Spring Boot入门
Spring Boot入门:
使用IDEA创建Spring Boot 项目:
选择

勾选Web
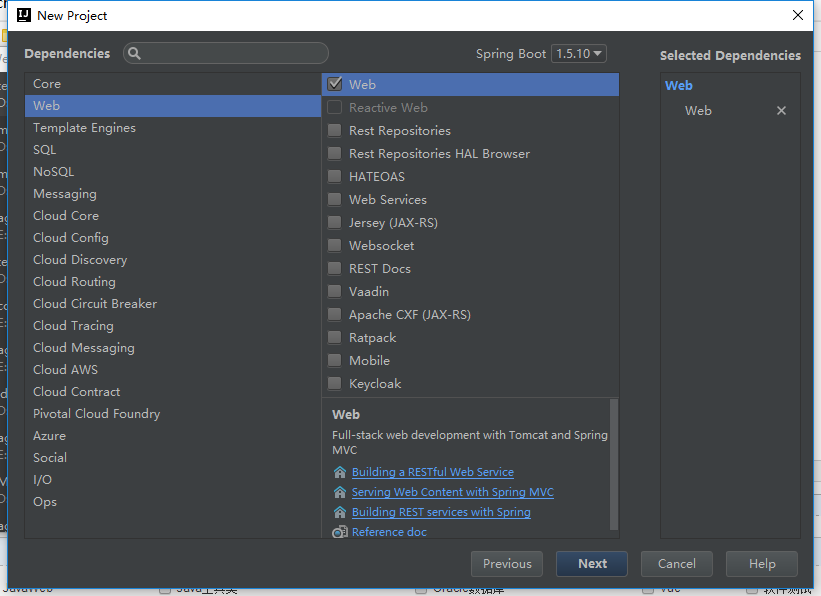
生成项目结构:
例子:
package com.example.testboot; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @GetMapping("/hello") public String say(){ return "hello"; } }
然后运行主程序:
package com.example.testboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; @SpringBootApplication public class TestbootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(TestbootApplication.class, args); } }
配置文件:
#端口号 server.port=8081 #项目前缀 server.context-path=/test
也可以使用yml格式配置文件:
server: port: 8081 cotent-path: /sd
可以区分生产环境和开发环境的多环境配置。
Controller的使用:
注解:
@RestController注解相当于@ResponseBody + @Controller合在一起的作用。
1)如果只是使用@RestController注解Controller,则Controller中的方法无法返回jsp页面,配置的视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver不起作用,返回的内容就是Return 里的内容。
例如:本来应该到success.jsp页面的,则其显示success.
2)如果需要返回到指定页面,则需要用 @Controller配合视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver才行。
3)如果需要返回JSON,XML或自定义mediaType内容到页面,则需要在对应的方法上加上@ResponseBody注解。
@GetMapping({"/hello","/hi"})
@PostMapping({"/hello","/hi"})
@RequestMapping({"/hello","/hi"})
可以使用集合的方式指定多个入口@RequestMapping也可以给Controller指定
@PathVaribale 获取url中的数据
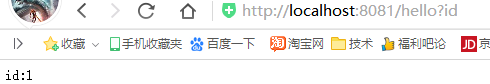
//@RequestMapping(value="/hello/{id}",method= RequestMethod.GET) @GetMapping("/hello/{id}") public String sayHello(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ return "id:"+id; }
效果:

注意,这里
@RequestMapping(value="/hello/{id}",method= RequestMethod.GET)
的效果等同于
@GetMapping("/hello/{id}")
同样,如果我们需要在url有多个参数需要获取,则如下代码所示来做就可以了。
@RequestMapping(value="/hello/{id}/{name}",method= RequestMethod.GET)
public String sayHello(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,@PathVariable("name") String name){
return "id:"+id+" name:"+name;
}
@RequestParam 获取请求参数的值
@RequestMapping(value="/hello",method= RequestMethod.GET) public String sayHello(@RequestParam("id") Integer id){ return "id:"+id; }

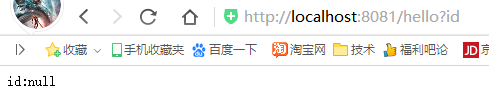
//@RequestMapping(value="/hello/{id}",method= RequestMethod.GET) @GetMapping("/hello") //required=false 表示url中可以不穿入id参数,此时就使用默认参数 public String sayHello(@RequestParam(value="id",required = false,defaultValue = "1") Integer id){ return "id:"+id; }

