【学习笔记】(24) 虚树
虚树常常被使用在树形dp中,当一次询问仅仅涉及到整颗树中少量结点时,为每次询问都对整棵树进行dp在时间上是不可接受的。此时,我们建立一颗仅仅包含部分关键结点的虚树,将非关键点构成的链简化成边或是剪去,在虚树上进行dp。
虚树包含所有的询问点及它们之间的lca。显然虚树的叶子节点必然是询问点,因此对于某次含有
最右链是虚树构建的一条分界线,表明其左侧部分的虚树已经完成构建。我们使用栈来维护所谓的最右链,top 为栈顶位置。值得注意的是,最右链上的边并没有被加入虚树,这是因为在接下来的过程中随时会有某个lca插到最右链中。
初始无条件将第一个询问点加入栈中。
将接下来的所有询问点顺次加入,假设该询问点为
由于
考虑
这时说明
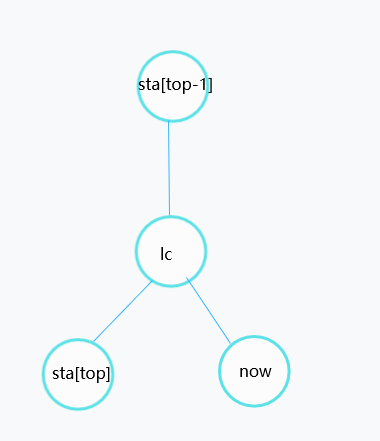
显然,此时最右链的末端从 sta[top-1]->sta[top] 变成了 sta[top−1]−>lc−>now,我们需要做的,首先是把边lc-stak[top]加入虚树,然后,把 sta[top]出栈,把lc和now入栈。
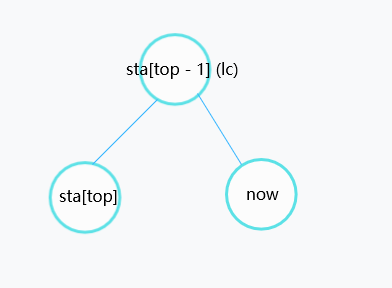
这种情况和第二种情况大同小异,唯一的区别就是
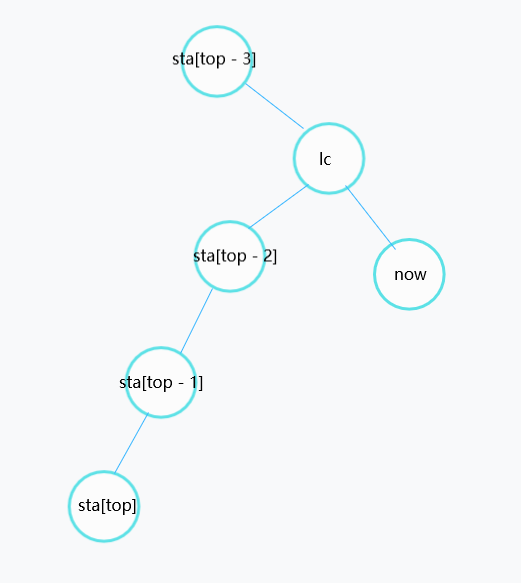
这种情况就一直 sta[top] 与 sta[top-1] 连边,然后弹出栈顶,直到
综上,得出以下代码
st[top = 1] = a[1]; for(int i = 2; i <= k; ++i){ int lc = lca(a[i], st[top]); while(top > 1 && dep[lc] <= dep[st[top - 1]]){ trans(st[top - 1], st[top]); top--; } if(lc != st[top]){ trans(lc, st[top]), st[top] = lc; } st[++top] = a[i]; }
一些结论与技巧
- 点集 S 的虚树边权和等于所有时间戳 循环相邻 的节点距离之和除以 2。换言之,将 S 按时间戳从小到大排序得到序列 a0,a2,⋯,a|S|−1,则虚树边权和为
- 当只对虚树进行一遍自底向上的 DP 时,不需要显式建出虚树后 dfs,而是在构建虚树的过程中直接转移,因为构建虚树时每条边被加入的顺序就是回溯顺序。
例题
Ⅰ. P2495 [SDOI2011] 消耗战
将每次的
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long #define min(a, b) (a < b ? a : b) using namespace std; const int N = 2.5e5 + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } bool _u; int n, m, k, tot, cnt, top; int hd[N], to[N << 1], nxt[N << 1], edge[N << 1]; int f[N][18], d[N], dfn[N], a[N]; int st[N]; ll minn[N]; bool vis[N]; bool cmp(int x, int y){return dfn[x] < dfn[y];} void add(int u, int v, int w){ to[++tot] = v, nxt[tot] = hd[u], hd[u] = tot, edge[tot] = w; } void add1(int u, int v){ to[++tot] = v, nxt[tot] = hd[u], hd[u] = tot; } void dfs(int x, int fa){ f[x][0] = fa, d[x] = d[fa] + 1, dfn[x] = ++cnt; for(int i = 1; i <= 17; ++i) f[x][i] = f[f[x][i - 1]][i - 1]; for(int i = hd[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){ int y = to[i]; if(y == fa) continue; minn[y] = min(minn[x], edge[i]), dfs(y, x); } return ; } int lca(int x, int y){ if(d[x] < d[y]) swap(x, y); for(int i = 17; i >= 0; --i) if(d[f[x][i]] >= d[y]) x = f[x][i]; if(x == y) return x; for(int i = 17; i >= 0; --i) if(f[x][i] != f[y][i]) x = f[x][i], y = f[y][i]; return f[x][0]; } ll dp(int x){ ll sum = 0; for(int i = hd[x]; i; i = nxt[i]) sum += dp(to[i]); hd[x] = 0; if(vis[x]){ vis[x] = 0; return minn[x]; } return min(minn[x], sum); } int main(){ n = read(); for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ int u = read(), v = read(), w = read(); add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); } minn[1] = 2e18, dfs(1, 0); m = read(); memset(hd, 0, sizeof(hd)); while(m--){ tot = 0, k = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) a[i] = read(), vis[a[i]] = 1; sort(a + 1, a + 1 + k, cmp); st[top = 1] = a[1]; for(int i = 2; i <= k; ++i){ int cur = a[i], lc = lca(cur, st[top]); while(d[lc] < d[st[top - 1]]) add1(st[top - 1], st[top]), top--; if(lc != st[top]){ add1(lc, st[top]); if(lc != st[top - 1]) st[top] = lc; else --top; } st[++top] = cur; } while(--top) add1(st[top], st[top + 1]); printf("%lld\n", dp(st[1])); } bool _v; // fprintf(stderr, "%.3lf\n", abs(&_u - &_v) / 1048576.0); return 0; }
Ⅱ. P4103 [HEOI2014] 大工程
建出虚树后进行 DP,维护子树内关键点数量
对于第一问,考虑每条边
被计算了多少次,其中
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long #define TIME 1e3 * clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC using namespace std; const int N = 1e6 + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } bool _u; int n, q, tot, cnt; int hd[N], to[N << 1], nxt[N << 1]; int dep[N], mi[20][N], lg[N], dfn[N]; int a[N], mn[N], mx[N], sz[N]; void add(int u, int v){ to[++tot] = v, nxt[tot] = hd[u], hd[u] = tot; } void dfs(int x, int fa){ dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1; mi[0][dfn[x] = ++cnt] = fa; for(int i = hd[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){ int y = to[i]; if(y == fa) continue; dfs(y, x); } } int get_min(int u, int v){return dep[u] < dep[v] ? u : v;} int lca(int u, int v){ if(u == v) return u; if((u = dfn[u]) > (v = dfn[v])) swap(u, v); int d = lg[v - u++]; return get_min(mi[d][u], mi[d][v - (1 << d) + 1]); } bool _v; int main(){ // cerr << abs(&_u - &_v) / 1048576.0 << " MB\n" << endl; n = read(); for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ int u = read(), v = read(); add(u, v), add(v, u); } dfs(1, 0); for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) lg[i] = lg[i >> 1] + 1; for(int i = 1; i <= lg[n]; ++i) for(int j = 1; j + (1 << i) - 1 <= n; ++j) mi[i][j] = get_min(mi[i - 1][j], mi[i - 1][j + (1 << i - 1)]); q = read(); while(q--){ int k = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) a[i] = read(), sz[a[i]] = 1, mn[a[i]] = mx[a[i]] = 0; sort(a + 1, a + 1 + k, [&](int x, int y){return dfn[x] < dfn[y];}); static int st[N], top = 0; st[top = 1] = a[1]; ll ans1 = 0; int ans2 = 1e8, ans3 = 0; auto trans = [&](int u, int v){ int d = dep[v] - dep[u]; ans1 += 1ll * sz[v] * (k - sz[v]) * d; ans2 = min(ans2, mn[u] + mn[v] + d); mn[u] = min(mn[u], mn[v] + d); ans3 = max(ans3, mx[u] + mx[v] + d); mx[u] = max(mx[u], mx[v] + d); sz[u] += sz[v]; }; for(int i = 2; i <= k; ++i){ int lc = lca(a[i], st[top]); while(top > 1 && dep[lc] <= dep[st[top - 1]]){ trans(st[top - 1], st[top]); top--; } if(lc != st[top]){ mn[lc] = 1e8, mx[lc] = 0, sz[lc] = 0; trans(lc, st[top]), st[top] = lc; } st[++top] = a[i]; } for(int i = top - 1; i; --i) trans(st[i], st[i + 1]); printf("%lld %d %d\n", ans1, ans2, ans3); } // cerr << TIME << " ms" << endl; return 0; }
