事件的介绍

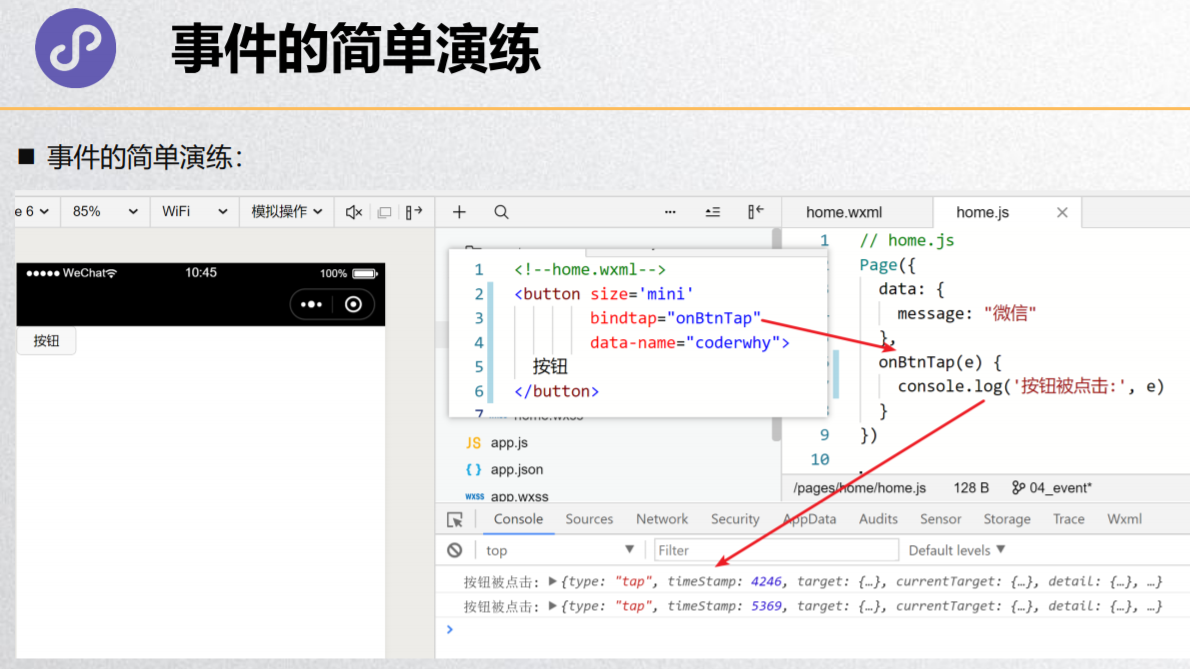
事件的简单演练
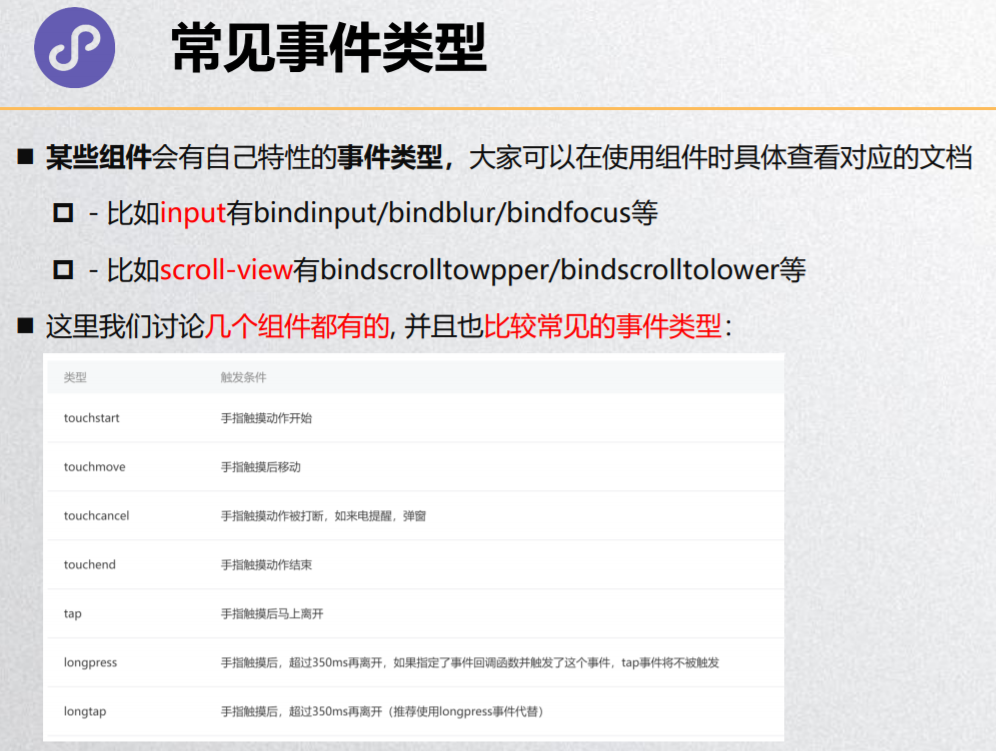
常见事件类型
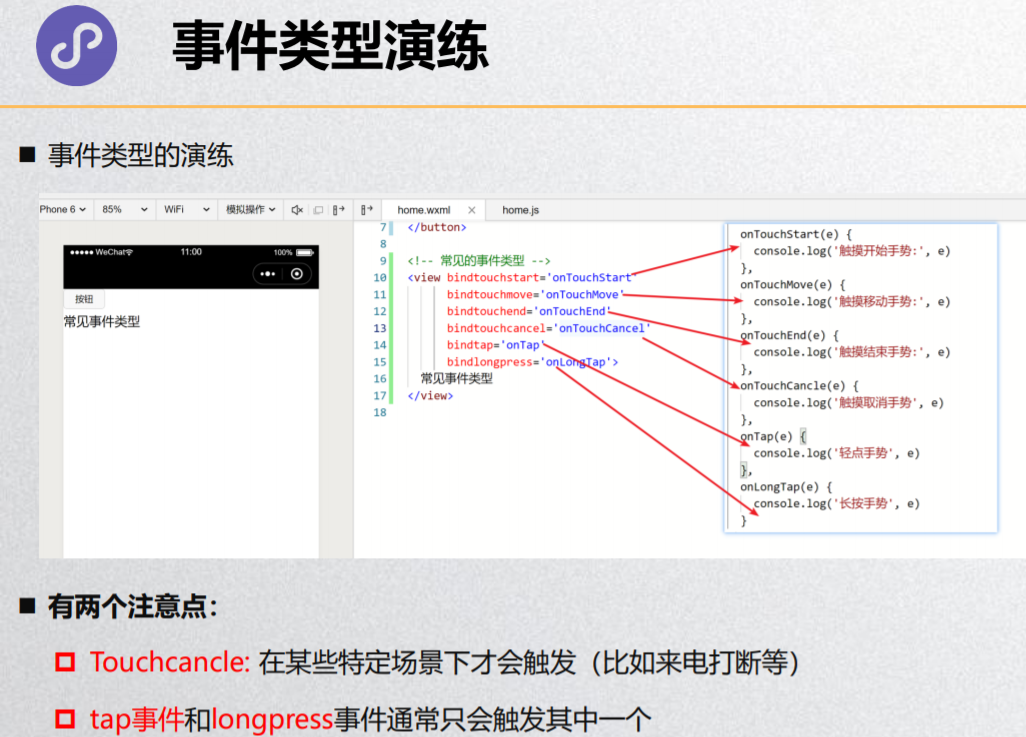
事件类型演练
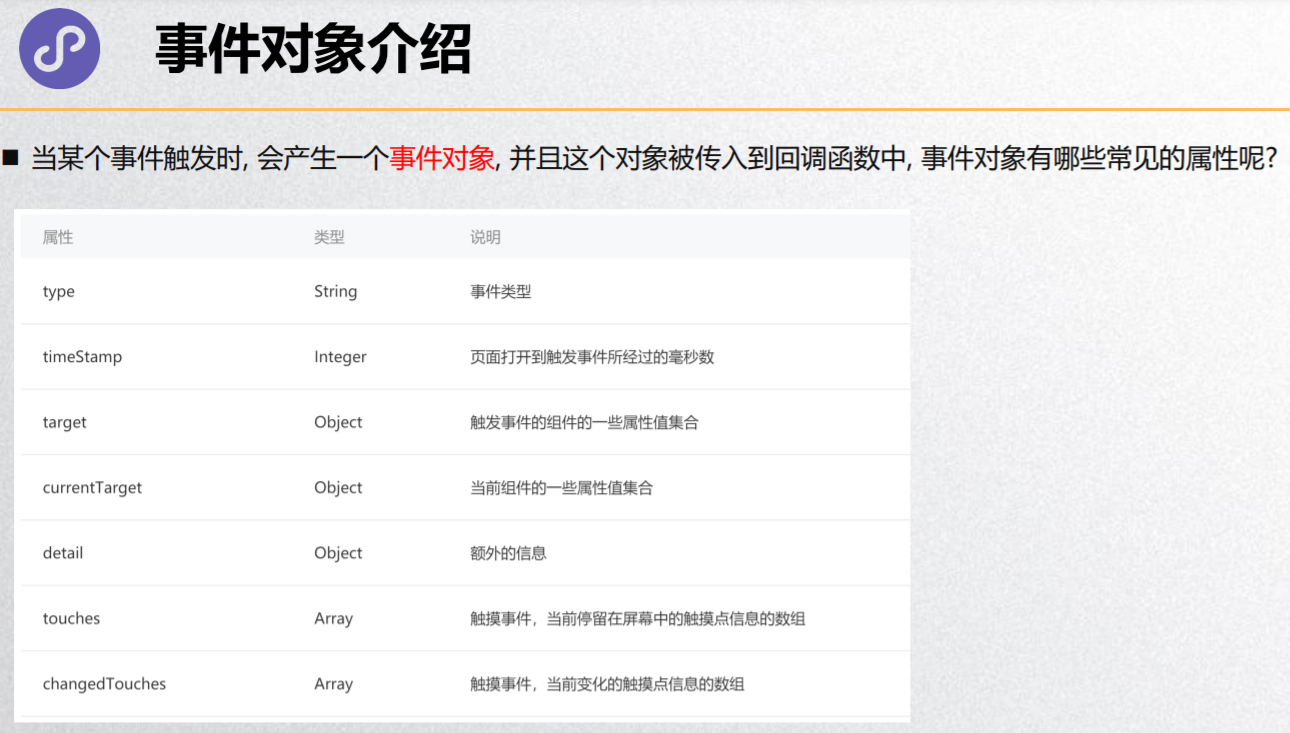
事件对象介绍
touches和changedTouches的区别

currentTarget和target的区别
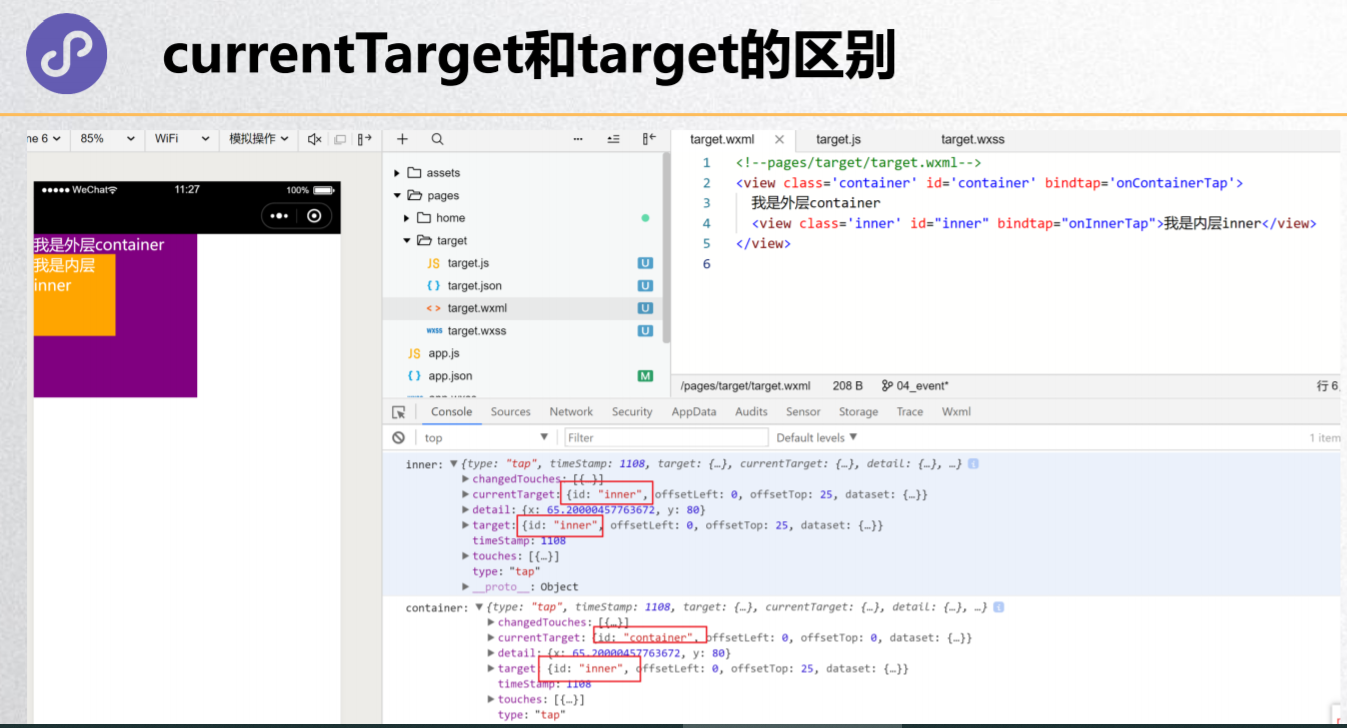
事件参数的传递
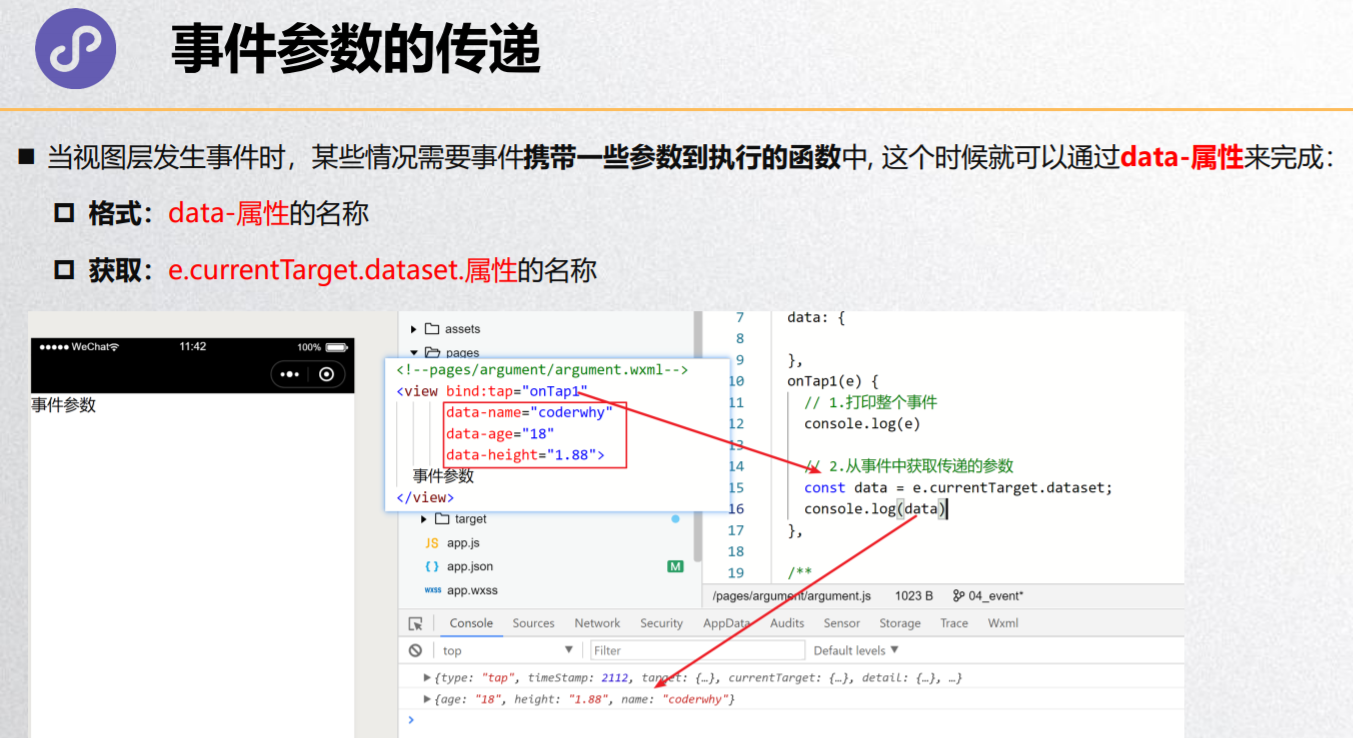
参数传递的练习
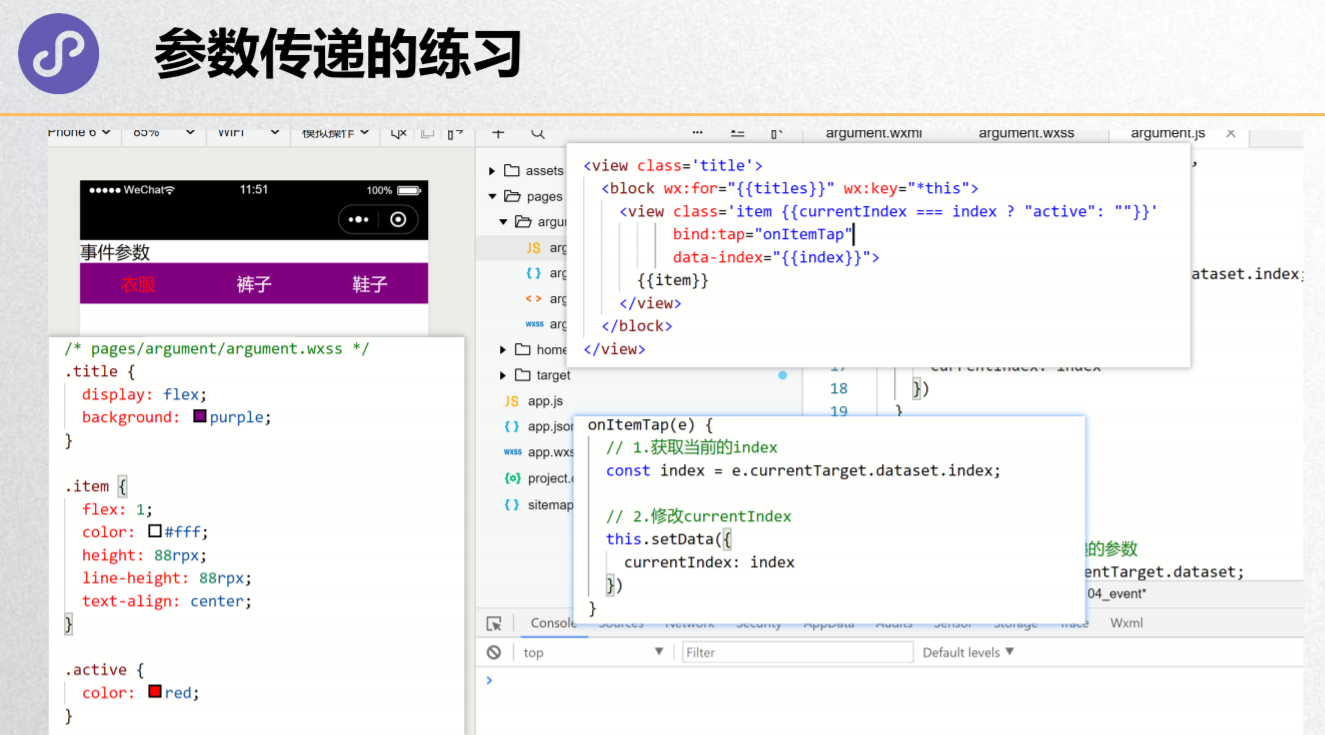
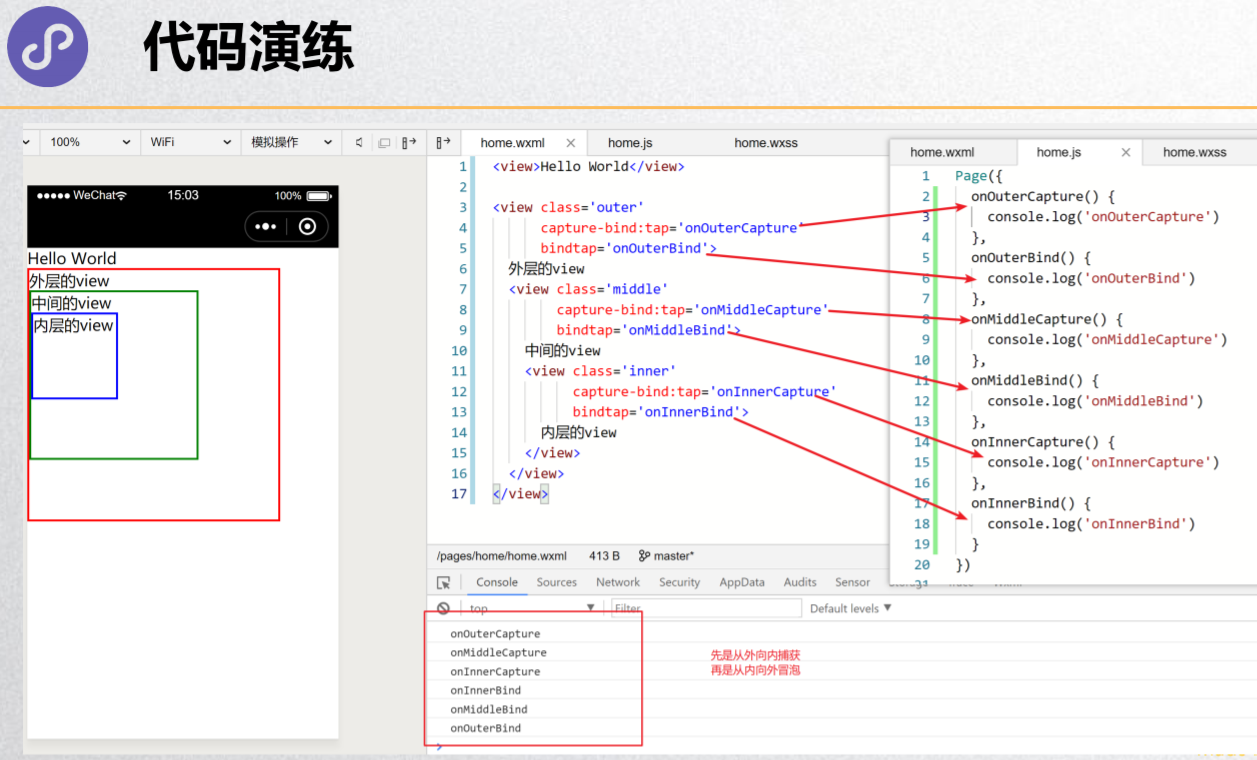
事件冒泡和事件捕获
代码演练
<!--pages/home/home.wxml-->
<!-- 1.事件处理的回顾 -->
<button bindtap='handleBtnClick' size='mini'>按钮</button>
<button bind:tap='handleBtnClick' size='mini'>按钮</button>
<button catch:tap='handleBtnClick' size='mini'>按钮</button>
<!-- 2.常见的一些事件 -->
<view class='box' bind:touchstart="handleTouchStart" bind:touchmove="handleTouchMove" bind:touchend="handleTouchEnd"
bind:tap="handleTap" bind:longpress="handleLongpress"></view>
<!-- 3.事件对象的分析 -->
<button id='btn' size='mini' bindtap='handleEventClick' bindtouchend='handleEventEnd'>事件对象</button>
<!-- 通过id区别。【target是事件源,是触发事件的对象,currentTarget可能是是触发事件的对象,也可能是被触发的对象。】 -->
<view class='outer' id='outer' bindtap='handleOuter'>
外层的view
<view class='inner' id='inner' bindtap='handleInner'>内层的view</view>
</view>
<!-- 4.事件的传递参数 【参数保存在event.currentTarget.dataset对象中,解构】 -->
<view class='container'>
<!-- wx:key="{{index}}"不需要{{}}包裹 -->
<block wx:for="{{titles}}" wx:key="{{index}}">
<view class='item' bindtap='handleItemClick' data-index="{{index}}" data-item="{{item}}">
{{item}}
</view>
</block>
</view>
<!-- 5.事件冒泡和事件捕获 - catch和bind区别 -->
<!-- bind: 一层层传递 -->
<!-- catch: 阻止事件的进一步传递 -->
