM和OS)环境变量和属性配置的获取和校验等。这里要说到两个接口 Environment 和 PropertySources。
Environment 是spring对系统环境的抽象,包括系统环境和属性配置,系统环境如JVM和OS参数,已经通过System.setProperty() 设置的参数。PropertySources 是 PropertySource 的集合,是spring管理和保存属性配置的关键接口。比如可以通过@PropertySource(*.properties) 指定配置文件。
getEnvironment() 方法,以Web应用为例,会创建 StandardServletEnvironment 类,在创建其父类 AbstractEnvironment 创建时会读取系统环境参数和属性配置。
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initialized " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " with PropertySources " + this.propertySources);
}
}
看下 customizePropertySources(this.propertySources) 方法
@Override protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) { propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties())); propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment())); }
获取属性配置 getSystemProperties() 其实就是调用的 System.getProperties() ,获取环境参数 getSystemEnvironment() 调用的 System.getenv()。
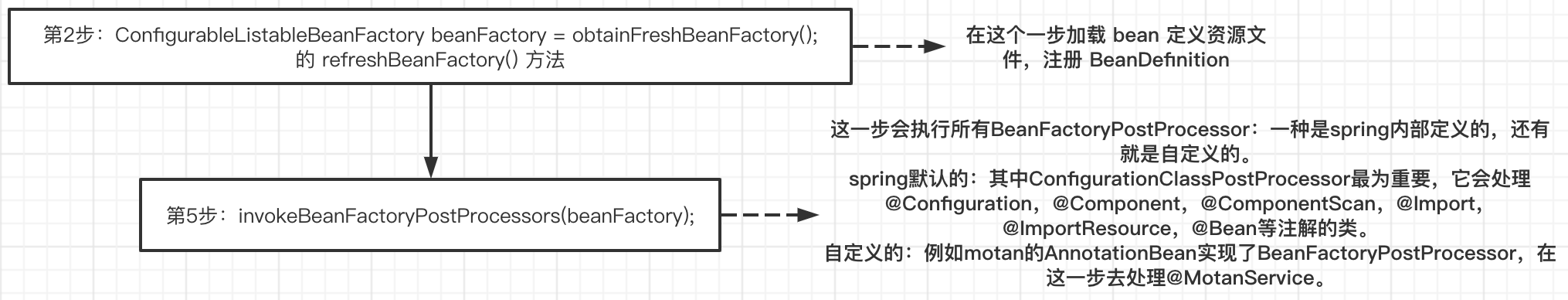
2、obtainFreshBeanFactory()
这个方法完成了容器初始化的最重要最基础的功能,Bean定义资源的Resource定位、载入解析和注册。
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { /** * 这里使用了委派设计模式,父类定义了抽象的refreshBeanFactory()方法,具体实现调用子类容器的refreshBeanFactory()方法 */ refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory;
}
先看下子类创建容器的 refreshBeanFactory() 方法:
* * 该实现真正执行上下文底层bean工厂的刷新,关闭之前存在的bean工厂(有过有的话),并初始化一个新的bean工厂 */ @Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //如果已经有容器,销毁容器中的bean,关闭容器 if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //创建IOC容器 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); //设置两个参数 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); /**
* 加载Bean定义数据,这里又使用了一个委派模式,在当前类中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体的实现调用子类容器
* 这一步也会将解析出的BeanDefinition 添加到BeanDefinitionMap中
*/
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory) 设置容器的两个属性配置:allowBeanDefinitionOverriding-是否允许bean覆盖(spring默认是true,SpringBoot默认是false),allowCircularReferences-是否允许循环依赖(默认为true)
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) { beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); } if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) { beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences); } }
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory) 方法又是一个委派模式,主要有xml、annotation等方式的解析
这里我们看下注解方式的实现:AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
//载入注解Bean定义资源 @Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { //为容器设置注解Bean定义读取器 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader = getAnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); //为容器设置类路径Bean定义扫描器 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = getClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory); //获取容器的Bean名称生成器 BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = getBeanNameGenerator(); //为注解Bean定义读取器和类路径扫描器设置Bean名称生成器 if (beanNameGenerator != null) { reader.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator); scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator); beanFactory.registerSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR, beanNameGenerator); } //获取容器的作用域元信息解析器 ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = getScopeMetadataResolver(); //为注解Bean定义读取器和类路径扫描器设置作用域元信息解析器 if (scopeMetadataResolver != null) { reader.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver); scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver); } if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Registering annotated classes: [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(this.annotatedClasses) + "]"); } reader.register(this.annotatedClasses.toArray(new Class<?>[this.annotatedClasses.size()])); } if (!this.basePackages.isEmpty()) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Scanning base packages: [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(this.basePackages) + "]"); } scanner.scan(this.basePackages.toArray(new String[this.basePackages.size()])); } //获取容器定义的Bean定义资源路径,这个资源路径是在 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext) 方法中设置的 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); //如果定位的Bean定义资源路径不为空 if (configLocations != null) { for (String configLocation : configLocations) { try { //使用当前容器的类加载器加载定位路径的字节码类文件 Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(configLocation, getClassLoader()); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Successfully resolved class for [" + configLocation + "]"); } reader.register(clazz); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not load class for config location [" + configLocation + "] - trying package scan. " + ex); } //如果容器类加载器加载定义路径的Bean定义资源失败 //则启用容器类路径扫描器扫描给定路径包及其子包中的类 int count = scanner.scan(configLocation); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { if (count == 0) { logger.info("No annotated classes found for specified class/package [" + configLocation + "]"); } else { logger.info("Found " + count + " annotated classes in package [" + configLocation + "]"); } } } } } }
其中bean的加载在loadBeanDefinitions,通过BeanDefinitionReader进行解析(包括xmlBeanDefinitionReader、annotationBeanDefinitionReader等)
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//为容器设置注解Bean定义读取器
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader = getAnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//为容器设置类路径Bean定义扫描器
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = getClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);
...............
reader.register(clazz);
...........
