C++ 实验二
task1
t.h代码:

1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <string> 4 5 // 类T: 声明 6 class T { 7 // 对象属性、方法 8 public: 9 T(int x = 0, int y = 0); // 普通构造函数 10 T(const T &t); // 复制构造函数 11 T(T &&t); // 移动构造函数 12 ~T(); // 析构函数 13 14 void adjust(int ratio); // 按系数成倍调整数据 15 void display() const; // 以(m1, m2)形式显示T类对象信息 16 17 private: 18 int m1, m2; 19 20 // 类属性、方法 21 public: 22 static int get_cnt(); // 显示当前T类对象总数 23 24 public: 25 static const std::string doc; // 类T的描述信息 26 static const int max_cnt; // 类T对象上限 27 28 private: 29 static int cnt; // 当前T类对象数目 30 31 // 类T友元函数声明 32 friend void func(); 33 }; 34 35 // 普通函数声明 36 void func();
t.cpp代码:

1 #include "t.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 5 using std::cout; 6 using std::endl; 7 using std::string; 8 9 // static成员数据类外初始化 10 const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"}; 11 const int T::max_cnt = 999; 12 int T::cnt = 0; 13 14 15 // 对象方法 16 T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} { 17 ++cnt; 18 cout << "T constructor called.\n"; 19 } 20 21 T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 22 ++cnt; 23 cout << "T copy constructor called.\n"; 24 } 25 26 T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 27 ++cnt; 28 cout << "T move constructor called.\n"; 29 } 30 31 T::~T() { 32 --cnt; 33 cout << "T destructor called.\n"; 34 } 35 36 void T::adjust(int ratio) { 37 m1 *= ratio; 38 m2 *= ratio; 39 } 40 41 void T::display() const { 42 cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ; 43 } 44 45 // 类方法 46 int T::get_cnt() { 47 return cnt; 48 } 49 50 // 友元 51 void func() { 52 T t5(42); 53 t5.m2 = 2049; 54 cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); cout << endl; 55 }
task1.cpp代码:

1 #include "t.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 void test(); 8 9 int main() { 10 test(); 11 cout << "\nmain: \n"; 12 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 13 } 14 15 void test() { 16 cout << "test class T: \n"; 17 cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl; 18 cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl; 19 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl; 20 21 22 T t1; 23 cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl; 24 25 T t2(3, 4); 26 cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl; 27 28 T t3(t2); 29 t3.adjust(2); 30 cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl; 31 32 T t4(std::move(t2)); 33 cout << "t3 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl; 34 35 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 36 37 func(); 38 }
运行结果截图:

问题1:
可以去掉line36(我也不知道为什么我去掉也可以运行,其他代码我友元函数也没在头文件中声明过)
问题2:
T(int x = 0, int y = 0) :此构造函数有默认形参值,即如果x/y不给实参值,则默认赋值为0,有实参值,则依旧把实参值赋给x和y 调用时机:在定义一个对象时,且实参类型不是引用类型,而是0/1/2个数字
T(const T &t) :赋值构造函数,支持将一个对象复制给另一个对象(即用另一个对象来初始化一个新对象,且形参中引用的对象不会被销毁) 调用时机:将一个对象赋值给另一个对象时,或者定义时对象的形参为引用类型
T(T &&t) :移动构造函数,对象 t 是使用右值引用的形式来传参,即将对象t 复制给一个对象,且复制完就把右值引用对象t 销毁 调用时机,只有对象的实参是一个右值引用类型时会调用,一般和move函数搭配使用
析构函数调用时机:对象生命周期结束被销毁时
问题3:
不能成功编译运行,因为静态数据成员需要在类定义(头文件)之外再重新定义(需要用这种方式为它们专门分配空间)
task2:
Complex.h 代码:

