【比赛】8.14
Ⅰ.妹子

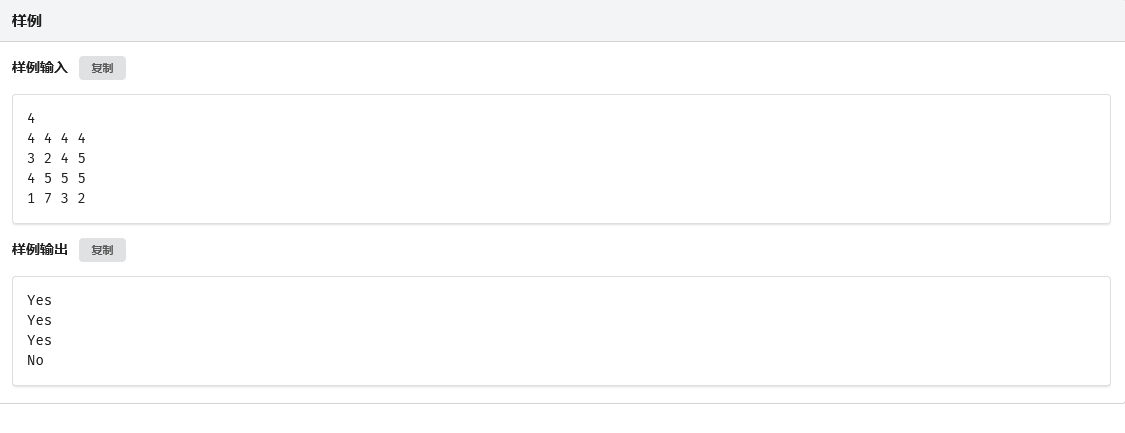

第一题考虑被包含的矩阵需不需要旋转,如上图,我们可以枚举 \(x\) 来判断是否可行。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define db double
#define eqs 1e-6
using namespace std;
int read(){
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
int T, a1, a2, b1, b2;
int main(){
// freopen("girls.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("girls.out", "w", stdout);
T = read();
while(T--){
bool flag = 0;
a1 = read(), b1 = read(), a2 = read(), b2 = read();
if(a1 > b1) swap(a1, b1);
if(a2 > b2) swap(a2, b2);
int s1 = a1 * b1, s2 = a2 * b2;
if(s1 == s2){
if(a1 == a2 && b1 == b2) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
continue;
}else if(s1 > s2) swap(a1, a2), swap(b1, b2);
if(a1 <= a2 && b1 <= b2){
printf("Yes\n"); continue;
}
db A1 = a1, A2 = a2, B1 = b1, B2 = b2;
for(int i = 1; i <= a1 * 100; ++i){
db x = i / 100.0;
db y = sqrt(a1 * a1 - x * x);
db xx = x * B1 / A1;
db yy = y * B1 / A1;
if(y + xx + eqs < B2 && x + yy + eqs < A2){
flag = 1;
printf("Yes\n");
break;
}
}
if(!flag) printf("No\n");
}
// fclose(stdin);
// fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
二.旅程


倒序+floyd
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define db double
#define eqs 1e-6
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e3 + 67, M = 1e5 + 67;
int read(){
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
int n, m;
struct Query{
int opt, x, y, ans;
}Q[M];
int a[N][N], dis[N][N];
int main(){
// freopen("journey.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("journey.out", "w", stdout);
n = read(), m = read();
