Youden's J statistic (Youden's index)
Youden's J statistic (also called Youden's index) is a single statistic that captures the performance of a dichotomous diagnostic test. Informedness is its generalization to the multiclass case and estimates the probability of an informed decision.

约登指数可与ROC曲线一起使用,使Youden's index最大化的点可作为最佳截断阈值。
The index gives equal weight to false positive and false negative values, so all tests with the same value of the index give the same proportion of total misclassified results. While it is technically possible to obtain a value of less than zero from this equation, e.g. Classification yields only False Positives and False Negatives, a value of less than zero just indicates that the positive and negative labels have been switched. After correcting the labels the result will then be in the 0 through 1 range.
该指标给予假阳性和假阴性值相同的权重,因此所有具有该指标相同值的测试在总误分类结果中所占的比例相同。虽然从这个等式中得到一个小于零的值在技术上是可能的,例如,分类只会产生假阳性和假阴性,但小于零的值只是表明正标签和负标签被切换了。在纠正标签之后,结果将在0到1的范围内。
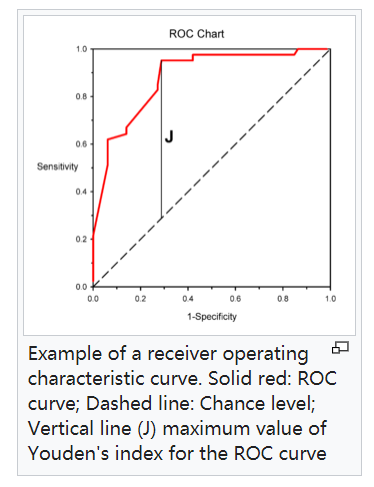
Youden's index is often used in conjunction with receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.[2] The index is defined for all points of an ROC curve, and the maximum value of the index may be used as a criterion for selecting the optimum cut-off point when a diagnostic test gives a numeric rather than a dichotomous result. The index is represented graphically as the height above the chance line, and it is also equivalent to the area under the curve subtended by a single operating point.
该指数图形上表示为ROC机会线之上的高度。
Youden's index is the probability of an informed decision (as opposed to a random guess) and takes into account all predictions.
约登指数是一个有根据的决策(而不是随机猜测)的概率,它考虑了所有的预测。
An unrelated but commonly used combination of basic statistics from information retrieval is the F-score, being a (possibly weighted) harmonic mean of recall and precision where recall = sensitivity = true positive rate, but specificity and precision are totally different measures. F-score, like recall and precision, only considers the so-called positive predictions, with recall being the probability of predicting just the positive class, precision being the probability of a positive prediction being correct, and F-score equating these probabilities under the effective assumption that the positive labels and the positive predictions should have the same distribution and prevalence,[3] similar to the assumption underlying of Fleiss' kappa. Youden's J, Informedness, Recall, Precision and F-score are intrinsically undirectional, aiming to assess the deductive effectiveness of predictions in the direction proposed by a rule, theory or classifier. Markedness (deltaP) is Youden's J used to assess the reverse or abductive direction,[3][6] and matches well human learning of associations; rules and, superstitions as we model possible causation;[4] while correlation and kappa evaluate bidirectionally.
Matthews correlation coefficient is the geometric mean of the regression coefficient of the problem and its dual, where the component regression coefficients of the Matthews correlation coefficient are Markedness (inverse of Youden's J or deltaP) and informedness (Youden's J or deltaP'). Kappa statistics such as Fleiss' kappa and Cohen's kappa are methods for calculating inter-rater reliability based on different assumptions about the marginal or prior distributions, and are increasingly used as chance corrected alternatives to accuracy in other contexts. Fleiss' kappa, like F-score, assumes that both variables are drawn from the same distribution and thus have the same expected prevalence, while Cohen's kappa assumes that the variables are drawn from distinct distributions and referenced to a model of expectation that assumes prevalences are independent.[6]
When the true prevalences for the two positive variables are equal as assumed in Fleiss kappa and F-score, that is the number of positive predictions matches the number of positive classes in the dichotomous (two class) case, the different kappa and correlation measure collapse to identity with Youden's J, and recall, precision and F-score are similarly identical with accuracy.[3][6]
来自:https://en.wikipedia.ahau.cf/wiki/Youden%27s_J_statistic



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号