Python 拼接字符串的几种方式
在学习Python(3x)的过程中,在拼接字符串的时候遇到了些问题,所以抽点时间整理一下Python 拼接字符串的几种方式。
方式1,使用加号(+)连接,使用加号连接各个变量或者元素必须是字符串类型(<class 'str'>)
例如:
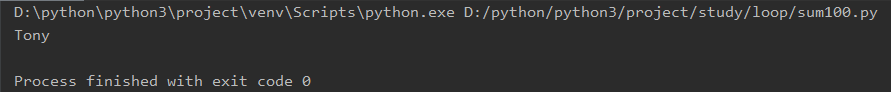
str_name1 = 'To' str_name2 = 'ny' str_name = str_name1 + str_name2 print(str_name)
输出结果:
下面的代码会出现错误
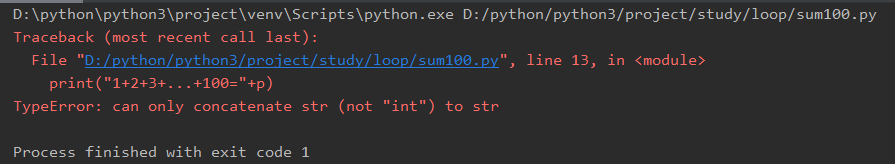
number=34 print('这个数是:'+number)
编译通过运行才发现行不通,出现了一下错误。
修改Python 代码:
number=34 print('这个数是:'+str(number))
方式三:使用.joiin(iterable) 拼接
print('-----------method3-----------') # method3 使用join拼接字符串 # str.join(iterable) # 可join的条件 join(iterable) iterable 可迭代的, 如果列表(list)为 非嵌套列表,列表元素为字符串(str)类型, # 序列类型,散列类型 都可以作为参数传入 # eg(1): list_good_night = ['晚', '上', '好', '!'] str_night = ''.join(list_good_night) print(str_night) # eg(2): # 拼接前缀 ('拼接前缀').join(iterable) str_night1 = '------>'.join(list_good_night) print(str_night1) # eg(3) 拼接 iterable = 字典 key,value 必须字符串 默认拼接key 的列表 dict_name = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'} str_key = ','.join(dict_name) # 拼接value 的列表 str_value = ','.join(dict_name.values()) print(str_key) print(str_value)
执行结果:

方式四:使用逗号(,)拼接
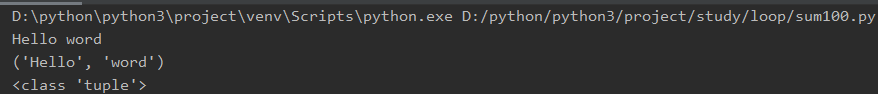
# method4 使用逗号(,)连接 # 使用,逗号形式要注意一点,就是只能用于print打印,赋值操作会生成元组: print('-----------method4-----------') a, b = 'Hello', 'word' c = a, b print(a, b) print(c) print(type(c))
输出结果:
方式五:直接拼接
# mehon5 直接连接 print('-----------method5-----------') print('hello''python')
方式六:format 拼接
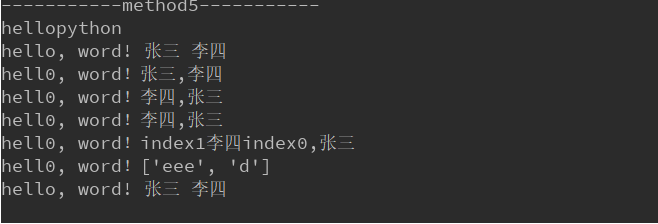
# mehon5 直接连接 print('-----------method5-----------') print('hello''python') # methon6 format 拼接 str.format(args,**kwargs) # eg(1) {} 充当占位符 str_word = 'hello, word! {} {}'.format('张三', '李四') print(str_word) # eg(2) {[index]} 按索引位置填充 .format([0]=value1, [1]= value1},) str_word_index0 = 'hell0, word!{0},{1}'.format('张三', '李四') str_word_index1 = 'hell0, word!{1},{0}'.format('张三', '李四') print(str_word_index0) print(str_word_index1) # eg(3) {[keyword]} str_word_keyword = 'hell0, word!{a},{b}'.format(b='张三', a='李四') print(str_word_keyword) # eg(4) {[keyword,indec]} keyword 放在最后 str_word1 = 'hell0, word!{1}{a}{0},{b}'.format('index0', 'index1', b='张三', a='李四') print(str_word1) # eg(5) format 参数类型不限,当为元祖,列表,集合,字典时输出 str_word2 = 'hell0, word!{b}'.format(b=['eee', 'd']) print(str_word2) # eg(6) 作为函数使用 str_word3 = 'hello, word! {} {}'.format word = str_word3('张三', '李四') print(word)
输出结果:
原创文章请随便转载。愿和大家分享,并且一起进步。-- 江 coder
分类:
Python3





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix