Java_8 常用容器
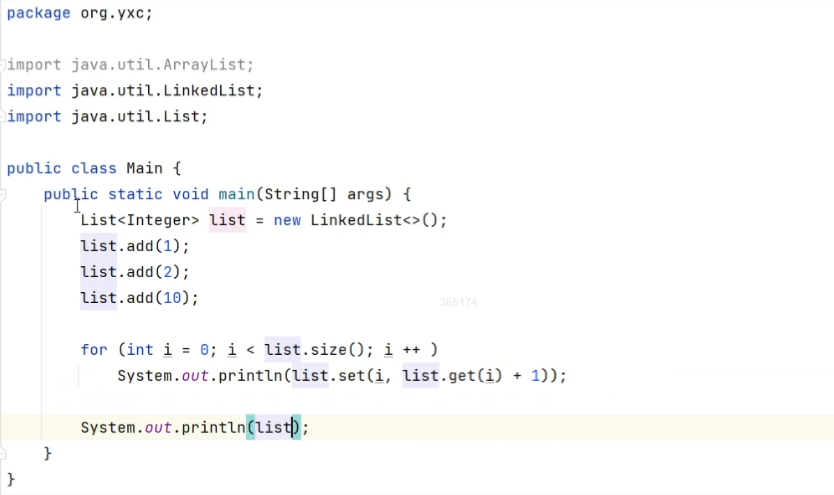
8.1 List
接口:java.util.List<>。
实现:
java.util.ArrayList<>:变长数组java.util.LinkedList<>:双链表
函数:
add():在末尾添加一个元素clear():清空size():返回长度isEmpty():是否为空get(i):获取第i个元素set(i, val):将第i个元素设置为val
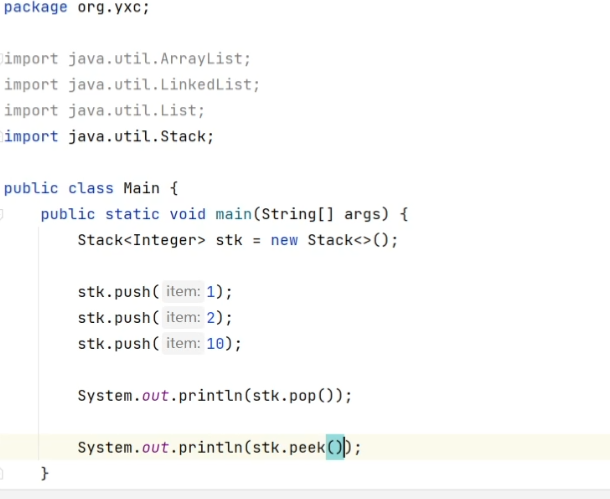
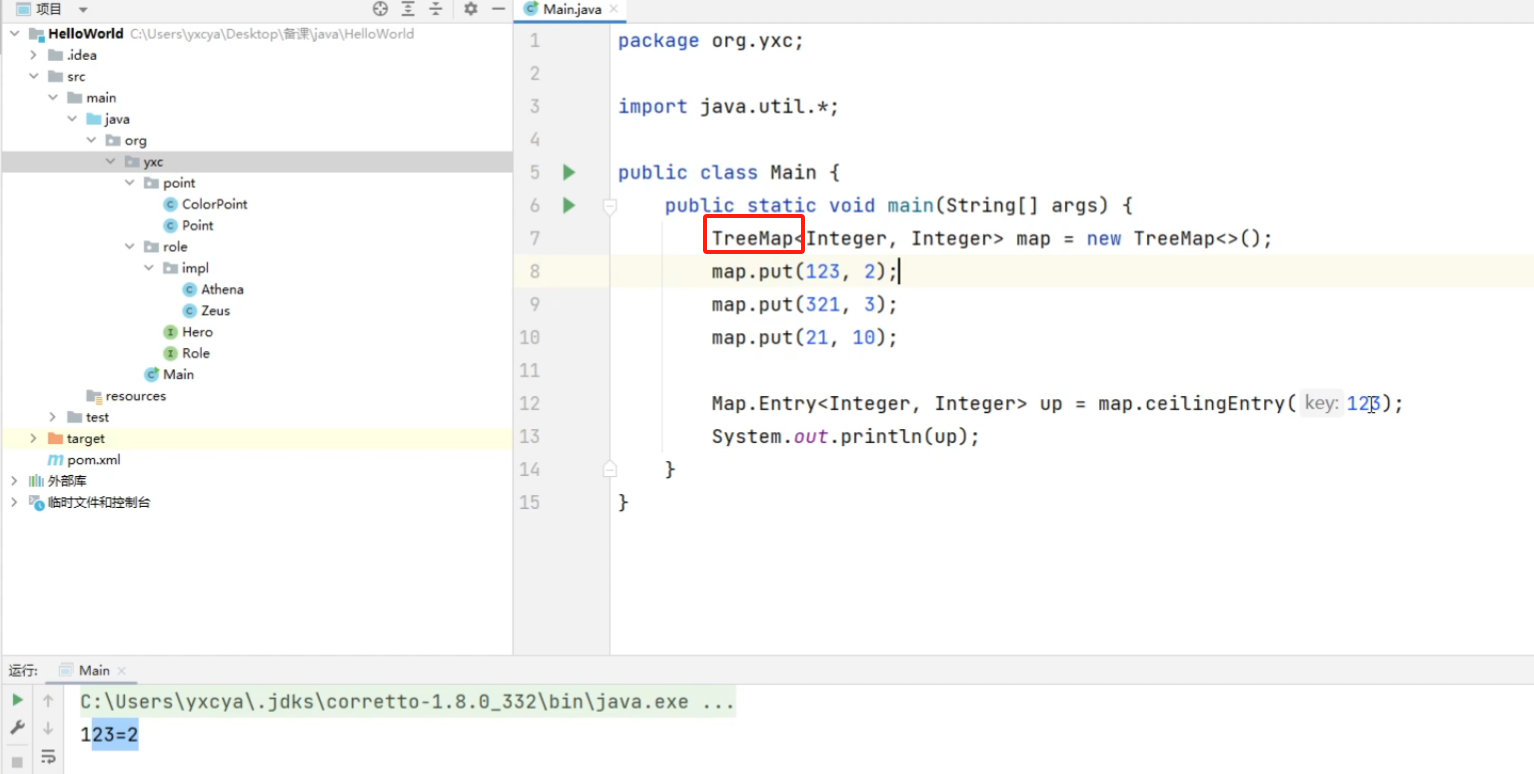
8.2 栈
类:java.util.Stack<>
函数:
push():压入元素pop():弹出栈顶元素,并返回栈顶元素peek():返回栈顶元素size():返回长度empty():栈是否为空clear():清空
8.3 队列
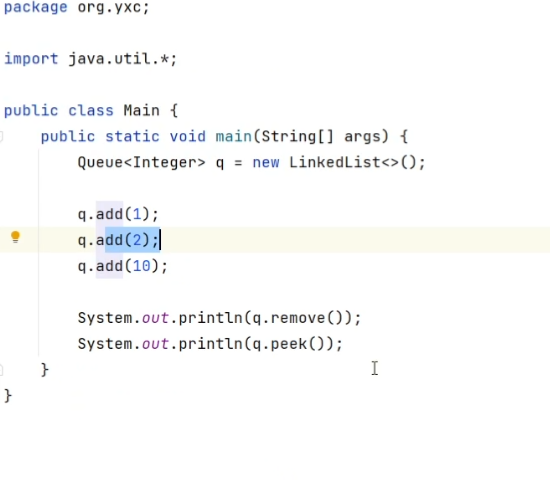