}
将解析出的BeanDefinition注册到beanDefinitionMap中
//向IOC容器注册解析的BeanDefiniton
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
..............// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
..............
}
3、prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory) 方法
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc. /** * 设置上下文类加载器 */ beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader()); /** * 添加bean表达式解释器,为了能够让我们的beanFactory去解析bean表达式 * 模板默认以前缀“#{”开头,以后缀“}”结尾 * 可以修改默认额前缀后缀 * 通过beanFactory.getBeanExpressionResolver()获得BeanExpressionResolver * 然后resolver.setExpressionPrefix("%{");resolver.setExpressionSuffix("}"); * * 那么什么时候用到这个解析器? * 就是在Bean进行初始化后会有属性填充的一步,方法如下: * protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) { * //属性填充 * applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); * } * 最终会通过AbstractBeanFactory中的evaluateBeanDefinitionString方法进行解析 * 然后这时候就进到StandardBeanExpressionResolver中的evaluate方法中进行解析了 */ beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); /** * spring内部的属性编辑器 * 添加PropertyEditor属性编辑器(可以将我们的property动态设置为bean里面对应的属性类型) * 比如:property赋值的是路径名(classpath/spring.xml),而对应bean属性设置的是Resource,则有spring的ResourceEditor完成转换 * springframework-bean下的propertyEditors包下有很多spring自带的属性编辑器 * 其中刚才提到的ResourceEditor在springframework-core下的io包里面 * * 可以自定义属性编辑器,通过实现PropertyEditorSupport接口,spring中自带的属性编辑器也是这么做的 * 使用ApplicationContext,只需要在配置文件中通过CustomEditorConfigurer注册即可。 * CustomEditorConfigurer实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,因而是一个Bean工厂后置处理器 * 在Spring容器中加载配置文件并生成BeanDefinition后会被执行。CustomEditorConfigurer在容器启动时有机会注册自定义的属性编辑器 */ beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment())); // Configure the bean factory with context callbacks. /** * 添加一个BPP * ApplicationContextAwareProcessor:能够在bean中获得各种*Aware */ beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this)); /** * 跳过以下6个属性的自动注入 * 因为在ApplicationContextAwareProcessor中已经完成了手动注入 */ beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); // BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory. // MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean. /** * 注册几个自动装配相关的类和实例 * 在应用代码就可以通过类型自动装配把工厂实例和ApplicationContext实例设置到自定义bean的属性中 * * 例如:这几个属性都会被自动设置,虽然没有在显示的在bean定义xml中注入它们 * private BeanFactory beanFactory; * private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; * private ApplicationEventPublisher appEventPublisher; * private ApplicationContext appContext; */ beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this); // Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners. /** * 添加一个,处理时间监听器 */ beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this)); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found. /** * 当容器检查到定义了名称为loadTimeWeaver的bean时 * 会注册一个LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor到容器中 * * 这个BPP用来处理LoadTimeWeaverAware接口的 * 把LTW实例设置到实现了LoadTimeWeaverAware接口的bean中 */ if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); // Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching. beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } // Register default environment beans. /** * 就是一些系统配置和系统环境信息 * 如果发现没有这些bean则spring自己注册 */ if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment()); } }
这里说几个点:
(1)设置属性编辑器 ResourceEditorRegistrar
属性编辑就是为了方便使用配置的,spring内置了很多属性编辑器,举个例子:
<bean id="sqlSessionFactorybbcbaseshop" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis/mybatis-sql.xml"></property>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSourceA"></property>
</bean>
上面配置的 configLocation 配置的是个文件地址,但是spring会将它的值转换成 Resource 类型,自动解析文件,将文件中对应的属性值设置到Resource中。
详细的属性配置可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/yu_kang/article/details/88395593
(2)添加后置处理器ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
添加了一个BeanPostProcessor,bean后置处理器,在实例化bean的时候会调用(这里是一个常用的扩展方式)
BeanPostProcessor接口有两个方法:
postProcessBeforeInitialization:初始化前执行
postProcessAfterInitialization:初始化后执行
看ApplicationContextAwareProcessor源码可知,实现重写了postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,会在实例化bean前调用
@Override @Nullable public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { AccessControlContext acc = null; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware || bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware || bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)) { acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext(); } if (acc != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); return null; }, acc); } else { invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); } return bean; } private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) { ((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment()); } if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) { ((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver); } if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) { ((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) { ((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) { ((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext); } } }
其中主要方法 invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) 意思就是当bean 实现以上*Aware 接口时,通过setter方法给bean赋予对应的属性参数。例如:可以通过实现 ApplicationContextAware 来获得上下文。
@Component public class Myservice implements ApplicationContextAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { applicationContext = this.applicationContext; } }
当然也可以简单使用@Autowired注入来获取上下文。
@Autowired private ApplicationContext appContext;
(3)添加后置处理器 ApplicationListenerDetector
也是一个BeanPostProcessor,在bean初始化完成后判断是不是监听器,是的话将它注册到应用的事件多播器上。
