第14周leetcode记录
12.14 66. 打家劫舍III
在上次打劫完一条街道之后和一圈房屋后,小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区。这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为“根”。 除了“根”之外,每栋房子有且只有一个“父“房子与之相连。一番侦察之后,聪明的小偷意识到“这个地方的所有房屋的排列类似于一棵二叉树”。 如果两个直接相连的房子在同一天晚上被打劫,房屋将自动报警。
计算在不触动警报的情况下,小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额。
输入: [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]
3
/ \
2 3
\ \
3 1
输出: 7
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
最优解
class Solution {
Map<TreeNode, Integer> f = new HashMap<TreeNode, Integer>();
Map<TreeNode, Integer> g = new HashMap<TreeNode, Integer>();
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return Math.max(f.getOrDefault(root, 0), g.getOrDefault(root, 0));
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
dfs(node.left);
dfs(node.right);
f.put(node, node.val + g.getOrDefault(node.left, 0) + g.getOrDefault(node.right, 0));
g.put(node, Math.max(f.getOrDefault(node.left, 0), g.getOrDefault(node.left, 0)) + Math.max(f.getOrDefault(node.right, 0), g.getOrDefault(node.right, 0)));
}
}
最优解思路
f(o)表示选择此点,最大值。g(0)表示不选择此点最大值。动态规划思路。
12.17 67. 2的幂
给定一个整数,编写一个函数来判断它是否是 2 的幂次方。
思路
位运算,2进制的规律,若n位2的幂,恒有n & (n - 1) == 0,因为:
n二进制最高位位1,其余为0,n-1最高位位0,其余为1.
最优解
class Solution:
def isPowerOfTwo(self, n: int) -> bool:
return n > 0 and n & (n - 1) == 0
最优解总结
2次幂数的内存规律要掌握。
12.18 68. 二叉搜索树的范围和
给定二叉搜索树的根结点 root,返回值位于范围 [low, high] 之间的所有结点的值的和。
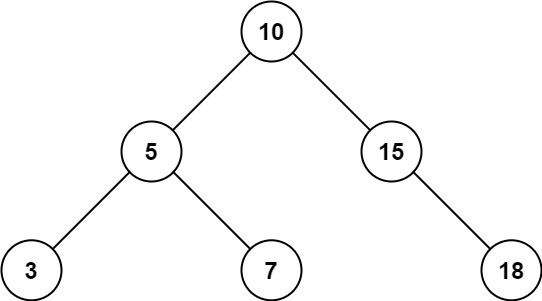
输入:root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15
输出:32
思路
遍历二叉搜索树,若节点的值等于low,入栈。high出
最优解思路
看该节点是否位于范围内,从根节点遍历,一直获取所有范围内的节点值。
最优解
class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int L, int R) {
int ans = 0;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
if (L <= node.val && node.val <= R)
ans += node.val;
if (L < node.val)
stack.push(node.left);
if (node.val < R)
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
12.19 69. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
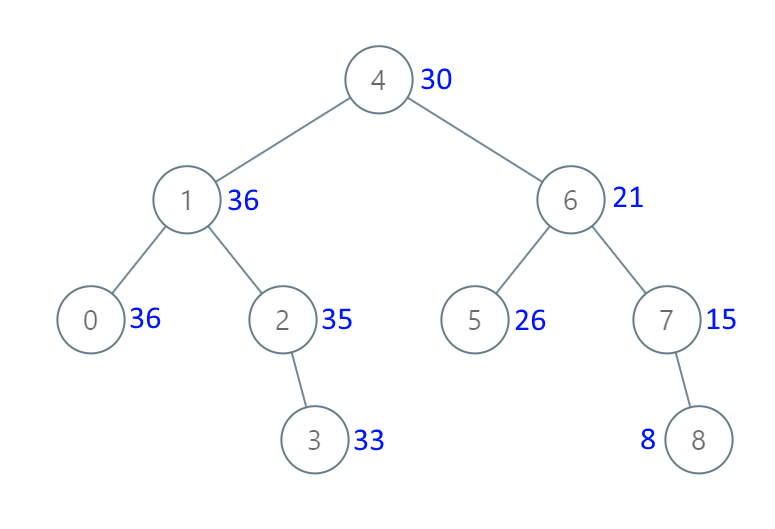
输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
最优解思路
重要:二叉搜索树的中序遍历是一个单调递增的有序序列。如果我们反序地中序遍历该二叉搜索树,即可得到一个单调递减的有序序列。
最优解
class Solution:
def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
def dfs(root: TreeNode):
nonlocal total
if root:
dfs(root.right)
total += root.val
root.val = total
dfs(root.left)
total = 0
dfs(root)
return root
12.20 70. 甲板上的战舰
给定一个二维的甲板, 请计算其中有多少艘战舰。 战舰用 'X'表示,空位用 '.'表示。 你需要遵守以下规则:
- 给你一个有效的甲板,仅由战舰或者空位组成。
- 战舰只能水平或者垂直放置。换句话说,战舰只能由 1xN (1 行, N 列)组成,或者 Nx1 (N 行, 1 列)组成,其中N可以是任意大小。
- 两艘战舰之间至少有一个水平或垂直的空位分隔 - 即没有相邻的战舰。
X..X
...X
...X
在上面的甲板中有2艘战舰。
...X
XXXX
...X
无效样例
思路
向右或向下遍历,一个set负责遍历过的坐标。如果按某一方向遍历到叉,把周围非当前方向的坐标加入到set。遍历到叉数量加一。
最优解思路
遍历矩阵,每找到一个 X(战舰)进行计数,并将其相邻的 X 改为 . 。利用while去找相邻的X
最优解
class Solution {
public int countBattleships(char[][] board) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'X') {
count++;
board[i][j] = '.';
int a = i + 1;
int b = j;
// 遍历行
while (a < board.length && board[a][b] == 'X') {
board[a++][b] = '.';
}
a = i;
b = j + 1;
// 遍历列
while (b < board[0].length && board[a][b] == 'X') {
board[a][b++] = '.';
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
}