Ⅲ.CF986E Prince's Problem
考虑值域内所有质数
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long #define mp make_pair #define pii pair<int, int> #define pb push_back using namespace std; const int N = 1e6 + 67, mod = 1e9 + 7, M = 1e7; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } bool _u; int n, q, cnt; int tot, hd[N], to[N << 1], nxt[N << 1]; int dep[N], mi[25][N], lg[N], dfn[N], ans[N], fa[N]; int st[N], top, p[N], qx[N], qy[N], s[N][25]; int ct, prim[M], bel[M]; vector<pii> buc[N], qr[N]; bool v[M]; void add(int u, int v){ to[++tot] = v, nxt[tot] = hd[u], hd[u] = tot; } void init(){ for(int i = 2; i <= M; ++i){ if(!v[i]) prim[++ct] = i, bel[i] = ct; for(int j = 1; j <= ct; ++j){ if(i > M / prim[j]) break; v[i * prim[j]] = 1; if(i % prim[j] == 0) break; } } } int qsm(int a, int b){ int res = 1; for(; b; b >>= 1, a = 1ll * a * a % mod) if(b & 1) res = 1ll * res * a % mod; return res; } void dfs(int x, int ff){ dep[x] = dep[ff] + 1, mi[0][dfn[x] = ++cnt] = ff; for(int i = hd[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){ int y = to[i]; if(y == ff) continue; dfs(y, x); } } int get_min(int u, int v){return dep[u] < dep[v] ? u : v;} int lca(int u, int v){ if(u == v) return u; if((u = dfn[u]) > (v = dfn[v])) swap(u, v); int d = lg[v - u++]; return get_min(mi[d][u], mi[d][v - (1 << d) + 1]); } bool cmp(int x, int y){return dfn[x] < dfn[y];} bool _v; int main(){ // cerr << abs(&_u - &_v) / 1048576.0 << " MB\n" << endl; init(), n = read(); for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ int u = read(), v = read(); add(u, v), add(v, u); } dfs(1, 0); for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) lg[i] = lg[i >> 1] + 1; for(int i = 1; i <= lg[n]; ++i) for(int j = 1; j + (1 << i) - 1 <= n; ++j) mi[i][j] = get_min(mi[i - 1][j], mi[i - 1][j + (1 << i - 1)]); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){ int x = read(); for(int j = 1; j <= ct && 1ll * prim[j] * prim[j] <= x; ++j){ if(x % prim[j] == 0){ int num = 0; while(x % prim[j] == 0) x /= prim[j], ++num; buc[j].pb(mp(i, num)); } } if(x > 1) buc[bel[x]].pb(mp(i, 1)); } q = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i){ ans[i] = 1; qx[i] = read(), qy[i] = read(); int x = read(); for(int j = 1; j <= ct && 1ll * prim[j] * prim[j] <= x; ++j){ if(x % prim[j] == 0){ int num = 0; while(x % prim[j] == 0) x /= prim[j], ++num; qr[j].pb(mp(i, num)); } } if(x > 1) qr[bel[x]].pb(mp(i, 1)); } for(int _ = 1; _ <= ct; ++_){ int num = 0, mx = 0; for(auto it : buc[_]) p[++num] = it.first, mx = max(mx, it.second); for(auto it : qr[_]) p[++num] = qx[it.first], p[++num] = qy[it.first]; sort(p + 1, p + 1 + num, cmp); num = unique(p + 1, p + 1 + num) - p - 1; st[top = 1] = p[1]; int nn = num; for(int i = 2; i <= num; ++i){ int lc = lca(st[top], p[i]); while(top > 1 && dep[lc] <= dep[st[top - 1]]) fa[st[top]] = st[top - 1], --top; if(lc != st[top]) fa[st[top]] = p[++nn] = lc, st[top] = lc; st[++top] = p[i]; } fa[st[1]] = 0; for(int i = top - 1; i; --i) fa[st[i + 1]] = st[i]; sort(p + 1, p + 1 + nn, cmp); for(int i = 1; i <= nn; ++i) memset(s[p[i]], 0, sizeof(s[p[i]])); for(auto it : buc[_]) s[it.first][it.second] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= nn; ++i) for(int j = 1; j <= mx; ++j) s[p[i]][j] += s[fa[p[i]]][j]; for(auto it : qr[_]){ int pw = 0, i = it.first, lc = lca(qx[i], qy[i]); for(int j = 1; j <= mx; ++j) pw += min(j, it.second) * (s[qx[i]][j] + s[qy[i]][j] - s[lc][j] - s[fa[lc]][j]); ans[i] = 1ll * ans[i] * qsm(prim[_], pw) % mod; } } for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i) printf("%d\n", ans[i]); return 0; }
Ⅳ.CF639F Bear and Chemistry
对原图进行边双缩点。
自然考虑对每组询问相关的所有点建出虚树。若图不连通,则可能为虚树森林。
因虚树保留了关键点在原图上的相对形态,故直接在虚树上添加新增的边,对新图检查所有
是否边双连通即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define pb push_back #define pii pair<int, int> #define mp make_pair using namespace std; const int N = 3e5 + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } struct BCC{ int dn, dfn[N], low[N], cn, col[N], top, stc[N]; int tot = 1, fr[N << 1], hd[N], to[N << 1], nxt[N << 1]; bool in[N]; vector<int> S; void add(int u, int v){ if(!in[u]) in[u] = 1, S.pb(u); to[++tot] = v, fr[tot] = u, nxt[tot] = hd[u], hd[u] = tot; } void clear(){ tot = 1, cn = dn = 0; for(auto it : S) hd[it] = in[it] = dfn[it] = 0; S.clear(); } void tarjan(int x, int ff){ if(!in[x]) in[x] = 1, S.pb(x); low[x] = dfn[x] = ++dn, stc[++top] = x; for(int i = hd[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){ int y = to[i]; if(i == (ff ^ 1)) continue; if(!dfn[y]) { tarjan(y, i); low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]); if(low[y] > dfn[x]){ ++cn; for(int u = 0; u != y; ) col[u = stc[top--]] = cn; } }else low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]); } if(!ff){ ++cn; while(top) col[stc[top--]] = cn; } } }g, h; bool _v; vector<int> e[N]; int n, m, q, R, dn; int bel[N], lg[N], mi[25][N], dep[N], dfn[N], comp[N]; int top, stc[N], p[N * 3]; map<pii, bool> H; int get_min(int x, int