@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) { /** * 判断 bean 是不是一个 ApplicationListener 监听器 */ if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) { // potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName); /** * 监听器要是单例才能被添加到监听器集合中,后面事件广播就是对监听器集合循环去执行 */ if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) { // singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean); } else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) { // inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " + "but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " + "because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " + "to be of non-singleton scope."); } this.singletonNames.remove(beanName); } } return bean; }
4、postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory) 方法
这个方法 AbstractApplicationContext 并没有具体实现,由子类去实现,注册一些特殊的beanPost事件。比如:子类 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext 的实现
@Override protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig)); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class); WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext); WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig); }
到这里位置已经注册了三个后置处理器:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor、ApplicationListenerDetector、ServletContextAwareProcessor
5、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { /** * getBeanFactoryPostProcessors获取自定义的beanFactoryPostProcessor * 这里自定义指的是:不通过注解形式扫描获取 * 而是通过手动context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(beanFactoryPostProcessor)完成自定义 * * getBeanFactoryPostProcessors默认是个空的List */ PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime // (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor) if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } }
这里有个重要的方法,就是 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法。
这个方法有点长,先概述下大体执行逻辑,大概可以分为两步来看:
(1)spring内部bean进行包的扫描和解析:spring 在解析内部bean ——>BeanDefinition 的时候,注册了一个类 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,这个类实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor (它又是BeanFactoryPostprocessor的子类),获取 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的 BeanDefinition 并实例化放入列表中,在循环列表执行。ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的主要作用就是扫描包、并将包下的类注册成 BeanDefinition。
(2)获取所有实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 BeanDefinition,实例化去执行。BeanFactoryPostProcessor 也是spring提供的一个扩展点,可以实现该接口来修改 BeanDefinition 元信息数据。
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); /**
*beanFactory就是DefaultListableBeanFactory,它实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry
*/ if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; /** * 常规的BeanFactoryPostProcessor */ List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<>(); /** * 实现自定义注册bean定义逻辑的BeanFactoryPostProcessor */ List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList<>(); /** * beanFactoryPostProcessors默认为空 * 除非通过context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(beanFactoryPostProcessor)添加 */ for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! // Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement // PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. /** * 这里得到一个 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor(其实也是BeanFactoryPostProcessor) * BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子类 * 这里的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 是spring自己在最开始注册的 * 在哪里注册的呢? * 是在解析 BeanDefinition 时注册的,AnnotationConfigUtils#registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 方法中, * 注册的类型 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor, * 这里断点可以看到,实际的类是 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。 */ String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { /** * 将实例化后的对象添加到列表中,在后面循环调用 */ currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } /** * 排序,其实这里只有一条数据 */ sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); /** * 这个方法比较关键 * 开始循环调用添加到列表中的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor * * 其中有一个spring内部的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors——>ConfigurationClassPostProcessor * 处理@Configuration/@Component等注解,扫描、注册包下的类 * 处理@Import/@ImportResource/@Bean等 */ invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); /** * 清空list,后面还要用 */ currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear. boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. /** * 前面执行的是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子类 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的回调 * 现在执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的回调 */ invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } else { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! /** * 在上面spring 已经通过提前注册的内部bean 进行了包下面类的扫描和注册,这里就可以获得到所有 BeanFactoryPostProcessor * 这里包括我们自己实现的类。这也是spring 提供的一个扩展点。可以通过实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 来修改类的 beanDefinition 元信息。 * * 下面也是循环执行了。 */ String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have // modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values... beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }
上面有个重要的方法 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry) ,调用链路:invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors ——>循环调用 postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry) ——> ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法。
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors( Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) { postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); } }
因为 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,所以最终调用的是 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry,继续跟进
@Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { /** * 通过hash来保证一个工厂的后置处理器只能执行一次 */ int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry); if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry); } if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry); } this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId); processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry); }
继续跟进 processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry),这个方法就是处理所有已经注册的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>(); /** * registry就是DefaultListableBeanFactory * 获取注册的所有beanName */ String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); /** * 循环处理所有BeanDefinition */ for (String beanName : candidateNames) { BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { /** * 如果BeanDefinition中的configurationClass属性为full或者lite,则意味着已经处理过了,直接跳过 * * 后面处理BeanDefinition时,会给 BeanDefinition 设置一个属性(key为configurationClass,value为full或者lite) */ if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef); } } /** * 判断当前 BeanDefinition 是否为 Configuration class * 这里要说明一下:full configuration 和 lite configuration * full configuration: 带有@Configuration注解的类,通过beanDef.setAttribute设置为full * lite configuration: 带@Component,@ComponentScan,@Import,@ImportResource,@Bean 5个注解中的任一个,通过beanDef.setAttribute设置的 */ else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName)); } } // Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found /** * 这里的configCandidates只有加了上述注解的BeanDefinition */ if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) { return; } // Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable /** * 如果加了@Order注解,则进行排序 */ configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> { int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition()); int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition()); return (i1 < i2) ? -1 : (i1 > i2) ? 1 : 0; }); // Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context /** * 当前传入的 DefaultListableBeanFactory 是 SingletonBeanRegistry 的子类 */ SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null; if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) { sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry; /** * 判断是否有自定义的beanName生成器 */ if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) { /** * 获取spring默认的beanName生成器,这里为空 */ BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR); if (generator != null) { /** * componentScanBeanNameGenerator与importBeanNameGenerator定义时就赋值了new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator() * 如果spring有默认的beanName生成器,则重新赋值 */ this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator; this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator; } } } if (this.environment == null) { this.environment = new StandardEnvironment(); } // Parse each @Configuration class /** * 实例化ConfigurationClassParser 为了解析各个配置类(带上述注解的类) * 初始化ConfigurationClassParser的一些属性 */ ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser( this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry); /** * 实例化两个set * candidates 用于将之前加入的 configCandidates 去重 * alreadyParsed 用于判断是否处理过了 */ Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates); Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size()); do { /** * 解析带有 * @Controller/ @Import/ @ImportResource/ @ComponentScan/ @ComponentScans/ @Bean * 的beanDefinition * * 开始扫描/注册包下的类 */ parser.parse(candidates); parser.validate(); /** * 获取在扫描时put进去的configurationClasses */ Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses()); configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed); // Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content if (this.reader == null) { this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader( registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment, this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry()); } /** * 在这里统一处理 * 没有注册的进行注册 */ this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses); alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses); candidates.clear(); if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) { String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames)); Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>(); for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) { alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); } for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) { if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) { BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) && !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) { candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName)); } } } candidateNames = newCandidateNames; } } while (!candidates.isEmpty()); // Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes if (sbr != null) { if (!sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) { sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry()); } } if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) { // Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op // for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext. ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache(); } }
