消息队列RabbitMQ
一、RabbitMQ简介
1. 应用场景
(1)任务异步处理
将不需要同步处理的并且耗时长的操作由消息队列通知消息接收方进行异步处理。缩短了应用程序的响应时间。
(2)应用程序解耦合
MQ相当于一个中介,生产方通过MQ与消费方交互,它将应用程序进行了解耦合。
2. 工作原理
下图是RabbitMQ的基本结构:
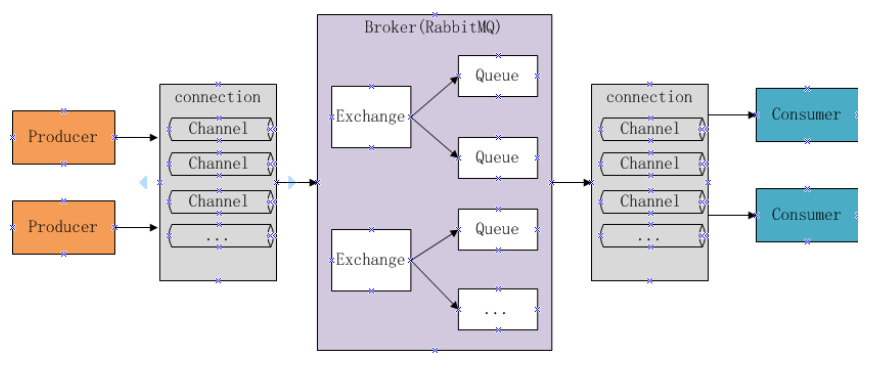
组成部分说明如下:
-
Broker:消息队列服务进程,此进程包括两个部分:Exchange和Queue。
-
Exchange:消息队列交换机,按一定的规则将消息路由转发到某个队列,对消息进行过滤。
-
Queue:消息队列,存储消息的队列,消息到达队列并转发给指定的消费方。
-
Producer:消息生产者,即生产方客户端,生产方客户端将消息发送到MQ。
-
Consumer:消息消费者,即消费方客户端,接收MQ转发的消息。
消息发布接收流程:
-----发送消息-----
(1)生产者和Broker建立TCP连接。
(2)生产者和Broker建立通道。
(3)生产者通过通道将消息发送给Broker,由Exchange将消息进行转发。
(4)Exchange将消息转发到指定的Queue(队列)
----接收消息-----
(1)消费者和Broker建立TCP连接。
(2)消费者和Broker建立通道。
(3)消费者监听指定的Queue(队列)。
(4)当有消息到达Queue时Broker默认将消息推送给消费者。
(5)消费者接收到消息。
二、RabbitMQ的6种工作模式
1. Work queues(工作队列模式)
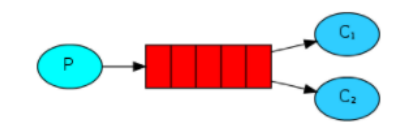
(1)一条消息只会被一个消费者接收。
(2)RabbitMQ采用轮询的方式将消息平均发送给消费者。
(3)消费者在处理完某条消息后,才会收到下一条消息。
应用场景:
对于任务过重或任务较多的情况使用工作队列可以提高任务处理的速度。
2. Publish/subscribe(发布订阅模式)
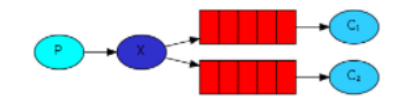
(1)每个消费者监听自己的队列。
(2)生产者将消息发给broker,由交换机将消息转发到绑定此交换机的每个队列,每个绑定交换机的队列都将接收到消息。
【注1】 publish/subscribe与work queues有什么区别?
区别:
-
work queues不用定义交换机,而publish/subscribe需要定义交换机。
-
publish/subscribe的生产方是面向交换机发送消息,work queues的生产方是面向队列发送消息(底层使用默认交换机)。
-
publish/subscribe需要设置队列和交换机的绑定,work queues不需要设置,实质上work queues会将队列绑定到默认的交换机 。
相同点:
- 两者实现的发布/订阅的效果是一样的,多个消费端监听同一个队列不会重复消费消息。
【注2】实际工作中用publish/subscribe还是work queues?
建议使用 publish/subscribe,发布订阅模式比工作队列模式更强大,并且发布订阅模式可以指定自己专用的交换机。
3. Routing(路由工作模式)
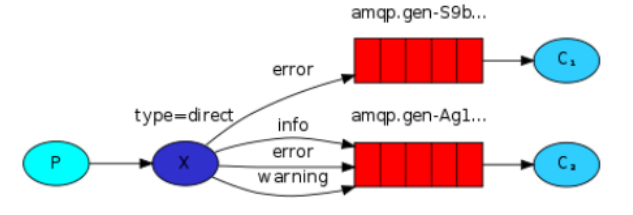
(1)每个消费者监听自己的队列,队列设置routingkey。
(2)生产者将消息发给交换机,发送消息时需要指定routingkey,由交换机根据routingkey来转发消息到指定的队列。
【注1】Routing与Publish/subscibe有什么区别?
