剑指offer 1~5
1.用两个栈实现队列
用两个栈实现一个队列。队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数 appendTail 和 deleteHead ,分别完成在队列尾部插入整数和在队列头部删除整数的功能。(若队列中没有元素,deleteHead 操作返回 -1 )
class CQueue {
//全局声明两个栈
LinkedList<Integer> A,B;
public CQueue(){
A = new LinkedList<>();
B = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void appendTail(int value){
//用A栈实现队列元素的添加
A.addLast(value);
}
public int deleteHead(){
//用栈B实现队首元素的删除
if(!B.isEmpty()) return B.removeLast();
//如果A栈为空就返回-1
if(A.isEmpty()) return -1;
//当A栈不为空时就将A栈的元素出栈到B栈,实现逆序
while(!A.isEmpty()) B.addLast(A.removeLast());
//B栈栈尾元素就是A栈栈首元素
return B.removeLast();
}
}
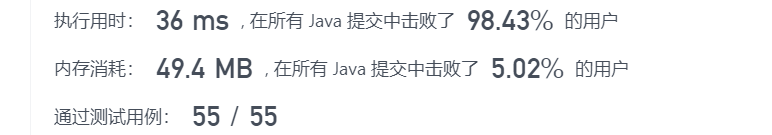
2.剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
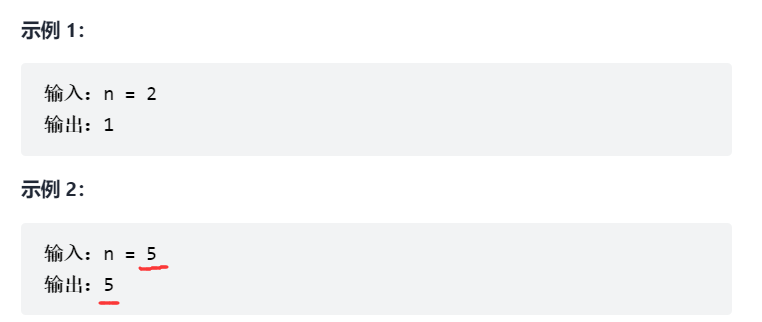
写一个函数,输入 n ,求斐波那契(Fibonacci)数列的第 n 项(即 F(N))。斐波那契数列的定义如下:
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
F(N) = F(N - 1) + F(N - 2), 其中 N > 1.
//注意:这个题算第零项,输入的n与数组下标为n的元素对应
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n==0) return 0;
if(n==1) return 1;
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++){
dp[i] = (dp[i-1] +dp[i-2])%1000000007;
}
return dp[n];
}
}
3.剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
HashMap
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(nums[i])) return nums[i];
else{
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int[] a = new int[nums.length];
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
a[nums[i]]++;
if(a[nums[i]] > 1) return nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
}
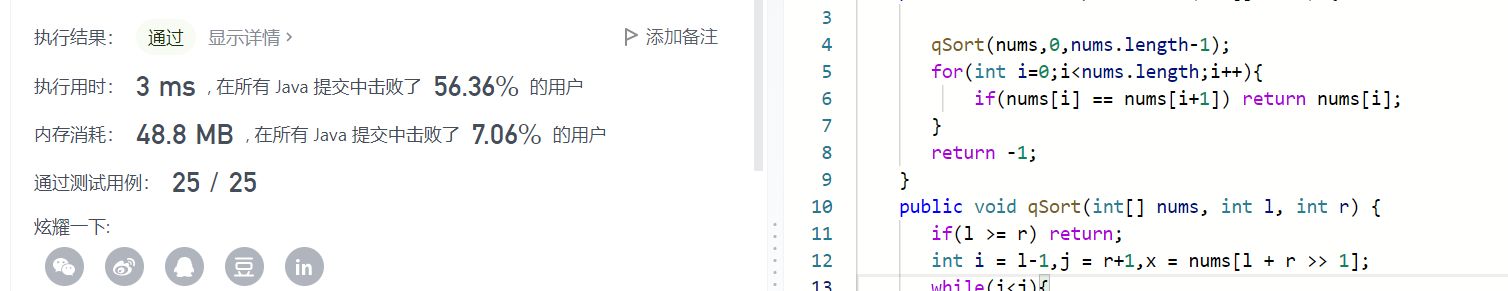
快排
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
qSort(nums,0,nums.length-1);
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i] == nums[i+1]) return nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
