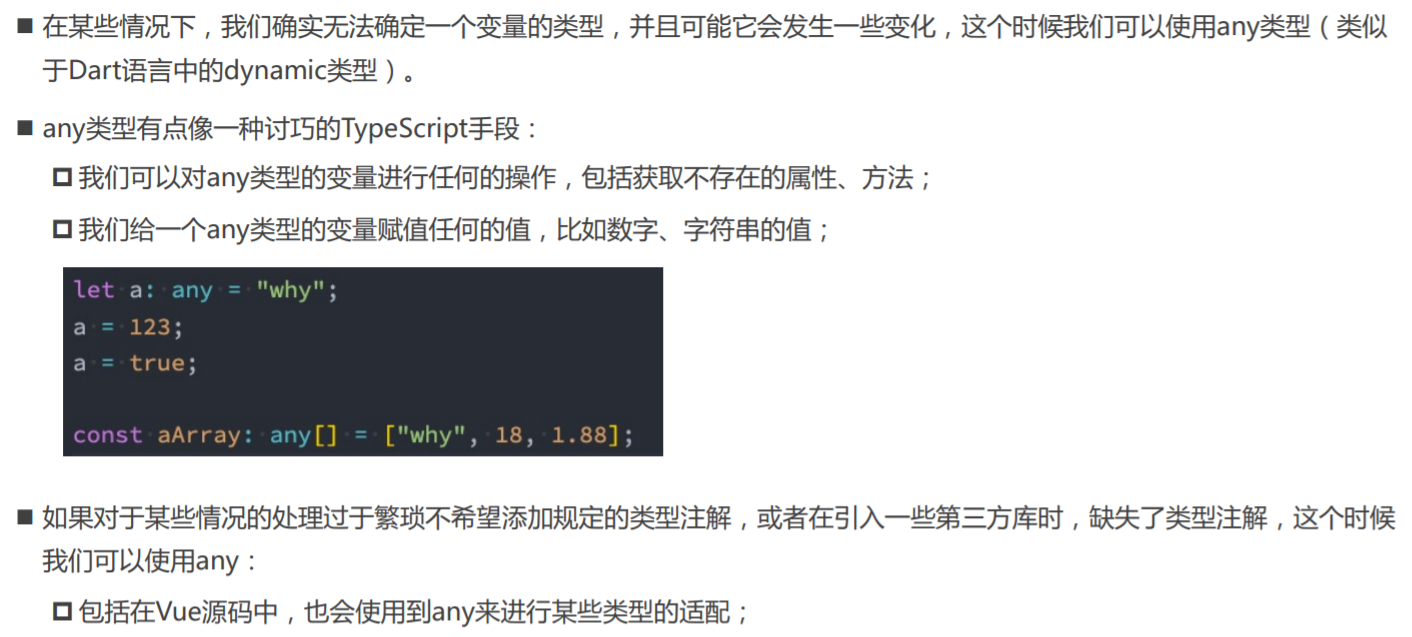
TypeScript类型 - any类型
TypeScript类型 - unknown类型