再看下筛选候选配置类的方法 ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate(BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) { String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName(); if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null) { return false; } AnnotationMetadata metadata; /** * 1.通过注解注入的BeanDefinition都是AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition,实现了AnnotatedBeanDefinition * 2.spring内部的BeanDefinition是RootBeanDefinition,实现了AbstractBeanDefinition * * 这里判断是不是带有主节点的BeanDefinition */ if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition && className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) { // Can reuse the pre-parsed metadata from the given BeanDefinition... metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata(); } /** * 判断是否spring默认的BeanDefinition */ else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) { // Check already loaded Class if present... // since we possibly can't even load the class file for this Class. Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass(); metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata(beanClass, true); } else { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className); metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); } catch (IOException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " + className, ex); } return false; } } /** * 判断当前BeanDefinition是否存在@Configuration注解 * * 如果存在@Configuration,spring认为他是一个全注解类 */ if (isFullConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { /** * 如果存在@Configuration注解,则为当前BeanDefinition设置configurationClass属性为full */ beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL); } /** * 判断是否存在以下注解的bd * candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName()); * candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName()); * candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName()); * candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName()); * 或者有方法带有@Bean的bd(metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName())) * * 如果存在spring认为他是一个部分解类 */ else if (isLiteConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { /** * 如果存在以上注解,则为当前BeanDefinition设置configurationClass属性为lite */ beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE); } else { return false; } // It's a full or lite configuration candidate... Let's determine the order value, if any. Integer order = getOrder(metadata); if (order != null) { beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order); } return true; }
小结:到这里,我们先梳理一下较为关键步骤。
6、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
这个方法注册BeanPostProcessor,包括spring默认的和自定义的。
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { /** * 获取容器中beanDefinition类型为BeanPostProcessor的bdName * 这里有spring默认的和自定义的 * spring默认的:初始化AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader时注册的三个() * AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor * RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor * CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor * 自定义的:(1)实现BeanPostProcessor接口 (2)通过@Enable导入 */ String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. /** * beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() 是指已经通过 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(bpp)添加到 List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors中的 * 通过debug可知,此时的 beanPostProcessors 中有三个spring默认的BPP: * 1、在 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory) 步骤添加的后置处理器——ApplicationContextAwareProcessor与ApplicationListenerDetector * 2、在 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory) 步骤添加的——ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor */ int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. /** * 下面就是分类注册进 beanPostProcessors 中 */ List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners, // moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc). beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); }
7、initMessageSource()
这一步没什么意思,就不看了。
8、initApplicationEventMulticaster()
这一步注册事件监听广播器。
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); /** * 判断容器中是否存在bdName为applicationEventMulticaster的bd * 也就是自定义的事件监听多路广播器,必须实现ApplicationEventMulticaster接口 */ if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { this.applicationEventMulticaster = beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); } } else { /** * 如果没有,则默认采用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster */ this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory); beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); } } }
9、onRefresh()
spring默认为空实现,供子类扩展。
10、registerListeners()
protected void registerListeners() { // Register statically specified listeners first. /** * getApplicationListeners就是获取applicationListeners * 是通过applicationListeners(listener)添加的 * 放入applicationListeners中 */ for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! /** * 从容器中获取所有实现了ApplicationListener接口的beanDefinition的bdName * 放入applicationListenerBeans */ String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false); for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); } // Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster... /** * 这里先发布早期的监听器,默认为空 */ Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents; this.earlyApplicationEvents = null; if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) { for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); } } }
11、finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)
实例化注册的所有BeanDefinition。
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Initialize conversion service for this context. /** * 判断是否有bdName为conversionService的bd(实现ConversionService接口),有的话注册为格式转换器服务类(默认没有) * 这是Spring3以后新加的代码,为容器指定一个转换服务(ConversionService) * 在对某些Bean属性进行转换时使用 */ if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } // Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor // (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before: // at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values. if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal)); } // Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early. /** * 获取LoadTimeWeaverAware类型的beanDefinition,提前实例化 */ String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { /** * getBean()就是具体的实例化方法 */ getBean(weaverAwareName); } // Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching. /** * 为了类型匹配,停止使用临时的类加载器 */ beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); // Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes. /** * 缓存容器中所有注册的BeanDefinition元数据,此时不允许再对BeanDefinition进行修改配置 */ beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. /** * 实例化所有的BeanDefinition */ beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
