vue源码解析实例(二)---vue 虚拟DOM篇
-
-
我们知道,Vue是数据驱动视图的,数据发生变化视图就要随之更新,在更新视图的时候难免要操作DOM,而操作真实DOM又是非常耗费性能的,这是因为浏览器的标准就把 DOM 设计的非常复杂,所以一个真正的 DOM 元素是非常庞大的,如下所示:
let div = document.createElement('div')let str = ''for (const key in div) { str += key + ''} console.log(str)
我们可以用JS的计算性能来换取操作DOM所消耗的性能。DOM-Diffpath整个patch无非就是干三件事:-
创建节点:新的VNode中有而旧的oldVNode中没有,就在旧的oldVNode中创建。
-
删除节点:新的VNode中没有而旧的oldVNode中有,就从旧的oldVNode中删除。
-
更新节点:新的VNode和旧的oldVNode中都有,就以新的VNode为准,更新旧的oldVNode。
-
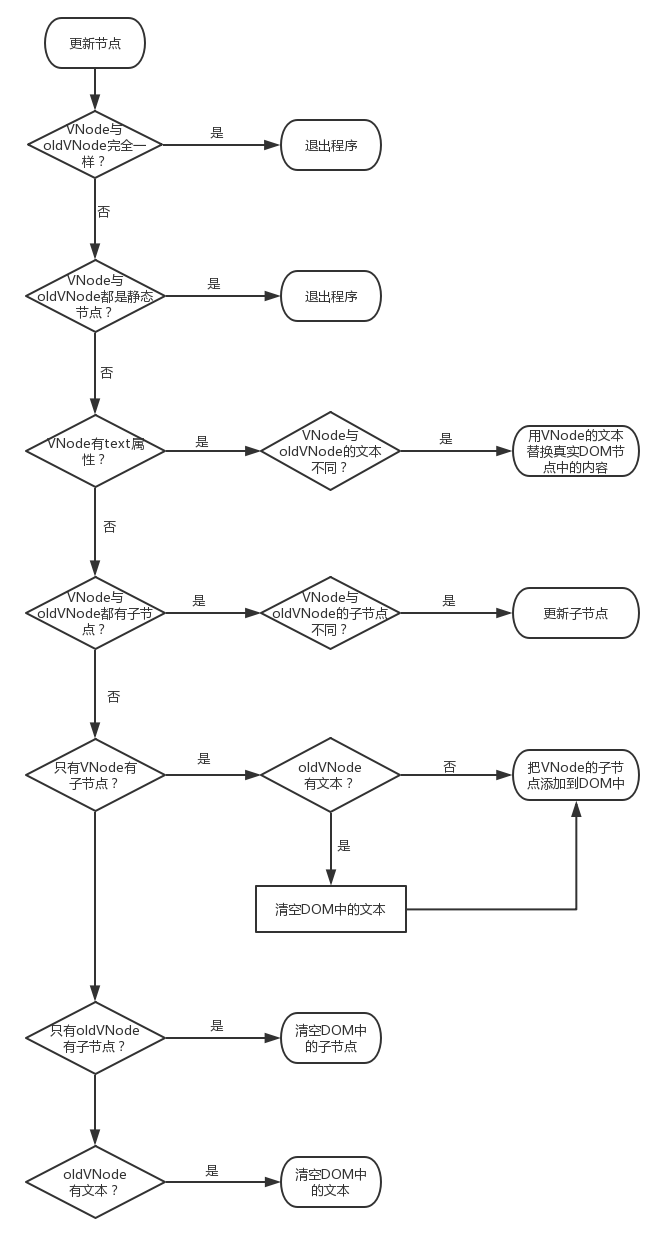
优化更新子节点function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) { let oldStartIdx = 0 // oldChildren开始索引 let newStartIdx = 0 /// newChildren开始索引 let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1 // oldChildren结束索引 let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0] // oldChildren中所有未处理节点中的最后一个 let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx] // oldChildren中所有未处理节点中的最后一个 let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1 // newChildren结束索引 let newStartVnode = newCh[0] // newChildren中所有未处理节点中的第一个 let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx] // newChildren中所有未处理节点中的最后一个 let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm // removeOnly is a special flag used only by <transition-group> // to ensure removed elements stay in correct relative positions // during leaving transitions const canMove = !removeOnly if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { checkDuplicateKeys(newCh) } // 以"新前"、"新后"、"旧前"、"旧后"的方式开始比对节点 while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) { if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) { oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // Vnode has been moved left // 如果oldStartVnode不存在,则直接跳过,比对下一个 } else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) { oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) { // 如果新前与旧前节点相同,就把两个节点进行patch更新 patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) { // 如果新后与旧后节点相同,就把两个节点进行patch更新 patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx) oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // Vnode moved right patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx) canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm)) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left // 如果新后与旧前节点相同,先把两个节点进行patch更新,然后把旧前节点移动到oldChilren中所有未处理节点之后 patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx) canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm) oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } else { // 如果不属于以上四种情况,就进行常规的循环比对patch if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key) ? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key] : findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) // 如果在oldChildren里找不到当前循环的newChildren里的子节点 if (isUndef(idxInOld)) { // New element // 新增节点并插入到合适位置 createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx) } else { // 如果在oldChildren里找到了当前循环的newChildren里的子节点 vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld] // 如果两个节点相同 if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) { // 调用patchVnode更新节点 patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx) oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined // canmove表示是否需要移动节点,如果为true表示需要移动,则移动节点,如果为false则不用移动 canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm) } else { // same key but different element. treat as new element createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx) } } newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } } if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) { /** * 如果oldChildren比newChildren先循环完毕, * 那么newChildren里面剩余的节点都是需要新增的节点, * 把[newStartIdx, newEndIdx]之间的所有节点都插入到DOM中 */ refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue) } else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) { /** * 如果newChildren比oldChildren先循环完毕, * 那么oldChildren里面剩余的节点都是需要删除的节点, * 把[oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx]之间的所有节点都删除 */ removeVnodes(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) } }
当开始位置大于结束位置时,表示所有节点都已经遍历过了。OK,有了这个概念后,我们开始读源码:-
如果oldStartVnode不存在,则直接跳过,将oldStartIdx加1,比对下一个
// 以"新前"、"新后"、"旧前"、"旧后"的方式开始比对节点while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) { if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) { oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] } } -
如果oldEndVnode不存在,则直接跳过,将oldEndIdx减1,比对前一个
else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) { oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] } -
如果新前与旧前节点相同,就把两个节点进行patch更新,同时oldStartIdx和newStartIdx都加1,后移一个位置
else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] }
-
如果新后与旧后节点相同,就把两个节点进行patch更新,同时oldEndIdx和newEndIdx都减1,前移一个位置
else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] }
-
如果新后与旧前节点相同,先把两个节点进行patch更新,然后把旧前节点移动到oldChilren中所有未处理节点之后,最后把oldStartIdx加1,后移一个位置,newEndIdx减1,前移一个位置
else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] }
-
如果新前与旧后节点相同,先把两个节点进行patch更新,然后把旧后节点移动到oldChilren中所有未处理节点之前,最后把newStartIdx加1,后移一个位置,oldEndIdx减1,前移一个位置
-
else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm) oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] }
-
-
如果不属于以上四种情况,就进行常规的循环比对patch
-
如果在循环中,oldStartIdx大于oldEndIdx了,那就表示oldChildren比newChildren先循环完毕,那么newChildren里面剩余的节点都是需要新增的节点,把[newStartIdx, newEndIdx]之间的所有节点都插入到DOM中
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) { refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue) }
-
如果在循环中,newStartIdx大于newEndIdx了,那就表示newChildren比oldChildren先循环完毕,那么oldChildren里面剩余的节点都是需要删除的节点,把[oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx]之间的所有节点都删除
else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) { removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) }
OK,处理完毕,可见源码中的处理逻辑跟我们之前分析的逻辑是一样的。总结
Vue为了避免双重循环数据量大时间复杂度升高带来的性能问题,而选择了从子节点数组中的4个特殊位置互相比对,分别是:新前与旧前,新后与旧后,新后与旧前,新前与旧后。对于每一种情况我们都通过图文的形式对其逻辑进行了分析。最后我们回到源码,通过阅读源码来验证我们分析的是否正确。幸运的是我们之前每一步的分析都在源码中找到了相应的实现,得以验证我们的分析没有错。以上就是Vue中的patch过程,即DOM-Diff算法所有内容了,到这里相信你再读这部分源码的时候就有比较清晰的思路了。 -
多多关照,多多指教,共同成长
---嘉煠