TypeScript类型 - void类型

TypeScript类型 - never类型

TypeScript类型 - tuple类型
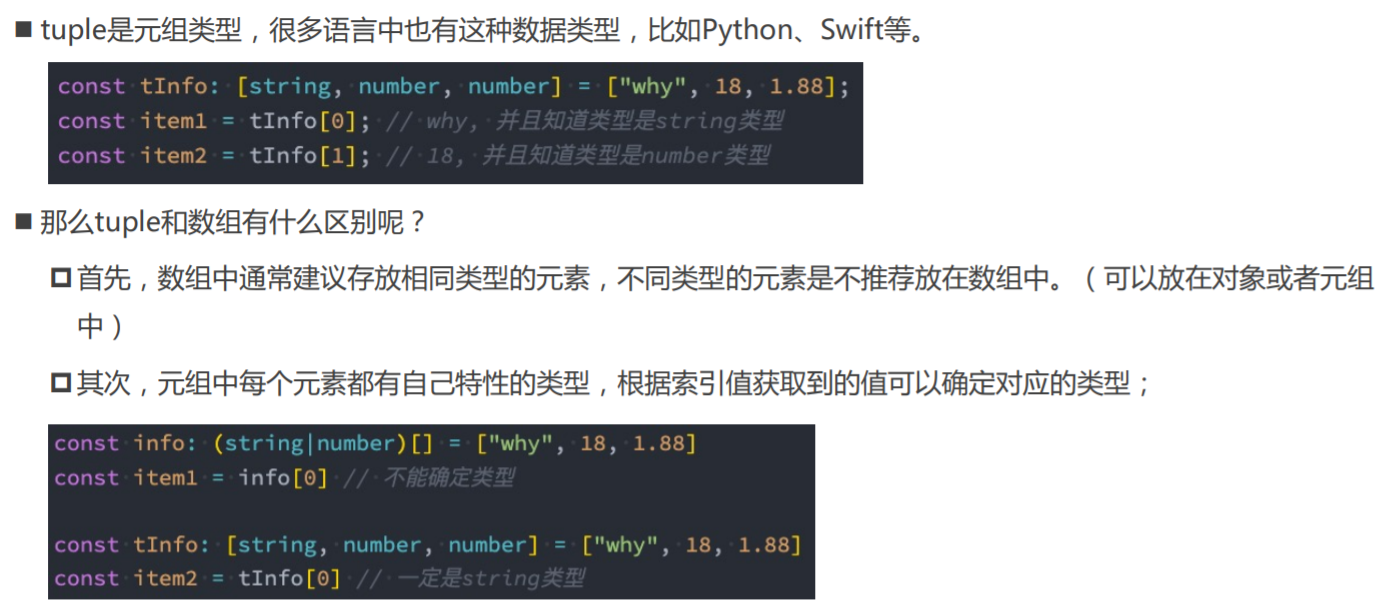
Tuples的应用场景

01_any类型的使用.ts
// 当进行一些类型断言 as any
// 在不想给某些JavaScript添加具体的数据类型时(原生的JavaScript代码是一样)
let message: any = 'Hello World'
message = 123
message = true
message = {}
// message()
// message.split(" ")
console.log(message)
const arr: any[] = [] // 【不推荐】
02_unknown类型的使用.ts
function foo() {
return 'abc'
}
function bar() {
return 123
}
// unknown类型只能赋值给any和unknown类型
// any类型可以赋值给任意类型
let flag = true
let result: unknown // 最好不要使用any
if (flag) {
result = foo()
} else {
result = bar()
}
// 补充
let aaa: any = result
let bbb: unknown = result
// let message: string = result
// let num: number = result
console.log(result) // abc
console.log(aaa) // abc
console.log(bbb) // abc
export {}
03_void类型的使用.ts
// 【此时,void可以省略不写。】
function sum(num1: number, num2: number) {
console.log(num1 + num2)
}
sum(20, 30)
// sum("abc", "cba")
04_never类型的使用.ts
// function foo(): never {
// // 死循环
// while(true) {
// }
// }
// function bar(): never {
// throw new Error()
// }
// 提前
// 封装一个核心函数
function handleMessage(message: string | number | boolean) {
switch (typeof message) {
case 'string':
console.log('string处理方式处理message')
break
case 'number':
console.log('number处理方式处理message')
break
case 'boolean':
console.log('boolean处理方式处理message')
break
default:
// 【增加boolean类型后,check报错,这样防止别人增加boolean类型后,不在函数体中编写对应的代码。】
// 【上面的case判断已经把所有的情况穷举完,代码不会执行到default中,message才会赋值给never类型的check。】
const check: never = message
}
}
handleMessage('abc')
handleMessage(123)
// 张三
handleMessage(true)
05_tuple类型的使用.ts
// tuple元组: 多种元素的组合
// "why" 18 1.88
// 1.数组的弊端
// const info: any[] = ["why", 18, 1.88]
// const infoObj = {
// name: "why",
// age: 18,
// height: 1.88
// }
// const name = info[0]
// console.log(name.length)
// 2.元组的特点
const info: [string, number, number] = ["why", 18, 1.88]
const name = info[0]
console.log(name.length)
// const age = info[1]
// console.log(age.length)
export {}
06_tuple的应用场景.ts
// hook: useState
// const [counter, setCounter] = {counter: , setCounter:}
function useState(state: any) {
let currentState = state
const changeState = (newState: any) => {
currentState = newState
}
const tuple: [any, (newState: any) => void] = [currentState, changeState]
return tuple
}
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(10);
setCounter(1000)
const [title, setTitle] = useState("abc")
export {}
07_tuple的应用场景(优化).ts
// hook: useState
// const [counter, setCounter] = {counter: , setCounter:}
function useState<T>(state: T) {
let currentState = state
const changeState = (newState: T) => {
currentState = newState
}
const info: [string, number] = ['abc', 18]
const tuple: [T, (newState: T) => void] = [currentState, changeState]
return tuple
}
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(10)
setCounter(1000)
const [title, setTitle] = useState('abc')
const [flag, setFlag] = useState(true)
// type MyFunction = () => void
// const foo: MyFunction = () => {}
函数的参数类型