跟进——> 看一下单例的实例化方法 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()。
@Override public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this); } // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions. // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine. /** * this.beanDefinitionNames就是所有注册beanDefinition的bdName的集合 */ List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans... for (String beanName : beanNames) { /** * 获取BeanDefinition,如果BeanDefinition有修改,会使用修改合并后的数据,所以BeanFactoryPostProcessor修改BeanDefinition就会在这是生效 */ RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); //Bean不是抽象的,是单态模式的,且lazy-init属性配置为false /** * Bean不是抽象的,是单态模式的,且lazy-init属性配置为false的才进行实例化,否则会在使用时才被实例化 */ if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { /** * 判断是否是FactoryBean,FactoryBean本身是Bean,但同时也能生产Bean */ if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { /** * FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX=”&”,当Bean名称前面加”&”符号时,获取的是产生容器对象本身,而不是容器产生的Bean. * 调用getBean方法,触发容器对Bean实例化和依赖注入过程 */ final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); //标识是否需要提前实例化 boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { //一个匿名内部类 isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) () -> ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit(), getAccessControlContext()); } else { isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); } if (isEagerInit) { //调用getBean方法,触发容器对Bean实例化和依赖注入过程 getBean(beanName); } } else { getBean(beanName); } } } // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans... for (String beanName : beanNames) { Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) { final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); } } } }
跟进——> bean初始化的核心逻辑getBean(),先看一张网上盗用的getBean流程图: 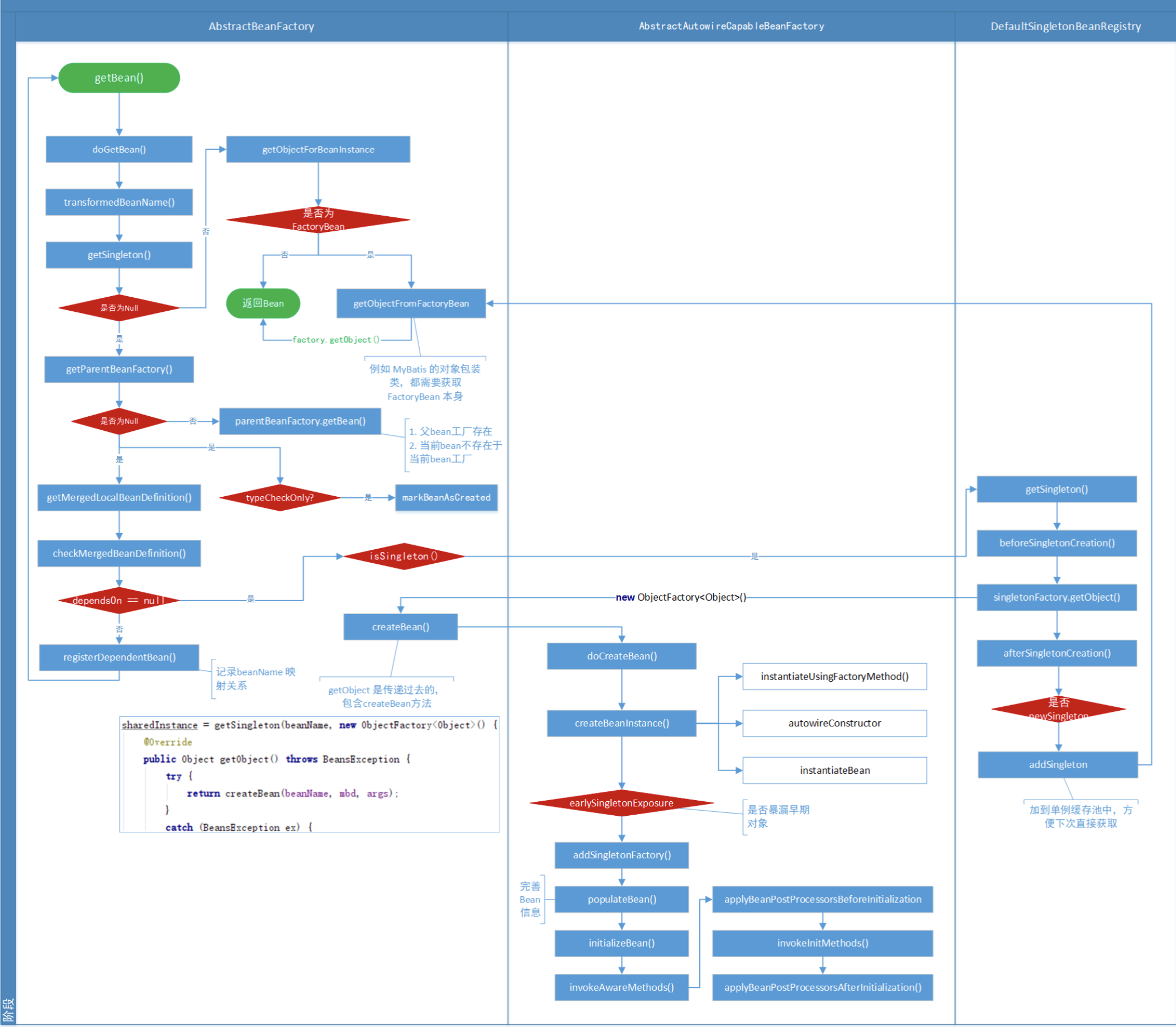
然后我们进入源码具体看下逻辑:
//获取IOC容器中指定名称的Bean @Override public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
//doGetBean才是真正向IoC容器获取被管理Bean的过程 return doGetBean(name, null, null, false); }
/** *真正实现向IOC容器获取Bean的功能,也是触发依赖注入功能的地方 */ protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { /** * 如果是FactoryBean,处理前面的& * 如果指定的是别名,将别名转换为规范的Bean名称 */ final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. /** * 先尝试从缓存中获取Bean实例,这个位置就是三级缓存解决循环依赖的方法 */ Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); //IOC容器创建单例模式Bean实例对象 if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); } else { logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } } /** * 1. 如果 sharedInstance 是普通的 Bean 实例,则下面的方法会直接返回 * 2. 如果 sharedInstance 是工厂Bean类型,则需要获取 getObject 方法,可以参考关于 FactoryBean 的实现类 */ bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); } else { // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: // We're assumably within a circular reference. /** * 循环依赖有三种,setter注入、多实例和构造函数,Spring 只能解决 setter 注入,所以这里是 Prototype 则会抛出异常 */ if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); } // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. /** * 1. 父 bean 工厂存在 * 2. 当前 bean 不存在于当前bean工厂,则到父工厂查找 bean 实例 */ BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); //当前容器的父级容器存在,且当前容器中不存在指定名称的Bean if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // Not found -> check parent. /** * 获取 name 对应的 beanName,如果 name 是以 & 开头,则返回 & + beanName */ String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); // 根据情况调用不同的父容器方法获取 bean 实例 if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) { return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean( nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly); } else if (args != null) { // Delegation to parent with explicit args. //委派父级容器根据指定名称和显式的参数查找 return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); } else { // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. //委派父级容器根据指定名称和类型查找 return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); } } /** * 1. typeCheckOnly,用于判断调用 getBean 方法时,是否仅是做类型检查 * 2. 如果不是只做类型检查,就会调用 markBeanAsCreated 进行记录 */ if (!typeCheckOnly) { markBeanAsCreated(beanName); } try { /** * 从容器 getMergedLocalBeanDefinition 获取 beanName 对应的 GenericBeanDefinition,转换为 RootBeanDefinition * 这一步是根据指定Bean名称获取其父级的Bean定义,主要解决Bean继承时子类合并父类公共属性问题 */ final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); // 检查当前创建的 bean 定义是否为抽象 bean 定义 checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. /** * 处理使用了 depends-on 注解的依赖创建 bean 实例 */ String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); if (dependsOn != null) { for (String dep : dependsOn) { /** * 监测是否存在 depends-on 循环依赖,若存在则会抛出异常 */ if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'"); } /** * 保存的是依赖beanName之间的映射关系:依赖beanName -> beanName的集合 */ registerDependentBean(dep, beanName); /** * 实例化 depends-on 依赖的bean(dep 是 depends-on 缩写) */ getBean(dep); } } // Create bean instance. /** * 创建单例 bean 实例 */ if (mbd.isSingleton()) { //这里使用了一个匿名内部类,创建Bean实例对象,把beanName和一个singletonFactory匿名内部类传入用于回调 sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> { try { /** * 创建一个指定Bean实例对象,如果有父级继承,则合并子类和父类的定义