- Routing要求队列在绑定交换机时要指定routingkey,消息会转发到符合routingkey的队列中。
4. Topic(通配符工作模式)

(1)每个消费者监听自己的队列,队列设置带通配符的routingkey。
(2)生产者将消息发给broker,由交换机根据routingkey来转发消息到指定的队列。
通配符规则:
中间以“.”分隔; 符号#可以匹配多个词,符号*可以匹配一个词语。
【注】Topic模式更多加强大,它可以实现Routing、publish/subscirbe模式的功能。
5. Header模式
header模式与routing不同的地方在于,header模式取消了routingkey,使用header中的 key/value(键值对)匹配队列。
6. RPC
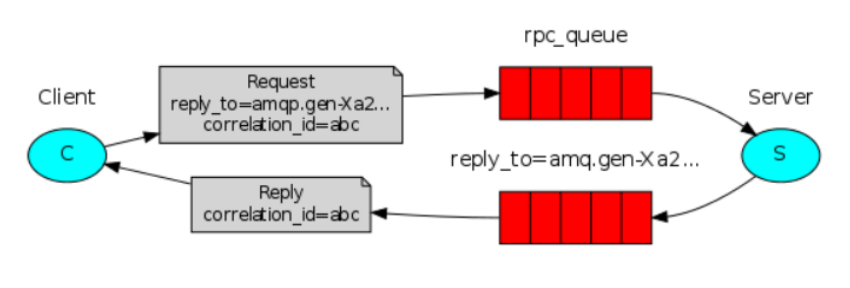
RPC即客户端远程调用服务端的方法 ,使用MQ可以实现RPC的异步调用,基于Direct交换机实现,流程如下:
(1)客户端既是生产者也是消费者,向RPC请求队列发送RPC调用消息,同时监听RPC响应队列。
(2)服务端监听RPC请求队列的消息,收到消息后执行服务端的方法,得到方法返回的结果。
(3)服务端将RPC方法返回的结果发送到RPC响应队列。
(4)客户端(RPC调用方)监听RPC响应队列,接收到RPC调用的结果。
三、Spring Boot整合RabbitMQ
1. 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 配置
(1)配置application.yml (配置连接RabbitMQ的参数)
server: port:
44000
spring:
application:
name: test‐rabbitmq‐producer
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
virtualHost: /
(2)定义RabbitConfifig类,配置Exchange、Queue、及绑定交换机(本例配置Topic交换机)
package com.xuecheng.test.rabbitmq.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitmqConfig {
public static final String QUEUE_INFORM_EMAIL = "queue_inform_email";
public static final String QUEUE_INFORM_SMS = "queue_inform_sms";
public static final String EXCHANGE_TOPICS_INFORM="exchange_topics_inform";
/**
* 交换机配置
* ExchangeBuilder提供了fanout、direct、topic、header交换机类型的配置
* @return the exchange
*/
@Bean(EXCHANGE_TOPICS_INFORM)
public Exchange EXCHANGE_TOPICS_INFORM() {
//durable(true)持久化,消息队列重启后交换机仍然存在
return ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange(EXCHANGE_TOPICS_INFORM).durable(true).build();
}
//声明队列
@Bean(QUEUE_INFORM_SMS)
public Queue QUEUE_INFORM_SMS() {
Queue queue = new Queue(QUEUE_INFORM_SMS);
return queue;
}
//声明队列
@Bean(QUEUE_INFORM_EMAIL)
public Queue QUEUE_INFORM_EMAIL() {
Queue queue = new Queue(QUEUE_INFORM_EMAIL);
return queue;
}
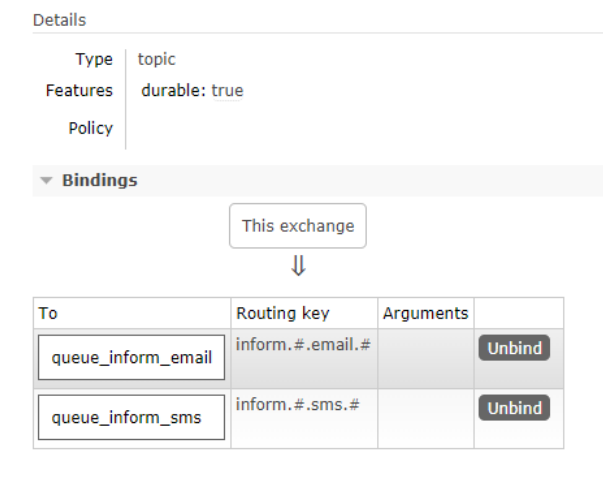
/** channel.queueBind(INFORM_QUEUE_SMS,"inform_exchange_topic","inform.#.sms.#"); * 绑定队列到交换机 .
*
* @param queue the queue
* @param exchange the exchange
* @return the binding
*/
@Bean
public Binding BINDING_QUEUE_INFORM_SMS(@Qualifier(QUEUE_INFORM_SMS) Queue queue, @Qualifier(EXCHANGE_TOPICS_INFORM) Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("inform.#.sms.#").noargs();
}
@Bean
public Binding BINDING_QUEUE_INFORM_EMAIL(@Qualifier(QUEUE_INFORM_EMAIL) Queue queue, @Qualifier(EXCHANGE_TOPICS_INFORM) Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("inform.#.email.#").noargs();
}
}
3. 生产端
使用RarbbitTemplate发送消息
package com.xuecheng.test.rabbitmq;
import com.xuecheng.test.rabbitmq.config.RabbitmqConfig;
import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class Producer05_topics_springboot {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void testSendByTopics(){
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
String message = "sms email inform to user"+i;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitmqConfig.EXCHANGE_TOPICS_INFORM,"inform.sms.email",message);
System.out.println("Send Message is:'" + message + "'");
}
}
}
4. 消费端
创建消费端工程,添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
使用@RabbitListener注解监听队列:
package com.xuecheng.test.rabbitmq.mq;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.xuecheng.test.rabbitmq.config.RabbitmqConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ReceiveHandler {
//监听email队列
@RabbitListener(queues = {RabbitmqConfig.QUEUE_INFORM_EMAIL})
public void receive_email(String msg,Message message,Channel channel){ System.out.println(msg);
}
//监听sms队列
@RabbitListener(queues = {RabbitmqConfig.QUEUE_INFORM_SMS})
public void receive_sms(String msg,Message message,Channel channel){ System.out.println(msg);
}
}
5. 测试