SWUSTOJ:348 花生采摘(使用C语言)
SWUST OJ:348 花生采摘
问题描述:
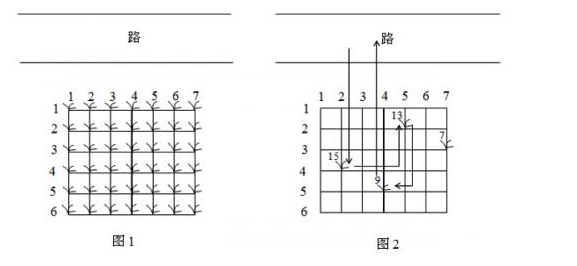
鲁宾逊先生有一只宠物猴,名叫多多。这天,他们两个正沿着乡间小路散步,突然发现路边的告示牌上贴着一张小小的纸条:“欢迎免费品尝我种的花生!——熊字”。 鲁宾逊先生和多多都很开心,因为花生正是他们的最爱。在告示牌背后,路边真的有一块花生田,花生植株整齐地排列成矩形网格(如图1)。
有经验的多多一眼就能看出,每棵花生植株下的花生有多少。为了训练多多的算术,鲁宾逊先生说:“你先找出花生最多的植株,去采摘它的花生;然后再找出剩下的植株里花生最多的,去采摘它的花生;依此类推,不过你一定要在我限定的时间内回到路边。” 我们假定多多在每个单位时间内,可以做下列四件事情中的一件:
1) 从路边跳到最靠近路边(即第一行)的某棵花生植株;
2) 从一棵植株跳到前后左右与之相邻的另一棵植株;
3) 采摘一棵植株下的花生;
4) 从最靠近路边(即第一行)的某棵花生植株跳回路边。
现在给定一块花生田的大小和花生的分布,请问在限定时间内,多多最多可以采到多少个花生?注意可能只有部分植株下面长有花生,假设这些植株下的花生个数各不相同。
例如在图2所示的花生田里,只有位于(2, 5), (3, 7), (4, 2), (5, 4)的植株下长有花生,个数分别为13, 7, 15, 9。沿着图示的路线,多多在21个单位时间内,最多可以采到37个花生。
输入:输入的第一行包括三个整数,M, N和K,用空格隔开;表示花生田的大小为M * N(1 <= M, N <= 20),多多采花生的限定时间为K(0 <= K <= 1000)个单位时间。接下来的M行,每行包括N个非负整数,也用空格隔开;第i + 1行的第j个整数Pij(0 <= Pij <= 500)表示花生田里植株(i, j)下花生的数目,0表示该植株下没有花生。
输出:输出包括一行,这一行只包含一个整数,即在限定时间内,多多最多可以采到花生的个数。
思路:1.先搜索有果实的花生的坐标,以及数量,存储在结构体中。按照数量大小对其进行排序。(这里使用的是冒泡排序)
2.进行预判,看是否能通过(距离时间 = 与下一个花生的路径产生的时间 + 返回路面的路径产生的时间)
代码实现:
#include "stdio.h" int n=0,m=0,k=0,timeNow=0,timefuter=0,num=0,temp=0; struct Node{ int data; int posx;//表示排 int posy;//表示列 }node[1000]; void search(int a[100][100]) { int i,j,posx,posy,data; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { for(j=0;j<m;j++) { if(a[i][j]!=0) { node[temp].data=a[i][j]; node[temp].posx=i; node[temp].posy=j; temp++; } } } for(i=0;i<temp-1;i++) { for(j=0;j<temp-1-i;j++) { if(node[j].data<node[j+1].data) { data=node[j].data; node[j].data=node[j+1].data; node[j+1].data=data; posx=node[j].posx; node[j].posx=node[j+1].posx; node[j+1].posx=posx; posy=node[j].posy; node[j].posy=node[j+1].posy; node[j+1].posy=posy; } } } } int time_count(int n) { struct Node a = node[n]; struct Node b = node[n+1]; int timex=0,timey=0; timex=(a.posx-b.posx)>0?a.posx-b.posx:b.posx-a.posx; timey=(a.posy-b.posy)>0?a.posy-b.posy:b.posy-a.posy; return timex+timey; } int can_return(int n) { timefuter = timeNow; timefuter += time_count(n); timefuter ++; timefuter = node[n+1].posx+timefuter+1; if(timefuter<=k) return 1; else return 0; } int run(int a[100][100]) { search(a); int i; if(((node[0].posx+1)*2+1)<=k) num = node[0].data; else return 0; timeNow = timeNow+node[0].posx+1; timeNow++; for(i=0;i<temp-1;i++) { if(can_return(i)==1) { timeNow = timeNow+time_count(i)+1; num+=node[i+1].data; } else break; } return num; } int main() { int i,j,a[100][100]; scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { for(j=0;j<m;j++) { scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); } } printf("%d\n",run(a)); }