1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Complex 6 { 7 public: 8 Complex(double x = 0, double y = 0) :real(x), imag(y) {} 9 Complex(const Complex& L); 10 double get_real(); 11 double get_imag(); 12 void add(Complex L2); 13 14 friend Complex add(Complex L1, Complex L2); 15 friend bool is_equal(Complex L1, Complex L2); 16 friend bool is_not_equal(Complex L1, Complex L2); 17 friend void output(Complex L); 18 friend double abs(Complex L); 19 20 static string doc; 21 22 private: 23 24 double real; 25 double imag; 26 27 };
Complex.cpp 代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include"Complex.h" 3 #include<cmath> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 string Complex::doc = "a simplified complex class"; 7 Complex::Complex(const Complex& L) 8 { 9 real = L.real; 10 imag = L.imag; 11 } 12 13 double Complex::get_real() 14 { 15 return real; 16 } 17 double Complex::get_imag() 18 { 19 return imag; 20 } 21 22 void Complex::add(Complex L2) 23 { 24 real += L2.real; 25 imag += L2.imag; 26 } 27 Complex add(Complex L1, Complex L2) 28 { 29 Complex L3; 30 L3.real = L1.real + L2.real; 31 L3.imag = L1.imag + L2.imag; 32 return L3; 33 } 34 bool is_equal(Complex L1, Complex L2) 35 { 36 if (L1.real == L2.real && L1.imag == L2.imag) 37 { 38 return true; 39 } 40 else 41 { 42 return false; 43 } 44 } 45 46 bool is_not_equal(Complex L1, Complex L2) 47 { 48 if (L1.real == L2.real && L1.imag == L2.imag) 49 { 50 return false; 51 } 52 else 53 { 54 return true; 55 } 56 57 } 58 void output(Complex L) 59 { 60 if (L.imag >= 0) 61 cout << L.real << "+" << L.imag << "i"; 62 else 63 { 64 cout << L.real << L.imag << "i"; 65 } 66 } 67 68 double abs(Complex L) 69 { 70 double c; 71 c = sqrt(L.real * L.real + L.imag * L.imag); 72 return c; 73 }
task2.cpp 代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "Complex.h" 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::boolalpha; 7 8 void test() { 9 cout << "类成员测试: " << endl; 10 cout << Complex::doc << endl; 11 12 cout << endl; 13 14 cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl; 15 Complex c1; 16 Complex c2(3, -4); 17 const Complex c3(3.5); 18 Complex c4(c3); 19 20 cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 21 cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl; 22 cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl; 23 cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 24 cout << "c4.real = " << c4.get_real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.get_imag() << endl; 25 26 cout << endl; 27 28 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 29 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 30 c1.add(c2); 31 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 32 cout << boolalpha; 33 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 34 cout << "c1 != c3 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c3) << endl; 35 c4 = add(c2, c3); 36 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 37 } 38 39 int main() { 40 test(); 41 }
这题我用的VS写的,不用加string.h的头文件好像也能编译成功(不知道为什么)
运行结果截图:
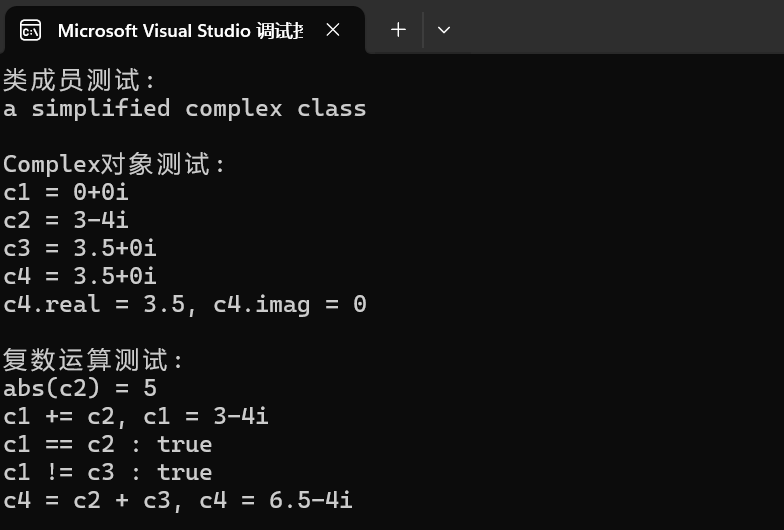
task3:
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <complex> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::boolalpha; 7 using std::complex; 8 9 void test() { 10 cout << "标准库模板类comple测试: " << endl; 11 complex<double> c1; 12 complex<double> c2(3, -4); 13 const complex<double> c3(3.5); 14 complex<double> c4(c3); 15 16 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl; 17 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl; 18 cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl; 19 cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl; 20 cout << "c4.real = " << c4.real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.imag() << endl; 21 cout << endl; 22 23 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 24 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 25 c1 += c2; 26 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl; 27 cout << boolalpha; 28 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl; 29 cout << "c1 != c3 : " << (c1 != c3) << endl; 30 c4 = c2 + c3; 31 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl; 32 } 33 34 int main() { 35 test(); 36 }
运行结果截图:
接口:
可以以对象名直接输出一个复数,对象名.real()即返回此对象的real数据成员,对象名.imag()即返回此对象的imag数据成员,abs()函数完成取模运算,对象之间可以之间进行运算(加减),可以直接进行判断是否相等
对比taks2:
1.输出时,可以用对象名进行输出,则直接输出一个复数(带括号),取模差不多,但对象之间直接可以进行运算(加减),判断是否相等
2.在程序设计中,多运用标准库中自带的模板类可以大大提高程序开发效率和节约时间,并且可以使代码整洁非常多
task4:
代码:
Fraction.h

