Wakelocks 框架设计与实现
Wakelocks 框架是基于Wakeup Source实现的为Android系统上层提供投票机制,以阻止系统进入休眠。
1.功能说明
该模块的支持受宏CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS控制。在使能该宏的情况下,PM Core初始化过程中会在sysfs下创建两个属性节点:
/sys/power/wake_lock:用户程序可以向其写入一个字符串来创建一个wakelock,该字符创即为wakelock的名字,该wakelock可阻止系统进入低功耗模式
/sys/power/wake_unlock:用户程序向其写入相同的字符串,即可注销该wakelock
配置宏CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_LIMIT可以限制系统所能创建的wakelock的数量。
使能宏CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_GC能打开wakelock的回收机制,使得wakelock在积累一定的数量后再去清除(释放空间),从而不需要在每次释放wakelock时都去清除。
2.主要数据结构和接口
2.1 wakelock结构体
struct wakelock {
char *name; //wakelock名字
struct rb_node node; //红黑树节点,所有wakelock以红黑树的方式组织在该模块里,便于管理
struct wakeup_source *ws; //wakelock对应的ws
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_GC
struct list_head lru; //与wakelock的回收机制有关,见后续介绍
#endif
};
2.2 模块重要变量
@ kernel/power/wakelock.c
static struct rb_root wakelocks_tree = RB_ROOT; //红黑树根节点,所有wakelock都会挂在这上面,便于管理
static LIST_HEAD(wakelocks_lru_list); //该链表用于管理已生成的wakelock,便于回收机制处理,后续称其为回收链表
//当 CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_LIMIT 配置大于0时,保存已存在的wakelock数量,用于限制存在的wakelock数量不超过CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_LIMIT
static unsigned int number_of_wakelocks;
//当 CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_GC 配置时,表示启动wakelock回收机制。该变量用于累计已解锁的wakelock的数量,当该变量超过WL_GC_COUNT_MAX(100)时,会触发回收work
static unsigned int wakelocks_gc_count;
2.3 主要接口
2.3.1 pm_wake_lock()接口
该接口是在向/sys/power/wake_lock写入字符串时调用,主要实现:
- 查找同名wakelock,找不到时创建wakelock,并持(超时)锁
- 配置
CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_LIMIT > 0的情况下,对wakelock数量计数并限制 - 将该wakelock移到回收链表前端,以防被优先回收
/* call by wake_lock_store()*/
int pm_wake_lock(const char *buf)
{
const char *str = buf;
struct wakelock *wl;
u64 timeout_ns = 0;
size_t len;
int ret = 0;
//解析传入的字符串,第一个参数为wakelock名称,第二个参数(可选)则是wakelock超时时间
while (*str && !isspace(*str))
str++;
len = str - buf;
if (!len)
return -EINVAL;
if (*str && *str != '\n') {
/* Find out if there's a valid timeout string appended. */
ret = kstrtou64(skip_spaces(str), 10, &timeout_ns);
if (ret)
return -EINVAL;
}
mutex_lock(&wakelocks_lock);
//查找wakelock,找不到时创建
wl = wakelock_lookup_add(buf, len, true);
if (IS_ERR(wl)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(wl);
goto out;
}
if (timeout_ns) { //如果传入了超时参数,则持锁,超时后会自动释放该锁
u64 timeout_ms = timeout_ns + NSEC_PER_MSEC - 1;
do_div(timeout_ms, NSEC_PER_MSEC);
__pm_wakeup_event(wl->ws, timeout_ms);
} else { //否则直接持锁
__pm_stay_awake(wl->ws);
}
wakelocks_lru_most_recent(wl); //将该wakelock移到回收链表前端,使得回收机制触发时靠后处理
out:
mutex_unlock(&wakelocks_lock);
return ret;
}
static struct wakelock *wakelock_lookup_add(const char *name, size_t len,
bool add_if_not_found)
{
struct rb_node **node = &wakelocks_tree.rb_node;
struct rb_node *parent = *node;
struct wakelock *wl;
//根据名称在红黑树上查找是否已经存在该wakelock
while (*node) {
int diff;
parent = *node;
wl = rb_entry(*node, struct wakelock, node);
diff = strncmp(name, wl->name, len);
if (diff == 0) {
if (wl->name[len])
diff = -1;
else
return wl; //找到同名wakelock,返回
}
if (diff < 0)
node = &(*node)->rb_left;
else
node = &(*node)->rb_right;
}
if (!add_if_not_found)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
//配置CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_LIMIT>0的情况下,会检测已创建的wakelock数量是否已经超过该配置