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
dis[i][j] = a[i][j] = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
Q[i].opt = read(), Q[i].x = read(), Q[i].y = read();
if(Q[i].opt == 1) dis[Q[i].x][Q[i].y] = INF;
}
for(int k = 1; k <= n; ++k)
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
dis[i][j] = min(dis[i][j], dis[i][k] + dis[k][j]);
for(int o = m; o; --o){
int x = Q[o].x, y = Q[o].y;
if(Q[o].opt == 1){
dis[x][y] = min(dis[x][y], a[x][y]);
for(int k = 1; k <= n; ++k) dis[x][k] = min(dis[x][k], dis[x][y] + dis[y][k]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
dis[i][j] = min(dis[i][j], dis[i][x] + dis[x][j]);
} else{
if(dis[x][y] == INF) Q[o].ans = -1;
else Q[o].ans = dis[x][y];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
if(Q[i].opt == 2) printf("%d\n", Q[i].ans);
}
// fclose(stdin);
// fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
Ⅲ.老大
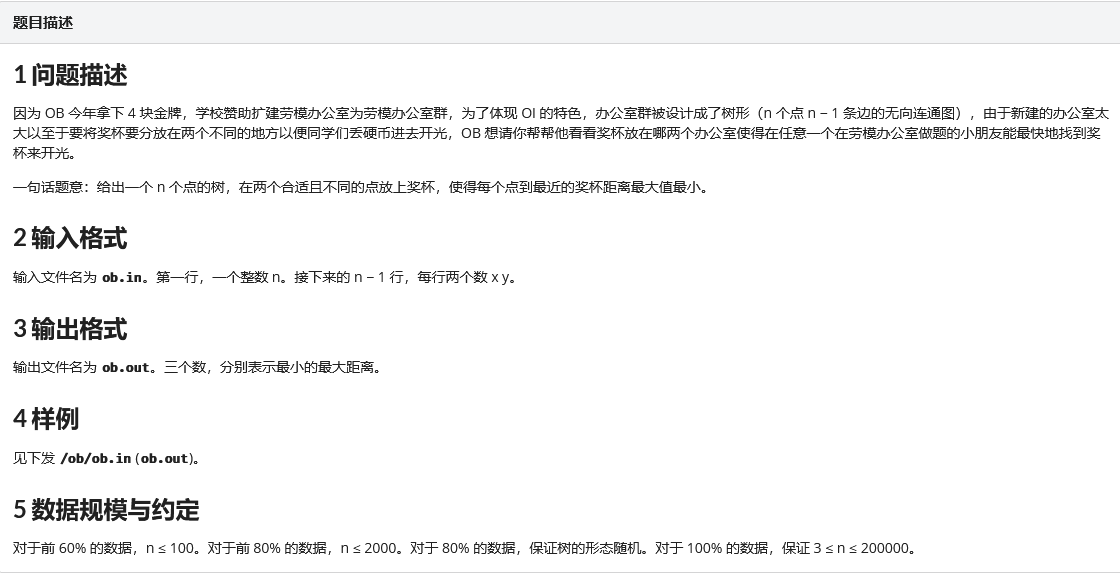
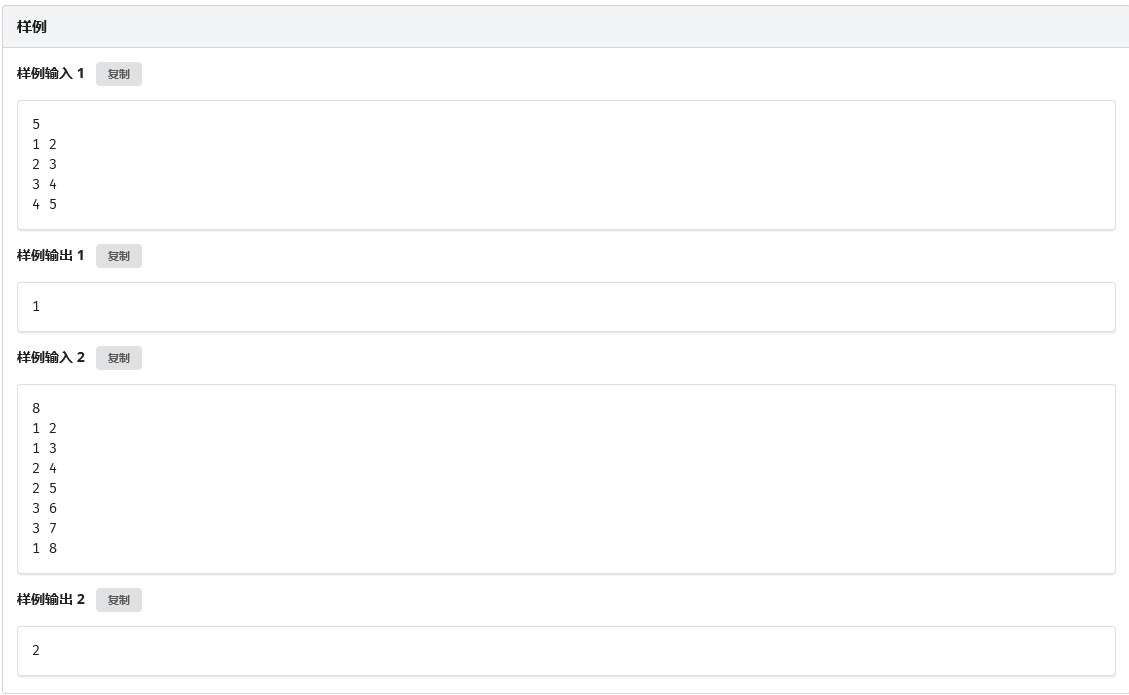
显然奖杯一定在直径上。求最大值最小,二分。最优解必定是对称的,都离直径端点二分的距离,在 \(O(n)\) 判断是否有可行。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define db double
#define eqs 1e-6
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 67;
int read(){
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
int n, tot, rt;
int Head[N], to[N << 1], Next[N << 1];
int d[N], nxt[N], col[N], D[N];
void add(int u, int v){
to[++tot] = v, Next[tot] = Head[u], Head[u] = tot;
}
void dfs1(int x, int fa){
d[x] = d[fa] + 1;
if(d[x] > d[rt]) rt = x;
for(int i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i]){
int y = to[i]; if(y == fa) continue;
