Oracle 子程序、过程、函数
一、子程序
子程序是一个数据库对象,存在于数据库中,里面存放的是PL/SQL代码,可以完成一定的共能,能被程序和客户端工具直接调用。子程序类似于java中的方法,可以接接收参数,按照是否有返回值,子程序可以分为过程和函数。
子程序可以被编译和存储在数据库中,它具有模块化、重用性、可维护性、可扩展性、安全性等特点。
模块化是将大的代码块分解为较小代码模块,在代码被模块化之后,模块可以被同一个程序重用,或被其他程序调用,而且较小的模块也更容易维护和调试。根据需求,可以将各个小模块组织起来,完成一些特定的功能,增强了系统的可扩展性。另外,子程序也是数据库对象,可以被授权执行,这样只有授权用户才能访问,增强了安全性。
子程序的程序结构如下:
<header> IS|AS 声明部分 BEGIN 可执行部分 EXCEPTION (可选) 异常部分 END;
程序结构中前两行是子程序说明部分,其中 header 确定 PL/SQL子程序的类型(过程或函数)、名称和参数列表,如果是函数的话,还会有 return 子句。
从声明部分开始到最后,属于子程序的主体。在 IS|AS 和 BEGIN 之间是声明部分(可以声明变量), BEGIN 和 END 之间是子程序的核心——可执行部分,其中至少包含一条语句,EXCEPTION 和 END 之间是一场部分,这部分用于捕获预先定义的错误。
二、存储过程
1.创建过程
语法形式:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] PROCEDURE pname --<header>
[( param1 [mode1] type1, --param:形参名称 、mode:参数模式(in默认,out,in out)
param2 [model] type2, --type:参数数据类型
......
)]
IS|AS
BEGIN
PL/SQL Block --PL/SQL Block:PL/SQL 代码块
END[pname]
【注意】:参数模式的主要总用是确定参数是从调用环境传递到过程还是从过程传递到调用环境。
IN 从调用环境传递到过程,OUT 从过程传递到调用环境,IN OUT 兼备IN 和 OUT 两个模式的功能。
2.创建过程的示例
①假设现在要创建这样的过程,实现的功能是要給指定的(通过雇员编号指定)雇员加薪,如果雇员编号在200以内加薪10%,雇员编号大于等于200则加薪15%,创建存储过程的SQL语句如下(用HR用户身份创建):
create or replace procedure raise_salary --<header> (p_id in employees.employee_id%type) -- %type 表示变量的类型和%前字段的类型一样,当然本例中也可以写为 number IS BEGIN if p_id <= 200 then begin update employees set salary = salary * 1.10 where employees.employee_id = p_id; end; end if; if p_id > 200 then begin update employees set salary = salary * 1.15 where employees.employee_id = p_id; end; end if; END raise_salary;
②定义变量代表员工表中的员工号,根据员工号获得员工工资,查询某员工工资,如果工资小于4000,输出到屏幕上的内容为员工姓名和增涨10%以后的工资,否则输出到屏幕上的内容为员工姓名和增涨5%以后的工资。
create or replace procedure raise_salary (p_id in emp.empno%type) IS v_sal emp.sal%type :=0; pname emp.ename%type; BEGIN select emp.sal,emp.ename into v_sal,pname from emp where emp.empno = p_id; if v_sal< 4000 then begin dbms_output.put_line('姓名:'||pname||' '||'工资增加10%后:'||v_sal*1.10); end; end if; if v_sal>= 4000 then begin dbms_output.put_line('姓名:'||pname||' '||'工资增加10%后:'||v_sal*1.05); end; end if; END raise_salary;
begin raise_salary(7839); end;
结果: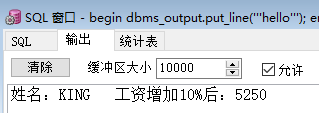
③创建存储过程PTEST,接受两个数相除并且显示结果,如果第二个数是0,则显示消息“not to divide by zero !”,不为0则显示结果。
create or replace procedure PTEST (i_cs1 in number , i_cs2 in number) IS o_res number ; begin select i_cs1/i_cs2 into o_res from dual; dbms_output.put_line('计算结果:'||o_res); exception when ZERO_DIVIDE then dbms_output.put_line('not to divide by zero !'); end; begin PTEST(5,3); end;
④创建函数Emp_Avg:根据员工号,返回员工所在部门的平均工资。
create or replace function Emp_Avg (i_empno in emp.empno%type) return number IS o_sal emp.sal %type; BEGIN select avg(sal) into o_sal from emp where emp.deptno = i_empno; return o_sal; END Emp_Avg; select emp_avg(30) from dual;
⑤创建一个过程Update_SAL,通过调用上题4中的函数,实现对每个员工工资的修改:如果该员工所在部门的平均工资小于1000,则该员工工资增加500;大于等于1000而小于5000,增加300;大于等于5000,增加100。
