Hibernate入门
https://www.cnblogs.com/Java3y/p/8520601.html
引入hibernate3.jar核心 + required 必须引入的(6个) + jpa 目录 + 数据库驱动包
编写对象和对象映射
编写一个User对象->User.java
public class User { private int id; private String username; private String password; private String cellphone; //各种setter和getter }
编写对象映射->User.hbm.xml。一般它和JavaBean对象放在同一目录下
<!--在domain包下--> <hibernate-mapping package="zhongfucheng.domain"> <!--类名为User,表名也为User--> <class name="User" table="user"> <!--主键映射,属性名为id,列名也为id--> <id name="id" column="id"> <!--根据底层数据库主键自动增长--> <generator class="native"/> </id> <!--非主键映射,属性和列名一一对应--> <property name="username" column="username"/> <property name="cellphone" column="cellphone"/> <property name="password" column="password"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
主配置文件
hibernate.cfg.xml
如果使用Intellij Idea生成的Hibernate可以指定生成出主配置文件hibernate.cfg.xml,它是要放在src目录下的
<hibernate-configuration> <!-- 通常,一个session-factory节点代表一个数据库 --> <session-factory> <!-- 1. 数据库连接配置 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///zhongfucheng</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">root</property> <!-- 数据库方法配置, hibernate在运行的时候,会根据不同的方言生成符合当前数据库语法的sql --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect</property> <!-- 2. 其他相关配置 --> <!-- 2.1 显示hibernate在运行时候执行的sql语句 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 2.2 格式化sql --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- 2.3 自动建表 --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">create</property> <!--3. 加载所有映射--> <mapping resource="zhongfucheng/domain/User.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
测试
建立customer 数据库测试
package zhongfucheng.domain; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.hibernate.classic.Session; /** * Created by ozc on 2017/5/6. */ public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建对象 User user = new User(); user.setPassword("123"); user.setCellphone("122222"); user.setUsername("nihao"); //获取加载配置管理类 Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); //不给参数就默认加载hibernate.cfg.xml文件, configuration.configure(); //创建Session工厂对象 SessionFactory factory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(); //得到Session对象 Session session = factory.openSession(); //使用Hibernate操作数据库,都要开启事务,得到事务对象 Transaction transaction = session.getTransaction(); //开启事务 transaction.begin(); //把对象添加到数据库中 session.save(user); //提交事务 transaction.commit(); //关闭Session session.close(); } }
值得注意的是:JavaBean的主键类型只能是int类型,因为在映射关系中配置是自动增长的,String类型是不能自动增长的。如果是你设置了String类型,又使用了自动增长,那么就会报出下面的错误!
Caused by: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.MySQLSyntaxErrorException: Table 'zhongfucheng.user' does
执行完程序后,Hibernate就为我们创建对应的表,并把数据存进了数据库了
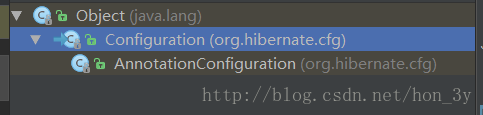
Configuration
配置管理类:主要管理配置文件的一个类
它拥有一个子类AnnotationConfiguration,也就是说:我们可以使用注解来代替XML配置文件来配置相对应的信息
configure方法
configure()方法用于加载配置文件
- 加载主配置文件的方法
- 如果指定参数,那么加载参数的路径配置文件
- 如果不指定参数,默认加载src/目录下的hibernate.cfg.xml
buildSessionFactory方法
buildSessionFactory()用于创建Session工厂
SessionFactory
SessionFactory-->Session的工厂,也可以说代表了hibernate.cfg.xml这个文件...hibernate.cfg.xml的就有<session-factory>这么一个节点
openSession方法
创建一个Session对象
getCurrentSession方法
创建Session对象或取出Session对象
Session
Session是Hibernate最重要的对象,Session维护了一个连接(Connection),只要使用Hibernate操作数据库,都需要用到Session对象
通常我们在DAO层中都会有以下的方法,Session也为我们提供了对应的方法来实现!
public interface IEmployeeDao { void save(Employee emp); void update(Employee emp); Employee findById(Serializable id); List<Employee> getAll(); List<Employee> getAll(String employeeName); List<Employee> getAll(int index, int count); void delete(Serializable id); }