1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Fraction 6 { 7 private: 8 int up, down; 9 10 11 public: 12 static const string doc; 13 Fraction(int x = 0, int y = 1); 14 Fraction(const Fraction& L); 15 int get_up(); 16 int get_down(); 17 Fraction negative(); 18 19 void yuefen(); 20 friend void output(Fraction L); 21 friend Fraction add(Fraction L1, Fraction L2); 22 friend Fraction sub(Fraction L1, Fraction L2); 23 friend Fraction mul(Fraction L1, Fraction L2); 24 friend Fraction div(Fraction L1, Fraction L2); 25 26 27 };
Fraction.cpp

1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cmath> 4 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const string Fraction::doc = "Fraction类v0.01版.\n目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加/减/乘/除运算"; 9 10 11 int gongyueshu(int a, int b) 12 { 13 int r; 14 while (b > 0) 15 { 16 r = a % b; 17 a = b; 18 b = r; 19 } 20 return a; 21 } 22 23 Fraction::Fraction(int x, int y):up(x),down(y) 24 { 25 if (down == 0) 26 { 27 cout << "分母不能为0"; 28 } 29 yuefen(); 30 } 31 32 Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction& L) 33 { 34 up = L.up; 35 down = L.down; 36 } 37 38 void Fraction::yuefen() 39 { 40 int shu = gongyueshu(abs(up), abs(down)); 41 up = up / shu; 42 down = down / shu; 43 44 } 45 46 47 48 int Fraction::get_up() 49 { 50 return up; 51 } 52 int Fraction::get_down() 53 { 54 return down; 55 } 56 Fraction Fraction::negative() 57 { 58 return Fraction(-up, down); 59 } 60 void output(Fraction L) 61 { 62 63 64 if (L.up * L.down < 0) 65 { 66 if (L.up % L.down == 0) 67 { 68 cout << "-" << abs(L.up) /abs( L.down); 69 } 70 else 71 { 72 cout << "-" << abs(L.up) << "/" << abs(L.down); 73 } 74 } 75 else 76 { 77 if (L.up % L.down == 0) 78 { 79 cout << abs(L.up) / abs(L.down); 80 } 81 else 82 { 83 cout << abs(L.up) << "/" << abs(L.down); 84 } 85 } 86 87 } 88 89 Fraction add(Fraction L1, Fraction L2) 90 { 91 int a, b; 92 b = L1.down * L2.down; 93 a = L1.up * L2.down + L2.up * L1.down; 94 return Fraction(a, b); 95 } 96 Fraction sub(Fraction L1, Fraction L2) 97 { 98 int a, b; 99 b = L1.down * L2.down; 100 a = L1.up * L2.down - L2.up * L1.down; 101 return Fraction(a, b); 102 } 103 Fraction mul(Fraction L1, Fraction L2) 104 { 105 int a, b; 106 a = L1.up * L2.up; 107 b = L1.down * L2.down; 108 return Fraction(a, b); 109 } 110 Fraction div(Fraction L1, Fraction L2) 111 { 112 int a, b; 113 a = L1.up * L2.down; 114 b= L1.down * L2.up; 115 return Fraction(a, b); 116 }
task4.cpp