create or replace procedure Update_SAL (i_empno in emp.empno%type) IS v_dpid emp.deptno%type; v_asal emp.sal%type; BEGIN select emp.deptno into v_dpid from emp where emp.empno = i_empno; dbms_output.put_line('部门编号是:'||v_dpid); select emp_avg(v_dpid) into v_asal from dual; if v_asal<1600 then begin update emp set sal = sal+ 500 where emp.empno = i_empno; end; elsif (v_asal>= 1600 and v_asal<2500) then begin update emp set sal = sal+ 300 where emp.empno = i_empno; end; else begin update emp set sal = sal +100 where emp.empno = i_empno; end; end if; END Update_SAL;
begin update_sal(7499); end;
⑥创建存储过程PrintEmp,将emp表中所有员工编号和姓名显示出来。
create or replace procedure PrintEmp IS cursor cemp is select emp.empno,emp.ename from emp; --声明部分,可以声明一个游标 o_id emp.empno%type; o_name emp.ename%type; BEGIN open cemp; loop fetch cemp into o_id,o_name ; exit when cemp%notfound; dbms_output.put_line('员工编号:'||o_id||' '||'员工姓名:'||o_name); end loop; close cemp; END; begin printemp; end;
【注意】:创建存储过程,在声明部分可以声明一个游标。
3.调用过程
调用方法1:编译该过程,通过 PL/SQL Dev 查看 Procedures 文件夹,右击 RAISE_SALARY ,再选择测试选项,在弹出的窗口中对应 p_id 这个形参输入实参值,输入实参207代表要给雇员编号为207的雇员加薪。
调用方法2:
begin raise_salary(207); end; commit;
4.删除过程
drop procedure raise_salary
三、函数
1.创建函数
语法形式:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION fname --<header>
[(param1 [mode1] type1, --param1 形参名称
param2 [mode2] type2,
...)]
RETURN type --return 子句
IS|AS
BEGIN
PL/SQL Block --PL/SQL 代码块
END[fname]
2.创建函数示例
①创建一个通过雇员编号获取部门经历编号的函数
create or replace function get_manager_id --<header> (p_id in employees.employee_id%type) return number --return 子句 IS v_manager_id employees.employee_id%type:=0 ; BEGIN --PL/SQL 代码块 select manager_id into v_manager_id from employees where p_id = employee_id; return v_manager_id; END get_manager_id;
②根据员工号,获得员工到目前为止参加工作年限(保留到整数),员工号不存在时提示“此员工号不存在”
create or replace function get_workyear (v_id in emp.empno%type) return varchar2 IS v_workyear integer; BEGIN select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy')-to_char(hiredate,'yyyy') --两个数字字符串相减的值存到整数型变量中 into v_workyear from emp where emp.empno = v_id; return v_workyear; EXCEPTION when no_data_found then dbms_output.put_line('此员工号不存在'); return -1; END get_workyear;
③编写一个函数,根据员工编号计算该员工进入公司的月数。
create or replace function cal_mon (i_empno in emp.empno%type) return number IS v_date emp.hiredate%type; o_mons number; BEGIN select emp.hiredate into v_date from emp where emp.empno = i_empno ; select trunc((sysdate - v_date)/30) into o_mons from dual; return o_mons; END cal_mon; select * from emp; select cal_mon(7369) from dual;
【注意】:
① %type 表示变量的类型与%前字段的类型一致;
② :=0 表示变量的初值为0;
③ 函数有一个 return 子句。
④ select...into... 语句
3.调用函数
调用方法1:编译该函数,再通过 PL/SQL Dev 查看 Function 文件夹 , 右击 get_manager_id 函数,选择 测试选项。在弹出的窗口中对应 p_id 这个形参输入实参207 ,执行该脚本,显示获得的部门经理编号为 103.
调用方法2:调用语句:
select get_manager_id(207) from dual;
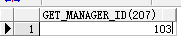
4.删除函数
drop function get_manager_id
四、函数与过程的区别
1.函数一般用于计算数据,过程用于完成特定的任务,比如增删改。增删改会产生事务,未将事务提交,会导致此行或此表锁住。
2.函数声明为 function ,过程声明为 procedure 。
3.函数需要描述返回类型,且 PL/SQL 块中至少有一个有效的 return 语句。过程无返回类型,可通过 OUT、IN OUT 参数返回多个值。
4.函数不能独立运行,必须作为表达式的一部分。过程可作为一个独立的 PL/SQL 语句运行。
5.在 DML 和 DQL 中可调用函数但不可调用过程。
参数与过程都有定义形参,形参的值是由外部输入的;
https://www.icourse163.org/learn/NUDT-438002?tid=1003251001#/learn/content