接口:java.util.Queue<>
实现:
java.util.LinkedList<>:双链表java.util.PriorityQueue<>:优先队列(存在排序)- 默认是小根堆,大根堆写法:
new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder())
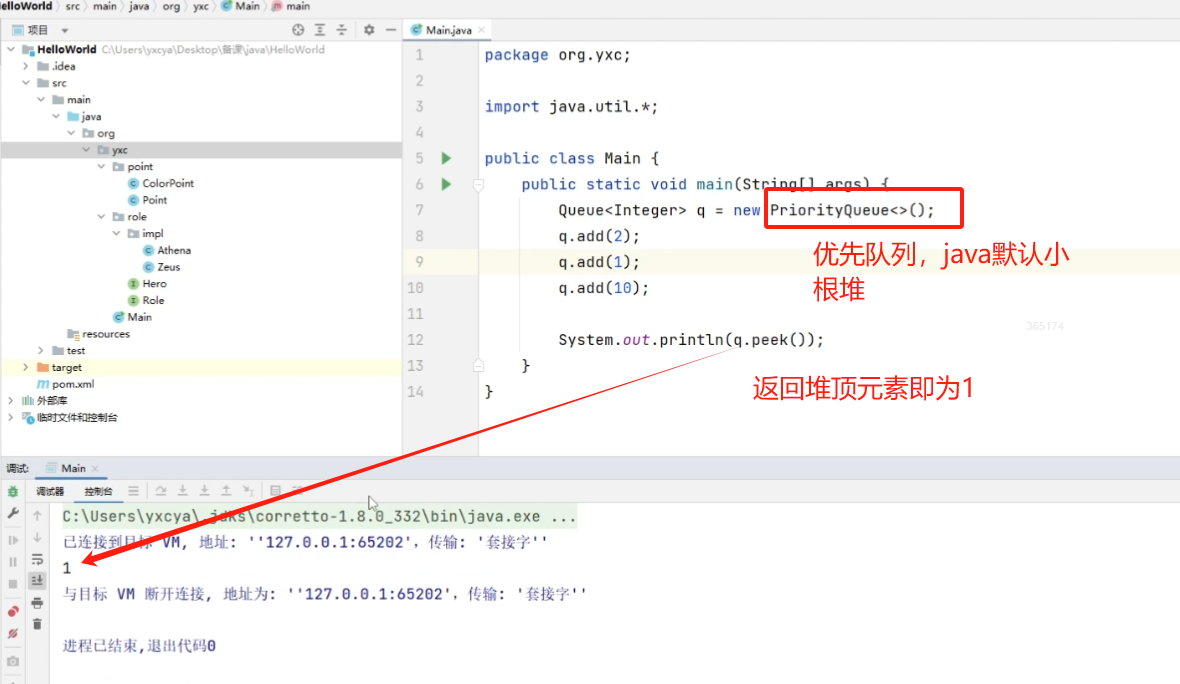