y){return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;} int lca(int u, int v){ if(u == v) return u; if((u = dfn[u]) > (v = dfn[v])) swap(u, v); int d = lg[v - u++]; return get_min(mi[d][u], mi[d][v - (1 << d) + 1]); } void dfs(int x, int ff){ dfn[x] = ++dn, dep[x] = dep[ff] + 1, mi[0][dn] = ff; for(auto y : e[x]) if(ff != y) dfs(y, x); } int rot(int x){return (x + R - 1) % n + 1;} bool _u; int main(){ cerr << abs(&_u - &_v) / 1048576.0 << " MB\n"; n = read(), m = read(), q = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){ int u = read(), v = read(); g.add(u, v), g.add(v, u); } for(int i = 1, c = 0; i <= n; ++i){ if(!g.dfn[i]) { int lst = g.cn; g.tarjan(i, 0), ++c; for(int j = lst + 1; j <= g.cn; ++j) comp[j] = c; } } memcpy(bel, g.col, sizeof(bel)); for(int i = 2; i <= g.tot; ++i){ if(bel[g.fr[i]] != bel[g.to[i]] && !H[mp(bel[g.fr[i]], bel[g.to[i]])]){ e[bel[g.fr[i]]].push_back(bel[g.to[i]]); H[mp(bel[g.fr[i]], bel[g.to[i]])] = 1; } } for(int i = 2; i <= g.cn; ++i) lg[i] = lg[i >> 1] + 1; for(int i = 1; i <= g.cn; ++i) if(!dfn[i]) dfs(i, 0); for(int i = 1; i <= lg[g.cn]; ++i) for(int j = 1; j + (1 << i) - 1 <= g.cn; ++j) mi[i][j] = get_min(mi[i - 1][j], mi[i - 1][j + (1 << i - 1)]); for(int _ = 1; _ <= q; ++_){ int nn = read(), mm = read(), cnt = 0; static int V[N], u[N], v[N]; for(int i = 1; i <= nn; ++i) V[i] = p[++cnt] = bel[rot(read())]; for(int i = 1; i <= mm; ++i){ u[i] = p[++cnt] = bel[rot(read())]; v[i] = p[++cnt] = bel[rot(read())]; } sort(p + 1, p + 1 + cnt), cnt = unique(p + 1, p + 1 + cnt) - p - 1; sort(p + 1, p + 1 + cnt, [&](int x, int y){return comp[x] < comp[y];}); h.clear(); for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; ++i){ int r = i; while(r < cnt && comp[p[r + 1]] == comp[p[r]]) ++r; sort(p + i, p + 1 + r, [&](int x, int y){return dfn[x] < dfn[y];}); stc[top = 1] = p[i]; for(int j = i + 1; j <= r; ++j){ int lc = lca(stc[top], p[j]); while(top > 1 && dep[lc] <= dep[stc[top - 1]]) h.add(stc[top], stc[top - 1]), h.add(stc[top - 1], stc[top]), top--; if(lc != stc[top]) h.add(lc, stc[top]), h.add(stc[top], lc), stc[top] = lc; stc[++top] = p[j]; } for(int j = top - 1; j; --j) h.add(stc[j], stc[j + 1]), h.add(stc[j + 1], stc[j]); i = r; } for(int i = 1; i <= mm; ++i) h.add(u[i], v[i]), h.add(v[i], u[i]); for(int i = 1; i <= nn; ++i) if(!h.dfn[V[i]]) h.tarjan(V[i], 0); bool flag = 1; for(int i = 2; i <= nn; ++i) flag &= (h.col[V[i]] == h.col[V[1]]); if(flag) puts("YES"), R = (R + _) % n; else puts("NO"); } return 0; }
本文作者:南风未起
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiangchen4122/p/17675723.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步