* 这是真正创建bean实例的地方 */ return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. //显式地从容器单例模式Bean缓存中清除实例对象 destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } }); //获取给定Bean的实例对象 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } //IOC容器创建原型模式Bean实例对象 else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. //原型模式(Prototype)是每次都会创建一个新的对象 Object prototypeInstance = null; try { //回调beforePrototypeCreation方法,默认的功能是注册当前创建的原型对象 beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); //创建指定Bean对象实例 prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { //回调afterPrototypeCreation方法,默认的功能告诉IOC容器指定Bean的原型对象不再创建 afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } //获取给定Bean的实例对象 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } //要创建的Bean既不是单例模式,也不是原型模式,则根据Bean定义资源中 //配置的生命周期范围,选择实例化Bean的合适方法,这种在Web应用程序中 //比较常用,如:request、session、application等生命周期 else { String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); //Bean定义资源中没有配置生命周期范围,则Bean定义不合法 if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'"); } try { //这里又使用了一个匿名内部类,获取一个指定生命周期范围的实例 Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } }); //获取给定Bean的实例对象 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " + "defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", ex); } } } catch (BeansException ex) { cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw ex; } } // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. //对创建的Bean实例对象进行类型检查 if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) { try { T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); if (convertedBean == null) { throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } return convertedBean; } catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex); } throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } } return (T) bean; }
这里我们看几个关键的方法,就是上面红色标注的三个方法:
(1)Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName)
这个方法是spring解决循环依赖的地方,但是spring只能解决setter的循环依赖问题。
@Override @Nullable public Object getSingleton(String beanName) { /** * 在这里系统一般是允许早期对象引用的allowEarlyReference通过这个参数可以控制解决循环依赖 */ return getSingleton(beanName, true); }
@Nullable protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) { /** * 第一步:尝试去一级缓存(单例缓存池中去获取对象,一般情况从该map中获取的对象是直接可以使用的) * IoC容器初始化加载单实例bean的时候第一次进来的时候 该map中一般返回空 */ Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); /** * 若在一级缓存中没有获取到对象,并且singletonsCurrentlyInCreation正在创建的单实例的list包含该beanName * IoC容器初始化加载单实例bean的时候第一次进来的时候 该list中一般返回空,但是循环依赖的时候可以满足该条件 */ if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { /** * 尝试去二级缓存中获取对象(二级缓存中的对象是一个早期对象) * 何为早期对象:就是bean刚刚调用了构造方法,还没给bean的属性进行赋值的对象就是早期对象 */ singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName); /** * 二级缓存中也没有获取到对象,allowEarlyReference为true(参数是有上一个方法传递进来的true) */ if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) { /** * 直接从三级缓存中获取ObjectFactory对象 这个对接就是用来解决循环依赖的关键所在 * 在getBean的过程中,当bean调用了构造方法的时候,把早期对象包裹成一个ObjectFactory暴露到三级缓存中 */ ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName); //从三级缓存中获取到对象不为空 if (singletonFactory != null) { /** * 在这里通过暴露的ObjectFactory包装对象中,通过调用他的getObject()来获取我们的早期对象 * 在这个环节中会调用到 getEarlyBeanReference()来进行后置处理 */ singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); //把早期对象放置在二级缓存 this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); //ObjectFactory 包装对象从三级缓存中删除掉 this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); } } } } return singletonObject; }
逻辑概述:
二级缓存:earlySingletonObjects,存储提前暴露的bean(只实例化还未属性注入)
作用:这是spring大量使用缓存提高性能的提现,如果每次都是通过三级缓存的工厂去获取对象,逻辑很复杂(如遍历后置处理器,判断是否要创建代理对象等),使用二级缓存可以提高bean创建流程。
三级缓存:singletonFactoris,维护着bean的ObjectFactory
获取bean:
通过getSingleton(beanName)获取bean时,先从一级缓存取,没有的话从二级缓存取,再没有的话如果允许循环依赖则从三级缓存取,取出singletonFactory,通过singletonFactory.getObject()获取bean,将从三级缓存得到的bean存入二级缓存,并清除三级缓存。
何时放入三级缓存:
在实例化bean后,spring会将实例化后的bean提前暴露,即在实例化后注入属性前,将bean对应的ObjectFactory(此处理解为bean对应的工厂类)放入三级缓存中。
(2)bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd)
//主要是完成FactoryBean的相关处理 protected Object getObjectForBeanInstance( Object beanInstance, String name, String beanName, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { // Don't let calling code try to dereference the factory if the bean isn't a factory. /** * 如果 beanName 以 & 开头,但 beanInstance 却不是 FactoryBean,则会抛出异常 */ if (BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name) && !(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean)) { throw new BeanIsNotAFactoryException(transformedBeanName(name), beanInstance.getClass()); } // Now we have the bean instance, which may be a normal bean or a FactoryBean. // If it's a FactoryBean, we use it to create a bean instance, unless the // caller actually wants a reference to the factory. /** * 这里判断就是这个 bean 是不是 FactoryBean,不是就直接返回了 */ if (!(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) || BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name)) { return beanInstance; } Object object = null; if (mbd == null) { /** * 如果 mbd 为空,则从缓存加载 bean(FactoryBean 生成的单例 bean 实例会缓存到 factoryBeanObjectCache 集合中,方便使用) */ object = getCachedObjectForFactoryBean(beanName); } //让FactoryBean生产给定名称的Bean对象实例 if (object == null) { // Return bean instance from factory. /** * 到这,beanInstance 是 FactoryBean 类型,所以就强转了 */ FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) beanInstance; // Caches object obtained from FactoryBean if it is a singleton. /** * mbd 为空且判断 containsBeanDefinition 是否包含 beanName */ if (mbd == null && containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { /** * 从容器中获取beanDefinition,如果继承基类,则合并基类相关属性 */ mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); } boolean synthetic = (mbd != null && mbd.isSynthetic()); /** * 调用FactoryBeanRegistrySupport类的getObjectFromFactoryBean方法, */ object = getObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName, !synthetic); } return object; }
(3)createBean(beanName, mbd, args)
这个方法是真正bean实例化的方法,这里也是处理BeanPostProcessor的地方,其实就是创建一个代理类。