if (wakelocks_limit_exceeded())
return ERR_PTR(-ENOSPC);
/* 未找到同名wakelock的情况下,开始创建wakelock */
wl = kzalloc(sizeof(*wl), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!wl)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
wl->name = kstrndup(name, len, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!wl->name) {
kfree(wl);
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
}
//本质wakelock是通过wakeup_source机制实现的
wl->ws = wakeup_source_register(NULL, wl->name);
if (!wl->ws) {
kfree(wl->name);
kfree(wl);
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
}
wl->ws->last_time = ktime_get();
//将该wakelock挂到红黑树上
rb_link_node(&wl->node, parent, node);
rb_insert_color(&wl->node, &wakelocks_tree);
wakelocks_lru_add(wl); //添加到回收链表
increment_wakelocks_number(); //wakelock数量+1
return wl;
}
2.3.2 pm_wake_unlock() 接口
该接口是在向/sys/power/wake_unlock写入字符串时调用,主要实现:
- 查找同名wakelock,找不到时返回错误
- 配置
CONFIG_PM_WAKELOCKS_GC开启回收机制的情况下,对wakelock数量计数并在超过上限时触发回收处理work
/* call by wake_unlock_store()*/
int pm_wake_unlock(const char *buf)
{
struct wakelock *wl;
size_t len;
int ret = 0;
len = strlen(buf);
if (!len)
return -EINVAL;
if (buf[len-1] == '\n')
len--;
if (!len)
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&wakelocks_lock);
//查找wakelock,找不到时直接返回错误
wl = wakelock_lookup_add(buf, len, false);
if (IS_ERR(wl)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(wl);
goto out;
}
__pm_relax(wl->ws); //释放锁
wakelocks_lru_most_recent(wl); //将该wakelock移到回收链表前端,使得回收机制触发时靠后处理
wakelocks_gc(); //已解锁的wakelock加1,并判断是否超过上限,触发回收处理work
out:
mutex_unlock(&wakelocks_lock);
return ret;
}
2.3.3 __wakelocks_gc()回收处理work
该接口在已解锁的wakelock数量超过上限WL_GC_COUNT_MAX(100)时调用,用于处理回收已创建的wakelock,释放空间。
static void __wakelocks_gc(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct wakelock *wl, *aux;
ktime_t now;
mutex_lock(&wakelocks_lock);
now = ktime_get();
//从回收链表尾部开始倒序遍历(越靠近链表头部的wakelock,越是最近才操作的wakelock)
list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(wl, aux, &wakelocks_lru_list, lru) {
u64 idle_time_ns;
bool active;
spin_lock_irq(&wl->ws->lock);
idle_time_ns = ktime_to_ns(ktime_sub(now, wl->ws->last_time)); //计算该锁有多长时间未被操作过
active = wl->ws->active; //获取锁的激活状态
spin_unlock_irq(&wl->ws->lock);
if (idle_time_ns < ((u64)WL_GC_TIME_SEC * NSEC_PER_SEC)) //如果锁空闲时间小于300s,则不再继续回收
break;
//如果锁已经失活,则注销该锁,从红黑树中移除,并移除出回收链表,释放空间,wakelock数量-1
if (!active) {
wakeup_source_unregister(wl->ws);
rb_erase(&wl->node, &wakelocks_tree);
list_del(&wl->lru);
kfree(wl->name);
kfree(wl);
decrement_wakelocks_number();
}
}
wakelocks_gc_count = 0; //重置回收锁计数
mutex_unlock(&wakelocks_lock);
}
使能回收机制的好处是:
1.上层频繁操作wakelock时,不用每次unlock时都耗时去释放资源;
2.如果频繁操作的是同一个wakelock,也不用反复创建/释放资源。
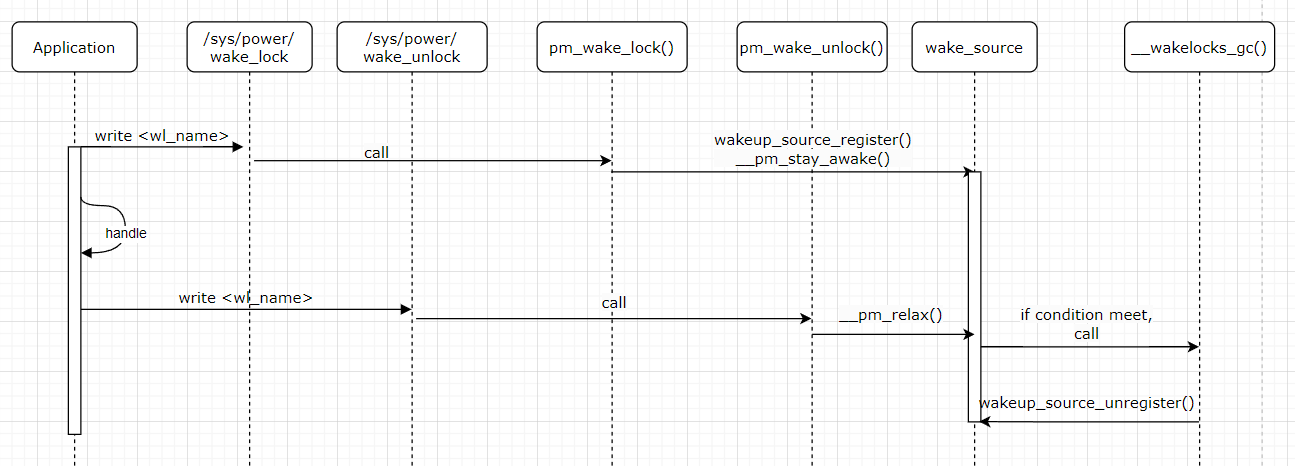
3. 工作时序
wakelock的工作时序如下:
1)应用程序在处理数据前不希望系统进入休眠状态,通过向/sys/power/wake_lock写入一个字符串作为wakelock名字,此时pm_wake_lock()被调用
2)在pm_wake_lock()里,会查找是否已存在同名wakelock,已存在则持锁,不存在则创建锁并持锁
3)应用程序在处理完数据后允许系统进入休眠状态时,通过向/sys/power/wake_unlock写入已持锁的wakelock名字,此时pm_wake_unlock()被调用
4)在pm_wake_unlock()里,会查找是否已存在同名wakelock,并释放该锁,同时判断此时是否要触发wakelock的回收机制
5)当wakelock回收链表里的wakelock数量达到上限后,触发wakelock的回收机制,将长时间未使用且已经解锁的wakelock注销,释放资源
关于wakelock的发展变化以及使用,强烈建议拜读:http://www.wowotech.net/pm_subsystem/wakelocks.html
注:此源码分析基于kernel-5.10。