dfs1(y, x);
}
}
void dfs2(int x, int fa){
for(int i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i]){
int y = to[i]; if(y == fa) continue;
dfs2(y, x);
if(d[y] + 1 > d[x]) d[x] = d[y] + 1, nxt[x] = y;
}
}
void dfs3(int x, int fa){
for(int i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i]){
int y = to[i]; if(y == fa) continue;
dfs3(y, x);
if(D[y] + 1 > D[x] && !col[y]) D[x] = D[y] + 1;
}
}
bool check(int len){
int x = rt, ll = 0, cnt = 0;
int f1 = 0, f2 = 0;
while(x){
if(ll >= len && !f1) f1 = x;
if(d[x] == len) f2 = x;
x = nxt[x];
++ll;
}
x = rt;
while(x){
if(abs(d[x] - d[f1]) + D[x]> len && abs(d[x] - d[f2]) + D[x] > len) return false;
x = nxt[x];
}
return true;
}
int main(){
// freopen("ob.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("ob.out", "w", stdout);
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
int u = read(), v = read();
add(u, v), add(v, u);
}
dfs1(1, 0);
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));
dfs2(rt, 0);
int x = rt;
while(x) col[x] = 1, x = nxt[x];
dfs3(rt, 0);
int l = 0, r = 200000, ans;
// cout << check(2) << endl;
while(l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(check(mid)) ans = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
// fclose(stdin);
// fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
Ⅳ.序列
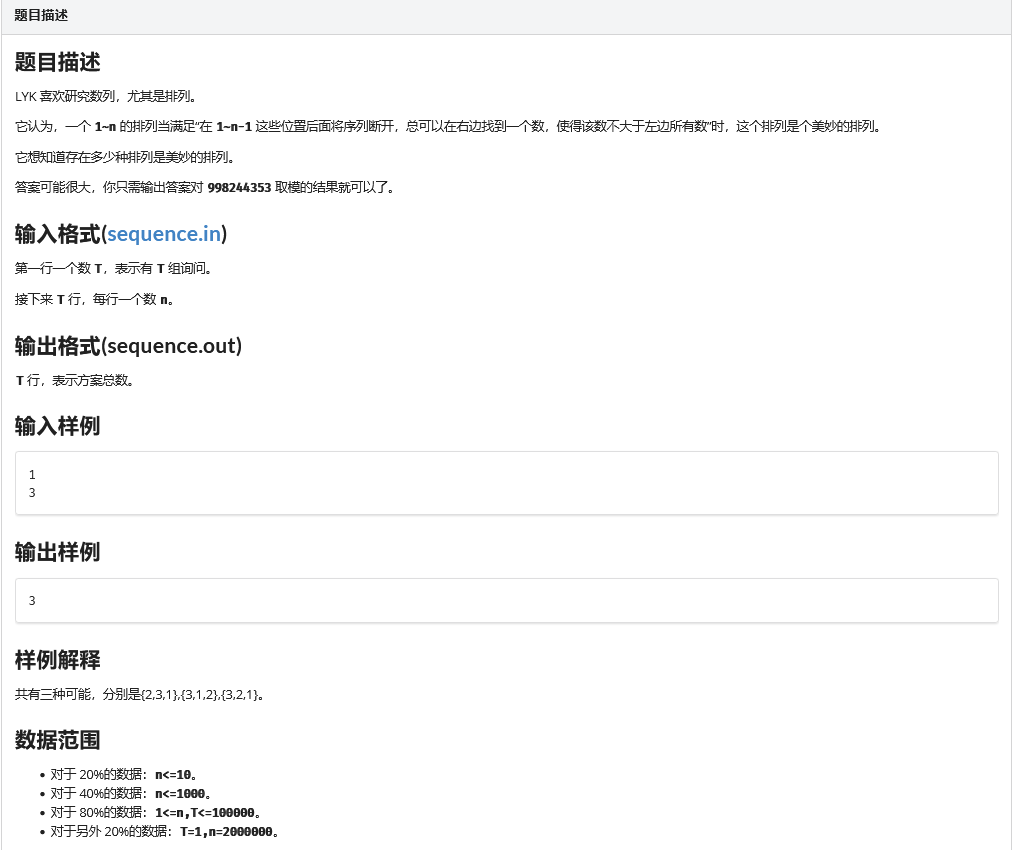
- 观察美妙的数列的性质。
- 即不存在一个数i(\(i<n\)),使得1 ~ i所在的数是1 ~ i的排列。
- 令\(f[n]\)表示存在多少n的排列是美妙的排列。
- 有\(f[n] = n! - \Sigma(j! \times f[n-j])\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^2)\)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号