1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 void test1() { 8 cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl; 9 cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl; 10 11 Fraction f1(5); 12 Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12); 13 Fraction f4(f3); 14 cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl; 15 cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl; 16 cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl; 17 cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl; 18 19 Fraction f5(f4.negative()); 20 cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl; 21 cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl; 22 23 cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 24 cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 25 cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 26 cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 27 cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl; 28 } 29 30 void test2() { 31 Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3); 32 cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl; 33 cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl; 34 cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl; 35 } 36 37 int main() { 38 cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n"; 39 test1(); 40 41 cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n"; 42 test2(); 43 }
代码截图:
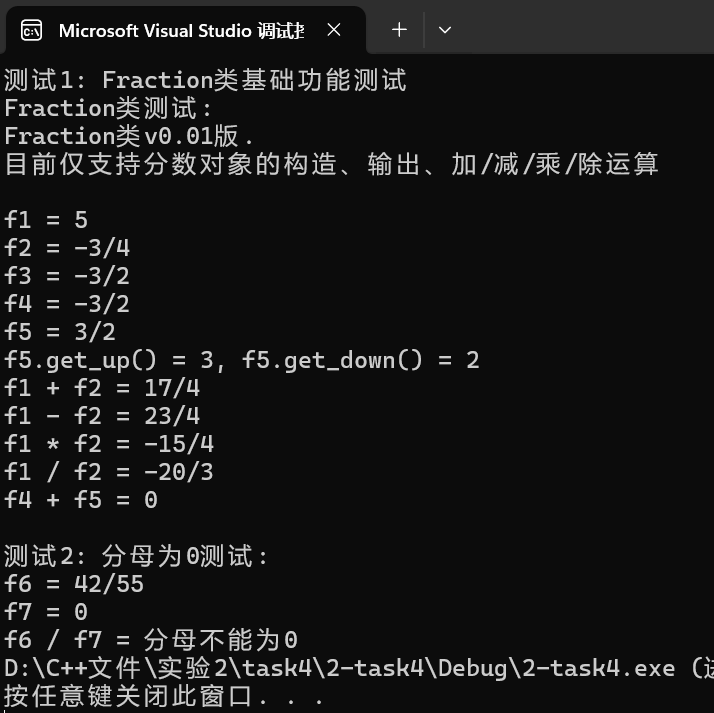
task5:
account.h

1 #pragma once 2 class SavingsAccount { 3 private: 4 int id; 5 double balance; 6 double rate; 7 int lastDate; 8 double accumulation; 9 static double total; 10 void record(int date, double amount); 11 double accumulate(int date) const 12 { 13 return accumulation + balance * (date - lastDate); 14 15 } 16 public: 17 SavingsAccount(int date, int id, double rate); 18 int getId()const { return id; } 19 double getBalance()const { return balance; } 20 double getRate()const { return rate; } 21 static double getTotal() { return total; } 22 void deposit(int date, double amount); 23 void withdraw(int date, double amount); 24 void settle(int date); 25 void show()const; 26 27 };
account.cpp

1 #include"account.h" 2 #include<cmath> 3 #include<iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 double SavingsAccount::total = 0; 6 SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(int date, int id, double rate) :id(id), balance(0), rate(rate), lastDate(date), accumulation(0) 7 { 8 cout << date << "\t#" << id << " is created" << endl; 9 } 10 11 void SavingsAccount::record(int date, double amount) 12 { 13 accumulation = accumulate(date); 14 lastDate = date; 15 amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; 16 balance += amount; 17 total += amount; 18 cout << date << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << endl; 19 20 } 21 void SavingsAccount::deposit(int date, double amount) { 22 record(date, amount); 23 24 } 25 void SavingsAccount::withdraw(int date, double amount) { 26 if (amount > getBalance()) 27 cout << "Error:not enough money" << endl; 28 else 29 { 30 record(date, -amount); 31 32 } 33 } 34 void SavingsAccount::settle(int date) { 35 double interest = accumulate(date) * rate / 365; 36 if (interest != 0) 37 record(date, interest); 38 accumulation = 0; 39 40 } 41 void SavingsAccount::show()const { 42 cout << "#" << id << "\tBalance:" << balance; 43 44 }
task5.cpp

1 #include"account.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() { 5 SavingsAccount sa0(1, 21325302, 0.015); 6 SavingsAccount sa1(1, 58320212, 0.015); 7 sa0.deposit(5, 5000); 8 sa1.deposit(25, 10000); 9 sa0.deposit(45, 5500); 10 sa1.withdraw(60, 4000); 11 sa0.settle(90); 12 sa1.settle(90); 13 sa0.show(); cout << endl; 14 sa1.show(); cout << endl; 15 cout << "Total: " << SavingsAccount::getTotal() << endl; 16 return 0; 17 18 }
运行截图:

感觉蛮合理的,以我目前水平,感觉优化不了,对代码的实现没有疑问,都看得懂
实验总结:
依旧对c++函数库了解比较少,其实很多函数都已经在函数库中给出了,比如求最大公约数gcd函数,还有模板库,比如Complex复数模板库,可以大大节省调代码的时间,并且功能还很多,也有重载类型(double,int等)
问题:
对类的代码书写还不太熟练,敲代码比较慢(练习较少)