函数的返回值类型

匿名函数的参数

对象类型

可选类型

联合类型

使用联合类型

可选类型补充

类型别名

01_函数的参数和返回值类型.ts
// 给参数加上类型注解: num1: number, num2: number
// 给返回值加上类型注释: (): number
// 在开发中, 通常情况下可以不写返回值的类型(自动推导)
function sum(num1: number, num2: number) {
return num1 + num2
}
// sum(123, 321)
02_匿名函数的参数类型.ts
// 通常情况下, 在定义一个函数时, 都会给参数加上类型注解的
function foo(message: string) {}
const names = ['abc', 'cba', 'nba']
// item根据上下文的环境推导出来的, 这个时候可以不添加的类型注解
// 上下文中的函数: 可以不添加类型注解 【自动类型推导。】
names.forEach(function (item) {
console.log(item.split(''))
})
03_对象类型.ts
// Point: x/y -> 对象类型
// {x: number, y: number}
function printPoint(point: { x: number; y: number }) {
console.log(point.x)
console.log(point.y)
}
printPoint({ x: 123, y: 321 })
export {}
04_可选类型.ts
// Point: x/y/z -> 对象类型
// {x: number, y: number, z?: number}
function printPoint(point: { x: number; y: number; z?: number }) {
console.log(point.x)
console.log(point.y)
console.log(point.z)