如果是有多个参数的情况:
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(@RequestParam("id") Integer id,@RequestParam("name") String name){
return "id:"+id+ " name:"+name;
}
@GetMapping
等同于@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
还有@PostMapping和@PutMapping等等
数据库操作:
配置yml文件:
server:
port: 8090
session-timeout: 30
tomcat.max-threads: 0
tomcat.uri-encoding: UTF-8
spring:
datasource:
url : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybill
username : root
password : root
driverClassName : com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
database : MYSQL
show-sql : true
hibernate:
ddl-auto : update
naming-strategy : org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
properties:
hibernate:
dialect : org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
配置实体类:
package com.example.testboot; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; @Entity public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue private Integer id; private String name; public User() { } public User(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
运行项目即可在数据库指定位置生成数据表。
数据库简单操作:
获取数据:
新建接口:
package com.example.testboot; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> { }
Controller:
package com.example.testboot; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.List; @RestController public class UserController { @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; /** * 返回用户列表 * @return */ @GetMapping("/getuser") public List<User> getUser(){ return userRepository.findAll(); } }

添加的方法:
/** * 添加 * @param id * @param name * @return */ @PostMapping("/getuser") public User addUser(@RequestParam("id")Integer id,@RequestParam("name")String name){ User user=new User(); user.setId(id); user.setName(name); return userRepository.save(user); }
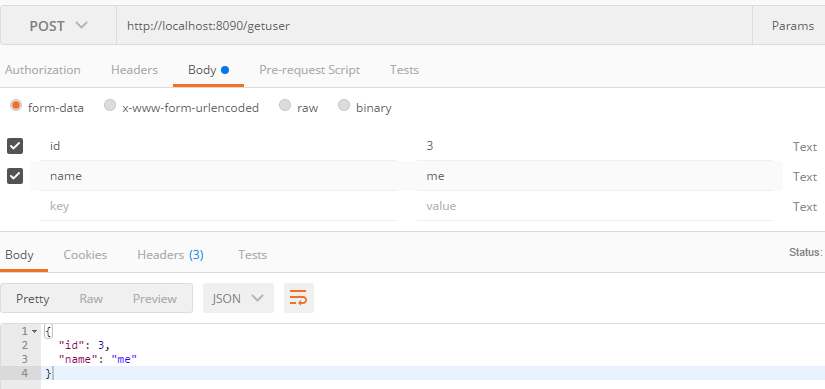
/** * 查询一个用户 * @param id * @return */ @GetMapping("/get/{id}") public User findUser(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ return userRepository.findOne(id); }
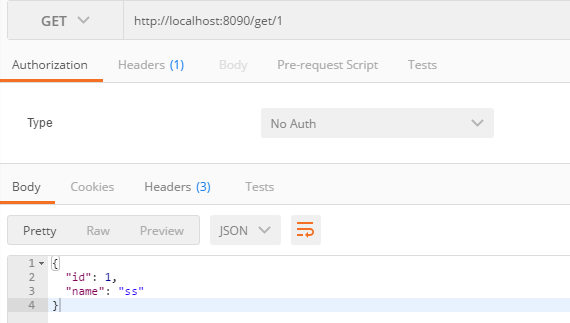
/** * 更新一个用户 * @param id * @param name * @return */ @PutMapping("/put/{id}") public User putUser(@PathVariable("id")Integer id,@RequestParam("name")String name){ User user=new User(); user.setId(id); user.setName(name); return userRepository.save(user); }
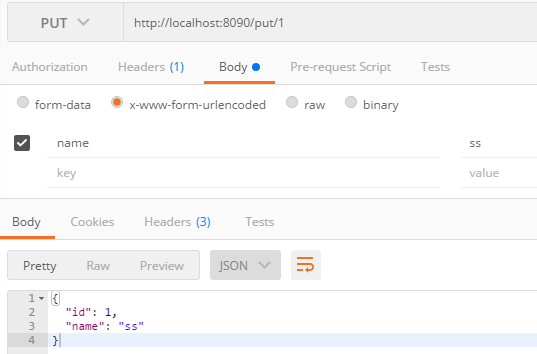
/** * 删除用户 * @param id */ @DeleteMapping("/del/{id}") public void delUser(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ userRepository.delete(id); }

事务管理:
@Transactional @DeleteMapping("/del/{id}") public void delUser(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ userRepository.delete(id); }
通过注解 @Transactional
使得操作一个不完成时都不完成,除了查询方法都应添加事务。