<!-- 必须用冒号:的形式 -->
<!-- 结果:handleCaptureView1 handleCaptureView2 handleCaptureView3 handleBindView3 handleBindView2 -->
<view class='view1' capture-bind:tap="handleCaptureView1" bindtap='handleBindView1'>
<!-- 【这里用了catchtap,阻止了事件的进一步传递】 -->
<view class='view2' capture-bind:tap="handleCaptureView2" catchtap='handleBindView2'>
<view class='view3' capture-bind:tap="handleCaptureView3" bindtap='handleBindView3'></view>
</view>
</view>
// pages/home/home.js
Page({
data: {
titles: ['衣服', '裤子', '鞋子']
},
handleBtnClick() {
console.log('按钮发生点击')
},
handleTouchStart() {
console.log('handleTouchStart')
},
handleTouchMove() {
console.log('handleTouchMove')
},
handleTouchEnd() {
console.log('handleTouchEnd')
},
handleTap() {
console.log('handleTap')
},
handleLongpress() {
console.log('handleLongpress')
},
handleEventClick(event) {
console.log('-------', event)
},
handleEventEnd(event) {
console.log('+++++++', event)
},
handleInner(event) {
console.log(event)
},
handleOuter(event) {
console.log(event)
},
// 事件的传递参数
handleItemClick(event) {
console.log(event)
// title - index
const dataset = event.currentTarget.dataset;
// 用解构完事
const title = dataset.item;
const index = dataset.index;
console.log(title, index)
},
// ---------- 事件冒泡和事件捕获
handleCaptureView1() {
console.log('handleCaptureView1')
},
handleBindView1() {
console.log('handleBindView1')
},
handleCaptureView2() {
console.log('handleCaptureView2')
},
handleBindView2() {
console.log('handleBindView2')
},
handleCaptureView3() {
console.log('handleCaptureView3')
},
handleBindView3() {
console.log('handleBindView3')
}
})
/* pages/home/home.wxss */
.title {
color: red;
font-size: 30px;
}
.box {
width: 300rpx;
height: 300rpx;
background: orange;
}
.outer {
width: 400rpx;
height: 400rpx;
background: red;
color: white;
}
.inner {
width: 200rpx;
height: 200rpx;
background: blue;
color: white;
}
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
}
.view1 {
width: 600rpx;
height: 600rpx;
background: red;
}
.view2 {
width: 400rpx;
height: 400rpx;
background: blue;
}
.view3 {
width: 200rpx;
height: 200rpx;
background: green;
}