}
printPoint({ x: 123, y: 321 })
printPoint({ x: 123, y: 321, z: 111 })
export {}
05_联合类型.ts
// number|string 联合类型
function printID(id: number | string | boolean) {
// 使用联合类型的值时, 需要特别的小心
// narrow: 缩小
if (typeof id === 'string') {
// TypeScript帮助确定id一定是string类型
console.log(id.toUpperCase())
} else {
console.log(id)
}
}
printID(123)
printID('abc')
printID(true)
06_可选类型和联合类型的关系.ts
// 让一个参数本身是可选的
// 一个参数一个可选类型的时候, 它其实类似于是这个参数是 类型|undefined 的联合类型
// function foo(message?: string) {
// console.log(message)
// }
function foo(message?: string) {
console.log(message)
}
foo()
07_类型别名.ts
// type:用于定义类型别名(type alias)
type IDType = string | number | boolean
type PointType = {
x: number
y: number
z?: number
}
function printId(id: IDType) {}
function printPoint(point: PointType) {}
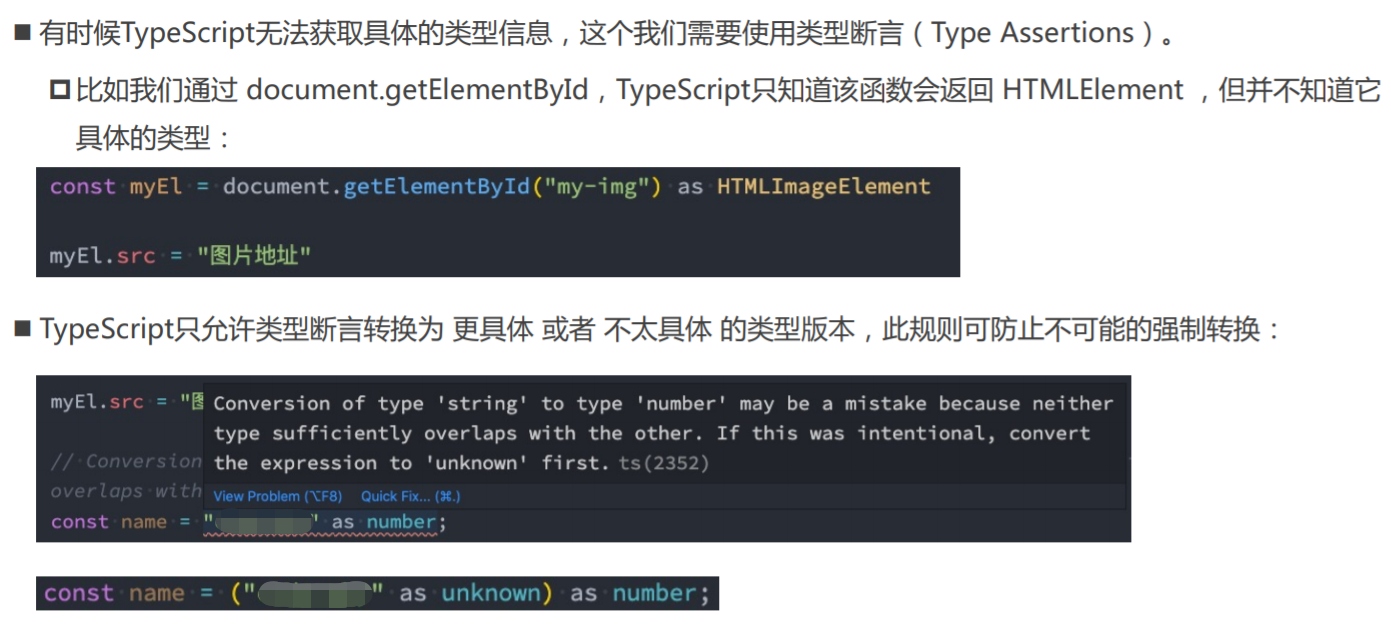
类型断言as
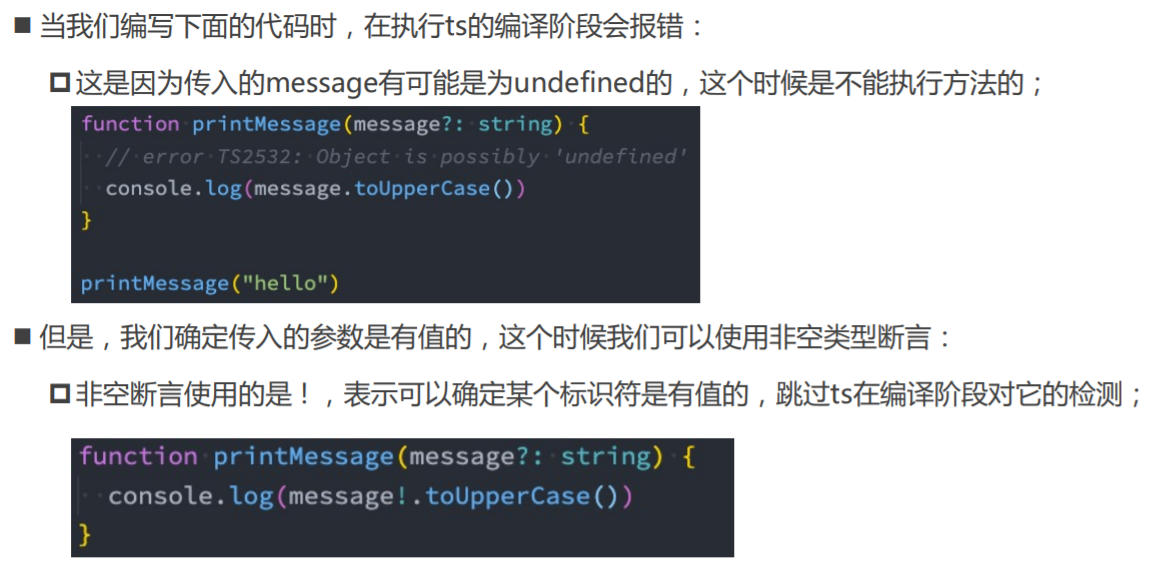
非空类型断言!
可选链的使用
??和!!的作用
字面量类型
字面量推理

