HttpClient
HTTP 协议可能是现在 Internet 上使用得最多、最重要的协议了,越来越多的 Java 应用程序需要直接通过 HTTP 协议来访问网络资源。虽然在 JDK 的 java net包中已经提供了访问 HTTP 协议的基本功能,但是对于大部分应用程序来说,JDK 库本身提供的功能还不够丰富和灵活。HttpClient 是 Apache Jakarta Common 下的子项目,用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持 HTTP 协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支持 HTTP 协议最新的版本和建议。
HTTP和浏览器有点像,但却不是浏览器。很多人觉得既然HttpClient是一个HTTP客户端编程工具,很多人把他当做浏览器来理解,但是其实HttpClient不是浏览器,它是一个HTTP通信库,因此它只提供一个通用浏览器应用程序所期望的功能子集,最根本的区别是HttpClient中没有用户界面,浏览器需要一个渲染引擎来显示页面,并解释用户输入,例如鼠标点击显示页面上的某处,有一个布局引擎,计算如何显示HTML页面,包括级联样式表和图像。javascript解释器运行嵌入HTML页面或从HTML页面引用的javascript代码。来自用户界面的事件被传递到javascript解释器进行处理。除此之外,还有用于插件的接口,可以处理Applet,嵌入式媒体对象(如pdf文件,Quicktime电影和Flash动画)或ActiveX控件(可以执行任何操作)。HttpClient只能以编程的方式通过其API用于传输和接受HTTP消息。
HttpClient的主要功能:
实现了所有 HTTP 的方法(GET、POST、PUT、HEAD、DELETE、HEAD、OPTIONS 等)
支持 HTTPS 协议
支持代理服务器(Nginx等)等
支持自动(跳转)转向
环境说明:JDK1.8、SpringBoot
第一步:在pom.xml中引入HttpClient的依赖
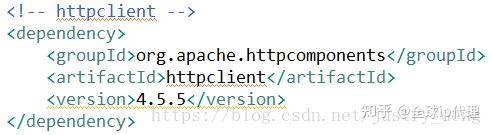
第二步:引入fastjson依赖
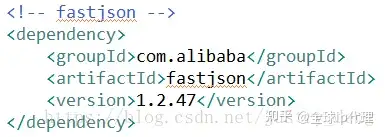
注:本人引入此依赖的目的是,在后续示例中,会用到“将对象转化为json字符串的功能”,也可以引其他有此功能的依赖。
注:SpringBoot的基本依赖配置,这里就不再多说了。
详细使用示例
声明:此示例中,以JAVA发送HttpClient(在test里面单元测试发送的);也是以JAVA接收的(在controller里面接收的)。
声明:下面的代码,本人亲测有效。
GET无参:
HttpClient发送示例:
/**
* GET---无参测试
*
* @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
*/
@Test
public void doGetTestOne() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Get请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://localhost:12345/doGetControllerOne");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 由客户端执行(发送)Get请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对应接收示例:

GET有参(方式一:直接拼接URL):
HttpClient发送示例:
/**
* GET---有参测试 (方式一:手动在url后面加上参数)
*
* @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:19:23
*/
@Test
public void doGetTestWayOne() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 参数
StringBuffer params = new StringBuffer();
try {
// 字符数据最好encoding以下;这样一来,某些特殊字符才能传过去(如:某人的名字就是“&”,不encoding的话,传不过去)
params.append("name=" + URLEncoder.encode("&", "utf-8"));
params.append("&");
params.append("age=24");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
// 创建Get请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://localhost:12345/doGetControllerTwo" + "?" + params);
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 配置信息
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
// 设置连接超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectTimeout(5000)
// 设置请求超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000)
// socket读写超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setSocketTimeout(5000)
// 设置是否允许重定向(默认为true)
.setRedirectsEnabled(true).build();
// 将上面的配置信息 运用到这个Get请求里
httpGet.setConfig(requestConfig);
// 由客户端执行(发送)Get请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对应接收示例:

GET有参(方式二:使用URI获得HttpGet):
HttpClient发送示例:
/**
* GET---有参测试 (方式二:将参数放入键值对类中,再放入URI中,从而通过URI得到HttpGet实例)
*
* @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:19:23
*/
@Test
public void doGetTestWayTwo() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 参数
URI uri = null;
try {
// 将参数放入键值对类NameValuePair中,再放入集合中
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("name", "&"));
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("age", "18"));
// 设置uri信息,并将参数集合放入uri;
// 注:这里也支持一个键值对一个键值对地往里面放setParameter(String key, String value)
uri = new URIBuilder().setScheme("http").setHost("localhost")
.setPort(12345).setPath("/doGetControllerTwo")
.setParameters(params).build();
} catch (URISyntaxException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
// 创建Get请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri);
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 配置信息
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
// 设置连接超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectTimeout(5000)
// 设置请求超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000)
// socket读写超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setSocketTimeout(5000)
// 设置是否允许重定向(默认为true)
.setRedirectsEnabled(true).build();
// 将上面的配置信息 运用到这个Get请求里
httpGet.setConfig(requestConfig);
// 由客户端执行(发送)Get请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对应接收示例:

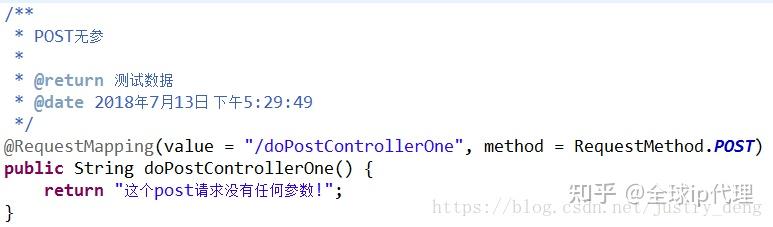
POST无参:
HttpClient发送示例:
/**
* POST---无参测试
*
* @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
*/
@Test
public void doPostTestOne() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Post请求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerOne");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对应接收示例:
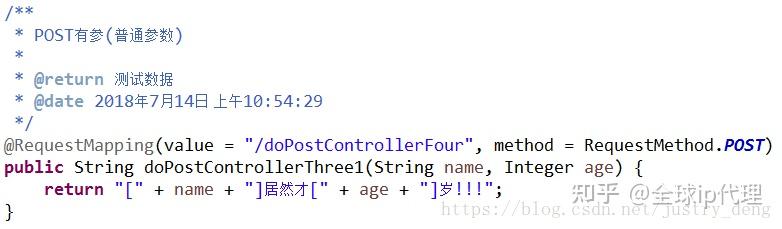
POST有参(普通参数):
注:POST传递普通参数时,方式与GET一样即可,这里以直接在url后缀上参数的方式示例。
HttpClient发送示例:
/**
* POST---有参测试(普通参数)
*
* @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
*/
@Test
public void doPostTestFour() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 参数
StringBuffer params = new StringBuffer();
try {
// 字符数据最好encoding以下;这样一来,某些特殊字符才能传过去(如:某人的名字就是“&”,不encoding的话,传不过去)
params.append("name=" + URLEncoder.encode("&", "utf-8"));
params.append("&");
params.append("age=24");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
// 创建Post请求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerFour" + "?" + params);
// 设置ContentType(注:如果只是传普通参数的话,ContentType不一定非要用application/json)
httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对应接收示例
POST有参(对象参数):
先给出User类
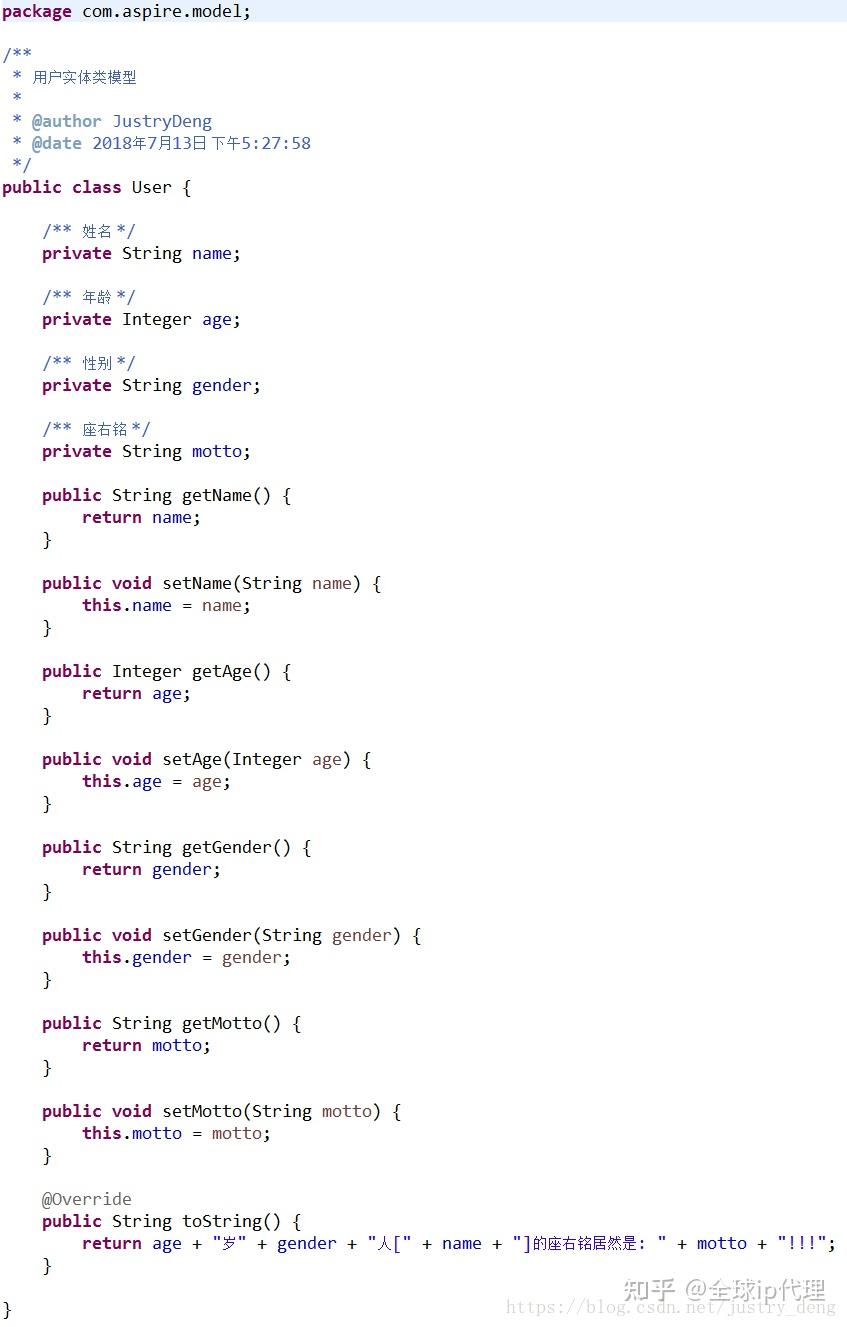
HttpClient发送示例:
/**
* POST---有参测试(对象参数)
*
* @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
*/
@Test
public void doPostTestTwo() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Post请求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerTwo");
User user = new User();
user.setName("潘晓婷");
user.setAge(18);
user.setGender("女");
user.setMotto("姿势要优雅~");
// 我这里利用阿里的fastjson,将Object转换为json字符串;
// (需要导入com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON包)
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);
StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(jsonString, "UTF-8");
// post请求是将参数放在请求体里面传过去的;这里将entity放入post请求体中
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对应接收示例:
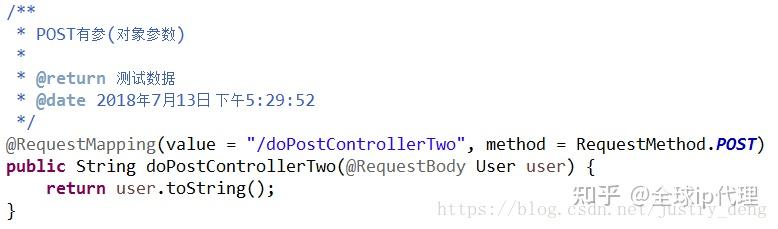
POST有参(普通参数 + 对象参数):
注:POST传递普通参数时,方式与GET一样即可,这里以通过URI获得HttpPost的方式为例。
先给出User类:

HttpClient发送示例:
/**
* POST---有参测试(普通参数 + 对象参数)
*
* @date 2018年7月13日 下午4:18:50
*/
@Test
public void doPostTestThree() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Post请求
// 参数
URI uri = null;
try {
// 将参数放入键值对类NameValuePair中,再放入集合中
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("flag", "4"));
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("meaning", "这是什么鬼?"));
// 设置uri信息,并将参数集合放入uri;
// 注:这里也支持一个键值对一个键值对地往里面放setParameter(String key, String value)
uri = new URIBuilder().setScheme("http").setHost("localhost").setPort(12345)
.setPath("/doPostControllerThree").setParameters(params).build();
} catch (URISyntaxException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(uri);
// HttpPost httpPost = new
// HttpPost("http://localhost:12345/doPostControllerThree1");
// 创建user参数
User user = new User();
user.setName("潘晓婷");
user.setAge(18);
user.setGender("女");
user.setMotto("姿势要优雅~");
// 将user对象转换为json字符串,并放入entity中
StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(JSON.toJSONString(user), "UTF-8");
// post请求是将参数放在请求体里面传过去的;这里将entity放入post请求体中
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对应接收示例:

原文:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/593661588
我曾七次鄙视自己的灵魂:
第一次,当它本可进取时,却故作谦卑;
第二次,当它在空虚时,用爱欲来填充;
第三次,在困难和容易之间,它选择了容易;
第四次,它犯了错,却借由别人也会犯错来宽慰自己;
第五次,它自由软弱,却把它认为是生命的坚韧;
第六次,当它鄙夷一张丑恶的嘴脸时,却不知那正是自己面具中的一副;
第七次,它侧身于生活的污泥中,虽不甘心,却又畏首畏尾。
时间仓促,如有错误欢迎指出,欢迎在评论区讨论,如对您有帮助还请点个推荐、关注支持一下
作者:博客园 - 角刀牛
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiaodaoniujava/
该文章来源互联网,本博仅以学习为目的,版权归原作者所有。
若内容有侵犯您权益的地方,请公告栏处联系本人,本人定积极配合处理解决。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号