public void qSort(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if(l >= r) return;
int i = l-1,j = r+1,x = nums[l + r >> 1];
while(i<j){
do i++; while(nums[i] < x);
do j--; while(nums[j] > x);
if(i<j){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
qSort(nums,l,j);
qSort(nums,j+1,r);
}
}
一点都不快
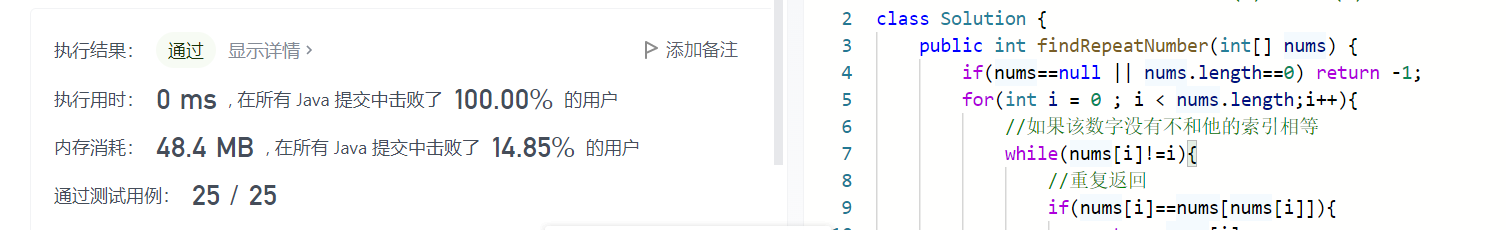
方法4:利用索引与数字的关系,时间O(n),空间O(1),修改了原数据
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null || nums.length==0) return -1;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length;i++){
//如果该数字没有不和他的索引相等
while(nums[i]!=i){
//重复返回
if(nums[i]==nums[nums[i]]){
return nums[i];
}
//不重复交换
int temp = nums[nums[i]];
nums[nums[i]] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
4.剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个高效的函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
思路:从右上角开始;小于目数就移动列,大于目标数就移动行。
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return false;
int m = matrix.length,n = matrix[0].length;
int row = 0,col = n-1;
while(row<m && col>=0){
if(matrix[row][col] > target) col--;
else if(matrix[row][col] < target) row++;
else return true;
}
return false;
}
}
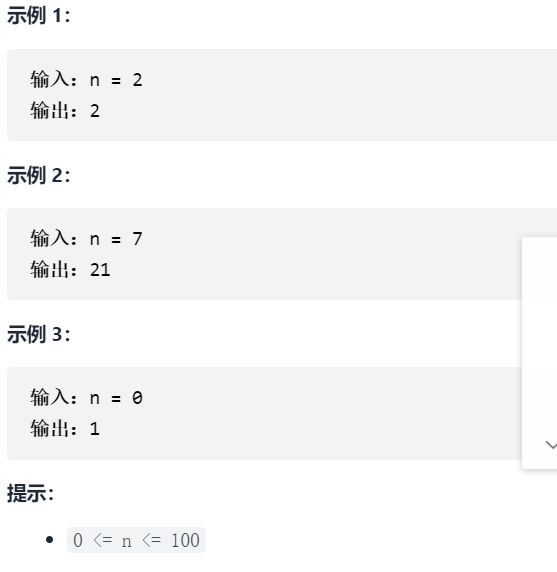
5.剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级台阶。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
答案需要取模 1e9+7(1000000007),如计算初始结果为:1000000008,请返回 1。
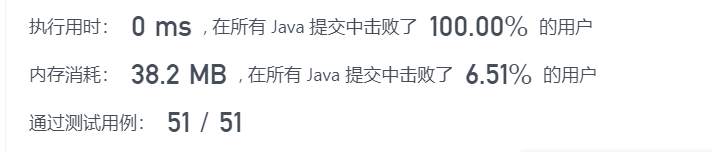
class Solution {
public int numWays(int n) {
if(n==0 || n==1) return 1;
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[0] = 1; dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
dp[i] = (dp[i-1] + dp[i-2]) % 1000000007;
}
return dp[n];
}
}
本文来自博客园,作者:蹇爱黄,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/jianjiana/p/15879405.html




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· 什么是nginx的强缓存和协商缓存
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?