类型缩小

typeof

平等缩小
instanceof
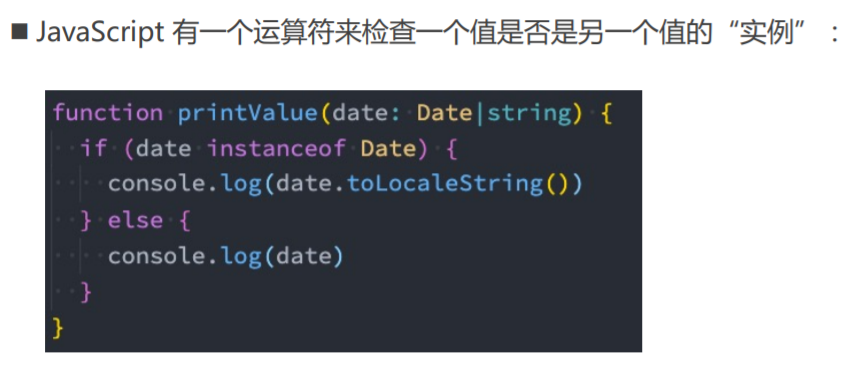
in

01_类型断言as.ts
// <img id="why"/>
// 1.类型断言 as 【从宽泛的HTMLElement中指定为具体的HTMLImageElement,这样就可以使用具体的类型中的属性、方法了。】
const el = document.getElementById('why') as HTMLImageElement
el.src = 'url地址'
// 2.另外案例: Person是Student的父类
class Person {}
class Student extends Person {
studying() {
console.log('study harding')
}
}
function sayHello(p: Person) {
;(p as Student).studying()
}
// 补充:这样写就不用使用as了,传入Student,而不是Person
function sayHello2(p: Student) {
p.studying()
}
const stu = new Student()
sayHello(stu)
// 3.了解: as any/unknown 【不推荐,除了特殊情况。】
const message = 'Hello World'
const num: number = message as unknown as number
02_非空类型断言.ts
// message? -> undefined | string
function printMessageLength(message?: string) {
// if (message) {
// console.log(message.length)
// }
// vue3源码 【确定某个标识符是有值的,跳过ts在编译阶段对它的检测,告诉tsc这个message是有值的,不用判断是否为空。】
console.log(message!.length)
}
printMessageLength('aaaa')
printMessageLength('hello world')
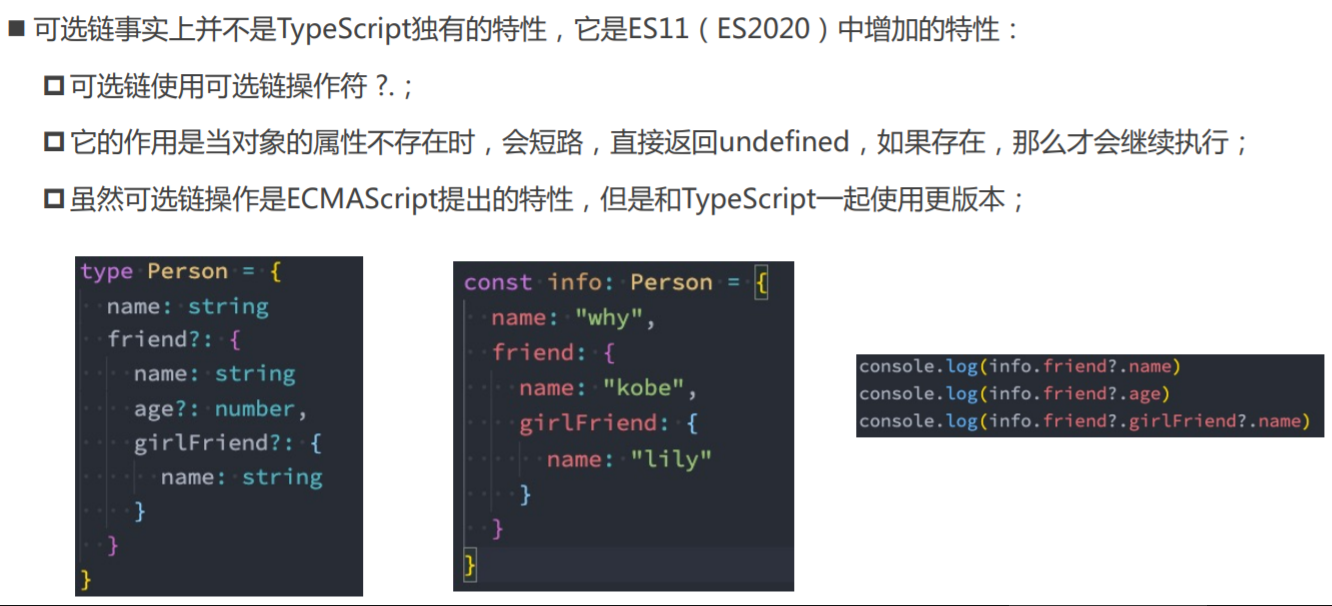
03_可选链的使用.ts
type Person = {
name: string
friend?: {
name: string
