【做题记录】2023年6月
记录 6月份 做的题(好吧,还有一些五月的)。
5.29
Ⅰ.Starry Phase
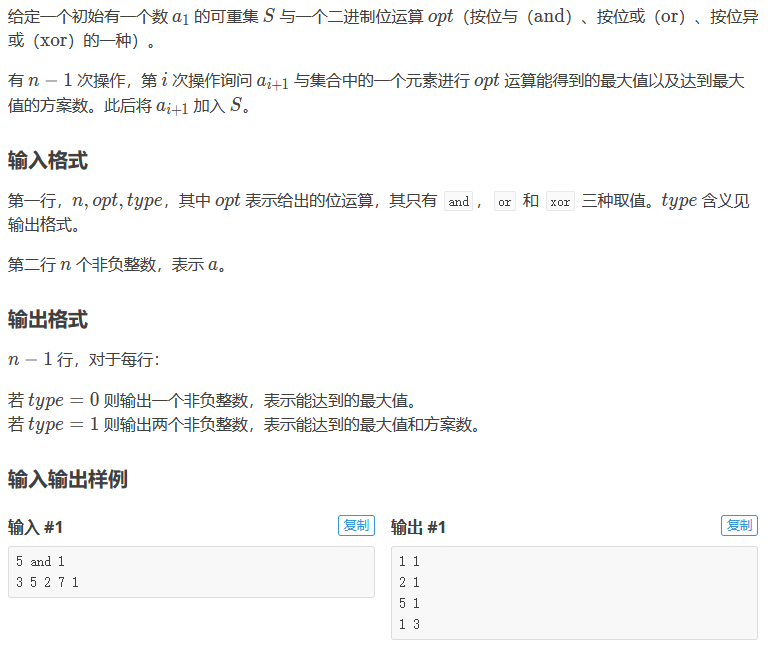
令
那么对于每次要找的数字,可以枚举 和 它操作的数字的前 8 位数字,然后就解决了。
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 1e5 + 67, M = (1 << 8); int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } int n, t; char s[5]; int a[N], f[M][M], g[M][M]; void insert(int x){ int v = x >> 8; x &= (M - 1); for(int i = 0; i < M; ++i){ int w = x; if(s[1] == 'a') w &= i; if(s[1] == 'o') w |= i; if(s[1] == 'x') w ^= i; if(f[v][i] < w) f[v][i] = w, g[v][i] = 1; else if(f[v][i] == w) ++g[v][i]; } } signed main(){ n = read(), scanf("%s", s + 1), t = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = read(); insert(a[1]); for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i){ int v = a[i] >> 8, vv = a[i] & (M - 1), mx = 0, mxn = 0; for(int j = 0; j < M; ++j){ int val = 0; if(!g[j][vv]) continue; if(s[1] == 'a') val = ((v & j) << 8) + f[j][vv]; if(s[1] == 'o') val = ((v | j) << 8) + f[j][vv]; if(s[1] == 'x') val = ((v ^ j) << 8) + f[j][vv]; if(val > mx) mx = val, mxn = g[j][vv]; else if(val == mx) mxn += g[j][vv]; } if(t) printf("%d %d\n", mx, mxn); else printf("%d\n", mx); insert(a[i]); } return 0; }
5.30
Ⅰ. P2868 [USACO07DEC]Sightseeing Cows G
0/1 分数规划 最有比例环,近乎板题。
点击查看代码
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #define ll long long #define db double #define eps 1e-5 using namespace std; const int N = 5e3 + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } int n, m; int tot, Head[N], to[N], Next[N], edge[N]; int a[N], in[N], vis[N], num[N]; db d[N]; void add(int u, int v, int w){ to[++tot] = v, Next[tot] = Head[u], Head[u] = tot, edge[tot] = w; } bool check(db r){ queue<int> q; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) q.push(i), d[i] = 0, vis[i] = num[i] = 0; while(!q.empty()){ int x = q.front(); q.pop(), vis[x] = 0; for(int i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i]){ int y = to[i]; db dis = edge[i] * r - a[x]; if(d[y] > d[x] + dis){ d[y] = d[x] + dis; if(!vis[y]){ q.push(y), vis[y] = 1; if(++num[y] >= n) return true; } } } } return false; } signed main(){ // freopen("1.in", "r", stdin); n = read(), m = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){ int u = read(), v = read(), w = read(); add(u, v, w); } db l = 0, r = 1e3, ans = 0; while(r - l > eps){ db mid = (l + r) / 2.0; if(check(mid)) ans = mid, l = mid; else r = mid; } printf("%.2lf\n", ans); return 0; }
6.8
Ⅰ. P2221 [HAOI2012]高速公路
Ⅱ. P4284 [SHOI2014] 概率充电器
树形 dp + 期望。
显然节点
1.它自己来电了 2.它的子树里有一个点来电了传了过来 3.它的子树外面有一个点来电了传了过来
两次 dfs 即可。
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define db double #define eps 1e-7 using namespace std; const int N = 5e5 + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } int n; int tot, Head[N], to[N << 1], Next[N << 1], edge[N << 1]; int a[N]; db f[N], ans; void add(int u, int v, int w){ to[++tot] = v, Next[tot] = Head[u], Head[u] = tot, edge[tot] = w; } void dfs1(int x, int fa){ for(int i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i]){ int y = to[i]; if(y == fa) continue; dfs1(y, x); db pa = f[y] * (0.01 * edge[i]); f[x] = f[x] + pa - f[x] * pa; } } void dfs2(int x, int fa){ ans += f[x]; for(int i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i]){ int y = to[i]; if(y == fa) continue; db pb = f[y] * (0.01 * edge[i]); if(pb + 1e-7 > 1.0 && pb - 1e-7 < 1.0){ dfs2(y, x); continue; } db pa = (f[x] - pb) / (1 - pb) * (0.01 * edge[i]); f[y] = f[y] + pa - f[y] * pa; dfs2(y, x); } } signed main(){ n = read(); for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ int u = read(), v = read(), w = read(); add(u, v, w), add(v, u, w); } for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = read(), f[i] = a[i] * 0.01; dfs1(1, 0), dfs2(1, 0); printf("%.6lf\n", ans); return 0; }