@Override protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { ... try { // Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance. /** * 如果Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor,则在这里生成代理对象(这里只是生成代理,并没有执行) */ Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); if (bean != null) { return bean; } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex); } try { /** * 创建Bean的入口 */ Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); } return beanInstance; } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { // A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already... throw ex; } catch (ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) { // An IllegalStateException to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry... throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex); } }
来看下resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse)方法,这里举一个应用的例子。
motan中的AnnotationBean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,前置处理器:解析Bean中带有@MotanReferer注解的setter方法或field,并完成调用方的初始化。
后置处理器:解析带有@MotanService注解的class,并将这个class作为motan服务注册到注册中心,暴露服务。
@Nullable protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { Object bean = null; if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) { // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd); if (targetType != null) { /** * 生成前置处理器代理对象 */ bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName); if (bean != null) { /** * 这里配置后置处理器代理 */ bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName); } } } mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null); } return bean; }
然后继续看bean创建的最终入口 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args)。
在这个方法中有对三级缓存的设置,就是在bean初始化前先将未初始化的bean的ObjectFactory工厂放入三级缓存,提前暴露,为了其他对象在注入该bean的时候能够获取。
接着这个方法里面还进行了属性赋值和初始化操作(BeanPOSTProcessor的前后处理器就是在这里执行的,在init方法的前后分别执行)。
//真正创建Bean的方法 protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean. /** * BeanWrapper是对Bean的包装,其接口中所定义的功能很简单包括设置获取被包装的对象,获取被包装bean的属性描述器 */ BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { /** * 先从缓存中获取,如果有返回并从缓存中清除 */ instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { /** * 缓存总没有则创建BeanWrapper(使用匹配的方式创建:工厂方法、默认无参构造函数、自动装配构造函数等) */ instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } /** * 从beanWrapper中获取早期对象(即未注入属性) */ final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance(); //获取实例化对象的类型 Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass(); if (beanType != NullBean.class) { mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; } // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { try { /** * 合并BeanDefinition信息,主要处理@PostConstruct,@Autowire,@Value,@Resource,@PreDestory等 */ applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex); } mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. /** * 如果当前bean是单例,且支持循环依赖,且当前bean正在创建,通过往singletonFactories(三级缓存)添加一个objectFactory, * 这样后期如果有其他bean依赖该bean 可以从singletonFactories获取到bean,getEarlyBeanReference可以对返回的bean进行修改,目前除了可能会返回动态代理对象,其他的都是直接返回bean */ boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } /** * 这里就是将objectFactory放入三级缓存 */ addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)); } // Initialize the bean instance. //Bean对象的初始化,依赖注入在此触发 //这个exposedObject在初始化完成之后返回,作为依赖注入完成后的Bean Object exposedObject = bean; try { /** * 属性赋值 */ populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); /** * 进一步初始化Bean * 注入 Aware 相关的对象 * 调用 后置处理器 BeanPostProcessor 的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 * 调用 init方法 * 调用 后置处理器 BeanPostProcessor 的postProcessAfterInitialization方法 */ exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { //earlySingletonReference 只有在检测到有循环依赖的情况下才会不为空 Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { //如果exposedObject 没有在初始化方法中被改变,也就是没有被增强 if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. //注册完成依赖注入的Bean try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
这里我们继续跟初始化方法 initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd)
//初始容器创建的Bean实例对象,执行BeanPostProcessor后置处理器 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { //JDK的安全机制验证权限 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { //实现PrivilegedAction接口的匿名内部类 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { //为Bean实例对象包装相关属性,如名称,类加载器,所属容器等信息 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; /** * 调用BeanPostProcessor后置处理器的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法 */ if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } /** * 先调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet,在调用我们定义的init方法 */ try { invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } /** * 调用BeanPostProcessor后置处理器的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法 */ if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
12、finishRefresh()
这一步主要是spring提供的一个生命周期扩展 LifeCycle 接口,其主要有三个方法 start( )、stop( )、isRunning( ),但是这几个方法需要手动显示调用才能生效,要自动跟随ApplicationContext的启动/停止,还有一个子类SmartLifecycle。关于spring的其他生命周期管理方式请参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/jing-yi/p/15343395.html
除了生命周期就是发布上下文刷新完毕事件。
protected void finishRefresh() { // Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning). clearResourceCaches(); // Initialize lifecycle processor for this context. /** * 为上下文初始化生命周期处理器(有自定义就是用自定义的,没有就是用spring默认的DefaultLifecycleProcessor) */ initLifecycleProcessor(); // Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first. /** * 获得所有实现 LifeCycle 或是其子类的Bean,然后执行启动方法 start() 方法 */ getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); // Publish the final event. /** * 发布上下文刷新完毕事件 */ publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); // Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active. LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); }