age?: number
girlFriend?: {
name: string
}
}
}
const info: Person = {
name: 'why',
friend: {
name: 'kobe',
girlFriend: {
name: 'lily',
},
},
}
// 另外一个文件中 【问号?:表示可能有,也可能没有,如果没有会逻辑短路,不再执行后面的代码,直接返回undefined。】
console.log(info.name)
// console.log(info.friend!.name)
console.log(info.friend?.name)
console.log(info.friend?.age)
console.log(info.friend?.girlFriend?.name)
// if (info.friend) {
// console.log(info.friend.name)
// if (info.friend.age) {
// console.log(info.friend.age)
// }
// }
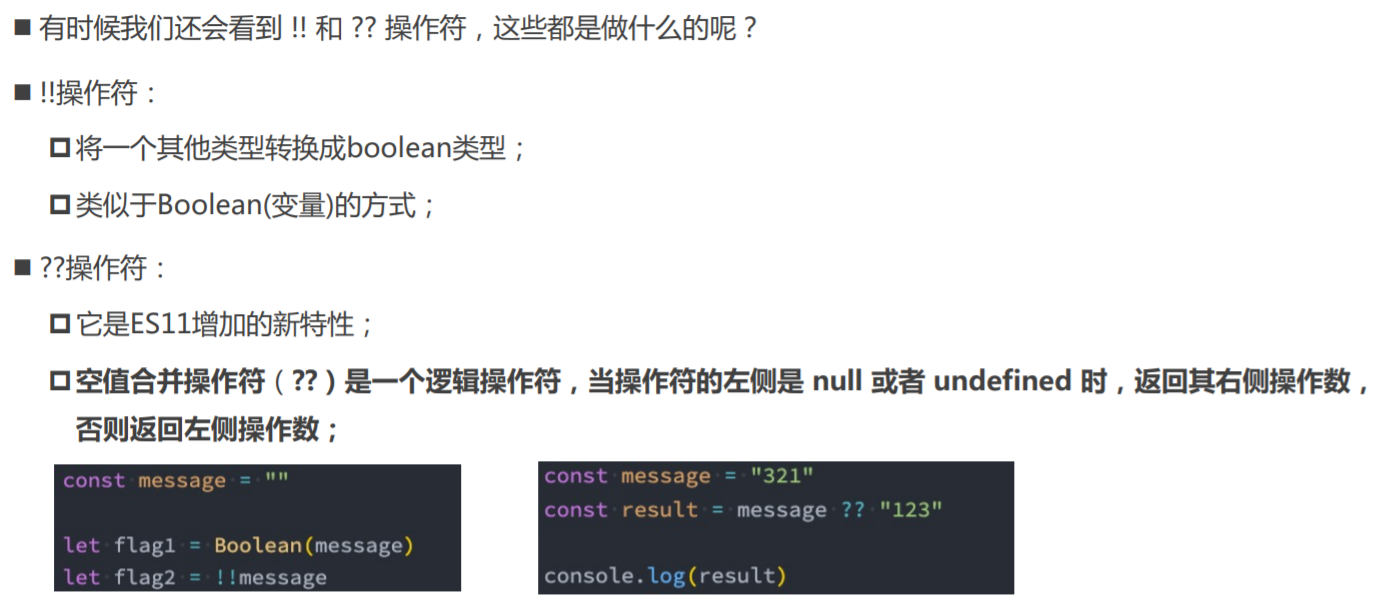
04_!!运算符.ts
const message = "Hello World"
// const flag = Boolean(message)
// console.log(flag)
const flag = !!message
console.log(flag)
05___运算符.ts
let message: string | null = 'Hello World'
const content = message ?? '你好啊, 哈哈'
// 【类似于逻辑或|| ,以及三目运算的简化。】
// const content = message ? message: "你好啊, 哈哈"
console.log(content)
// 补充
let msg1: string | null | undefined = 'aaa'
let msg2: string | null | undefined = null
let msg3: string | null | undefined = undefined
let res1 = msg1 ?? 'haha'
let res2 = msg2 ?? 'xixi'
let res3 = msg3 ?? 'hehe'
console.log(res1, res2, res3) // aaa xixi hehe