Ⅲ. P2473 [SCOI2008] 奖励关
dp 式子不难想到,就是关于为什么要逆推,以下是我自己的理解:
1.首先顺推过来的话,因为求的是期望,我们要知道情况数,但由于有些情况是不存在的,所以情况数无法知道,所以只能逆推。
2.有后效性
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define db double using namespace std; const int N = 1e2 + 67, M = (1 << 15) + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } int K, n; int p[N], sta[N]; db f[N][M]; signed main(){ K = read(), n = read(); for(int i = 1, x; i <= n; ++i){ p[i] = read(); while(x = read()) sta[i] |= (1 << x - 1); } for(int i = K; i; --i){ for(int j = 0; j < (1 << n); ++j){ for(int k = 1; k <= n; ++k) if((j & sta[k]) == sta[k]) f[i][j] += max(f[i + 1][j], f[i + 1][j | (1 << k - 1)] + p[k]); else f[i][j] += f[i + 1][j]; f[i][j] /= n; } } printf("%.6lf\n", f[1][0]); return 0; }
Ⅳ. P3750 [六省联考 2017] 分手是祝愿
先求出至少需要按多少个灯。
显然每个灯最多按一次,且每一个灯按去的效果都是独一无二的,所以直接从大到小按就行了。
设
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long using namespace std; const int mod = 1e5 + 3, N = 1e5 + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } int n, k, cnt; int a[N]; ll f[N]; ll qsm(ll a, int b){ ll res = 1; for(; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a % mod) if(b & 1) res = res * a % mod; return res; } signed main(){ n = read(), k = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i] = read(); for(int i = n; i; --i){ if(!a[i]) continue; ++cnt; for(int j = 1; j * j <= i; ++j) if(i % j == 0){ a[j] ^= 1; if(j * j != i) a[i / j] ^= 1; } } for(int i = n; i; --i){ ll tmp = ((ll)(n - i) * f[i + 1] + n) % mod; tmp = tmp * qsm(i, mod - 2) % mod; f[i] = tmp; } ll ans = 0; if(cnt <= k) ans = cnt; else{ for(int i = cnt; i > k; --i) ans = (ans + f[i]) % mod; ans = (ans + k) % mod; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) ans = ans * i % mod; printf("%lld\n", ans); return 0; }
Ⅴ. P3830 [SHOI2012]随机树
- 考虑第一问
设
则
故有
即
-
考虑第二问
-
先证明一个小结论:设扩展
将扩展过程表示为序列,则其中 “扩展左子树” 有
再考虑
同理,右子树的形态数有
故考虑扩展先后、树的形态,生成一个左子树有
与
- 前置芝士:整数概率公式
正整数随机变量
证明:
- 计算概率
设
解释如下,首先考虑左、右子树深度不小于
前文我们证明过,左子树叶节点数为
初始条件,
由整数概率公式可知,期望深度
摘自 https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/emptyset/solution-p3830
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define db double using namespace std; const int N = 1e2 + 67; int read(){ int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();} while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();} return x * f; } int opt, n; db ans, f[N][N]; void solve1(){ for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) ans += 2.0 / i; } void solve2(){ for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) f[i][0] = 1; for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) for(int j = 1; j < i; ++j) for(int k = 1; k < i; ++k) f[i][j] += (f[k][j - 1] + f[i - k][j - 1] - f[k][j - 1] * f[i - k][j - 1]) / (i - 1); for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) ans += f[n][i]; } signed main(){ opt = read(), n = read(); if(opt & 1) solve1(); else solve2(); printf("%.6lf\n", ans); return 0; }
Ⅵ. P3600 随机数生成器
本文作者:南风未起
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiangchen4122/p/17444621.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步