export {}
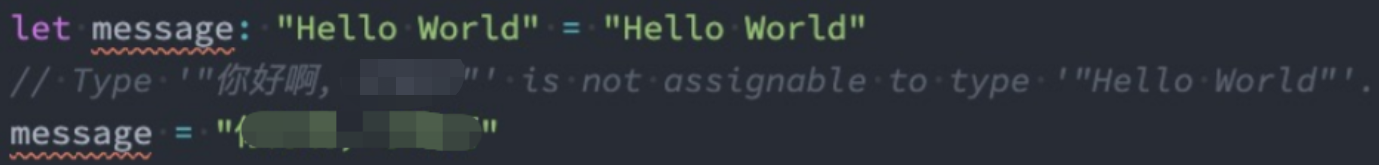
06_字面量类型.ts
// "Hello World"也是可以作为类型的, 叫做字面量类型
const message: 'Hello World' = 'Hello World'
// 【字面量类型:值和类型要一致,不能修改。】
// let num: 123 = 123
// num = 321
// 字面量类型的意义, 就是必须结合联合类型
type Alignment = 'left' | 'right' | 'center'
let align: Alignment = 'left'
align = 'right'
align = 'center'
// align = 'hehehehe'
07_字面量推理.ts
// const info = {
// name: "why",
// age: 18
// }
// info.name = "kobe"
type Method = 'GET' | 'POST'
function request(url: string, method: Method) {}
// 【方法1:推荐这种做法,一开始就把类型规定好。】
type Request = {
url: string
method: Method
}
// 【方法2:as const 在这里叫字面量推理,里面的属性就是只读了。】
const options = {
url: 'https://www.haha.org/abc',
method: 'POST',
} as const
// const options = {
// url: 'https://www.haha.org/abc',
// method: 'POST',
// }
// 【ts认为options.method就是字符串,不一定是 'GET' | 'POST',所以报错。】
request(options.url, options.method)
// 方法3:as Method 【个人觉得这种方法最简单,as规定options.method为Method即可。】
// request(options.url, options.method as Method)
export {}
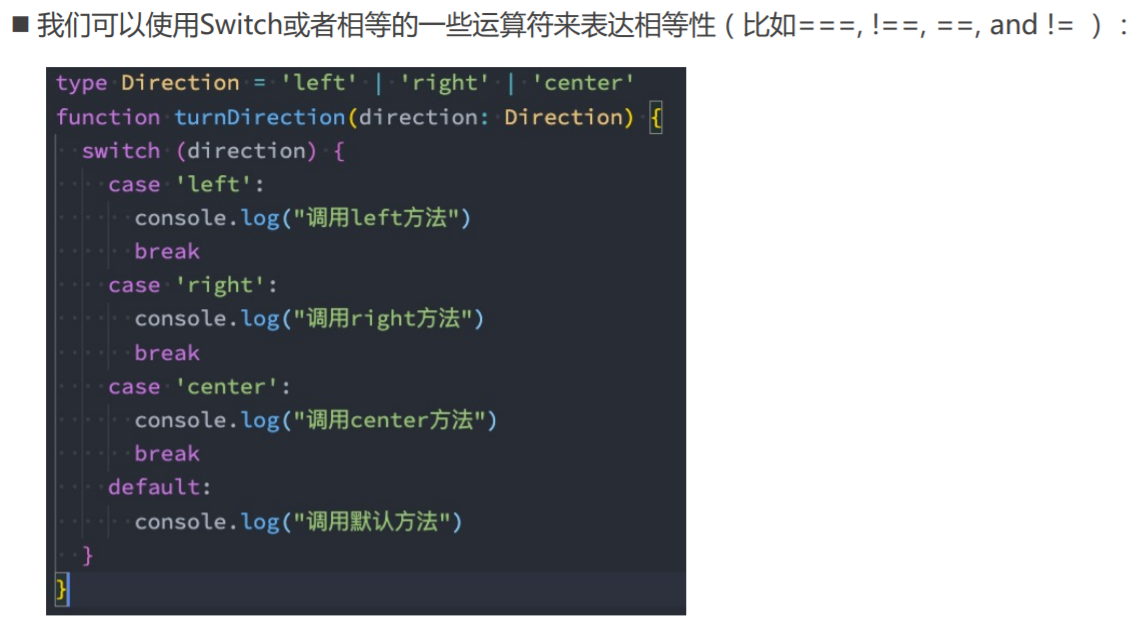
08_类型缩小.ts
// 1.typeof的类型缩小
type IDType = number | string
function printID(id: IDType) {
if (typeof id === 'string') {
console.log(id.toUpperCase())
} else {
console.log(id)
}
}
// 2.平等的类型缩小(=== == !== !=/switch)
type Direction = 'left' | 'right' | 'top' | 'bottom'
function printDirection(direction: Direction) {
// 1.if判断
// if (direction === 'left') {
// console.log(direction)
// } else if ()
// 2.switch判断
// switch (direction) {
// case 'left':
// console.log(direction)
// break;
// case ...
// }
}
// 3.instanceof
function printTime(time: string | Date) {
if (time instanceof Date) {
console.log(time.toUTCString())
} else {
console.log(time)
}
}
class Student {
studying() {}
}
class Teacher {
teaching() {}
}
function work(p: Student | Teacher) {
if (p instanceof Student) {
p.studying()
} else {
p.teaching()
}
}
const stu = new Student()
work(stu)
// 4. in
type Fish = {
swimming: () => void
}
type Dog = {
running: () => void
}
function walk(animal: Fish | Dog) {
if ('swimming' in animal) {
animal.swimming()
} else {
animal.running()
}
}
const fish: Fish = {
swimming() {
console.log('swimming')
},
}
walk(fish)




