- 默认是小根堆,大根堆写法:
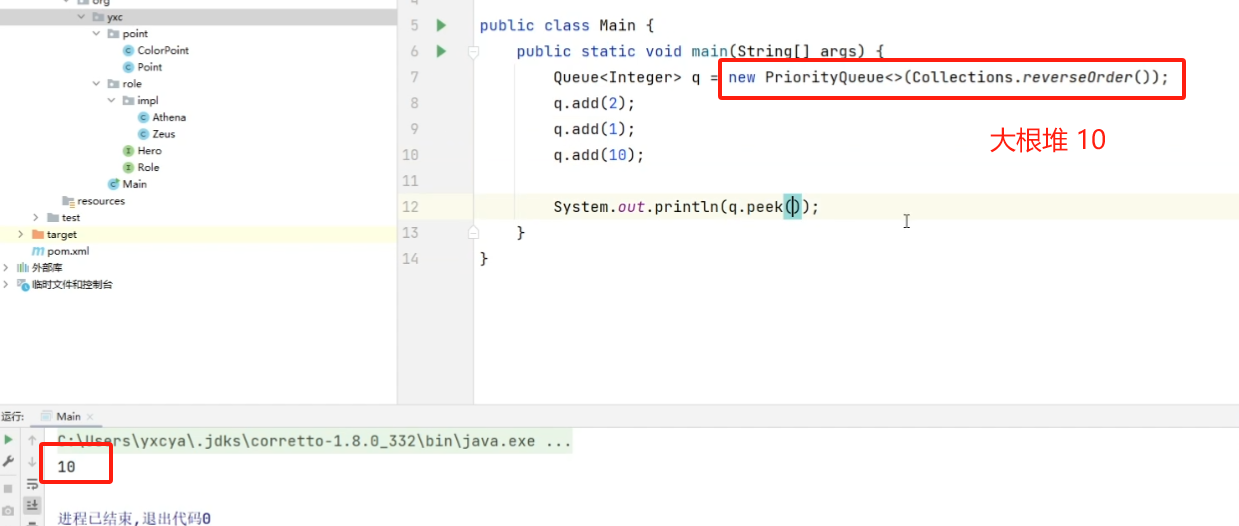
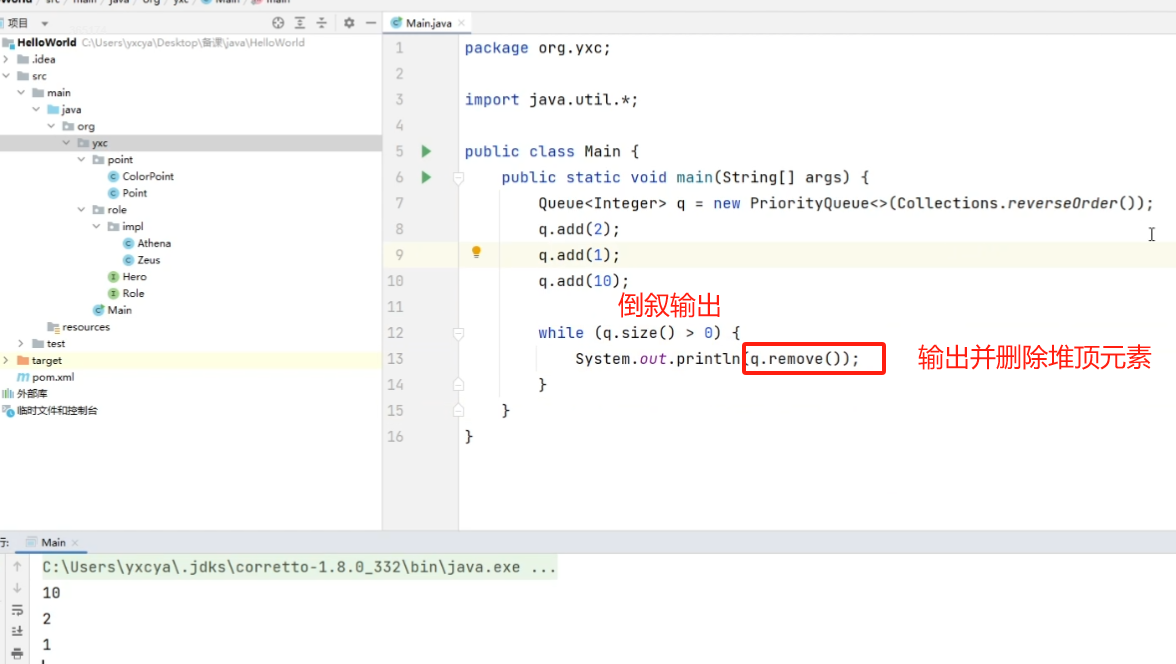
函数:
add():在队尾添加元素remove():删除并返回队头isEmpty():是否为空size():返回长度peek():返回队头clear():清空
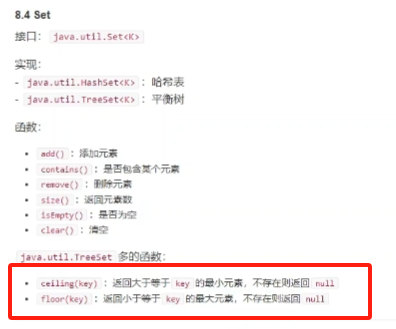
8.4 Set
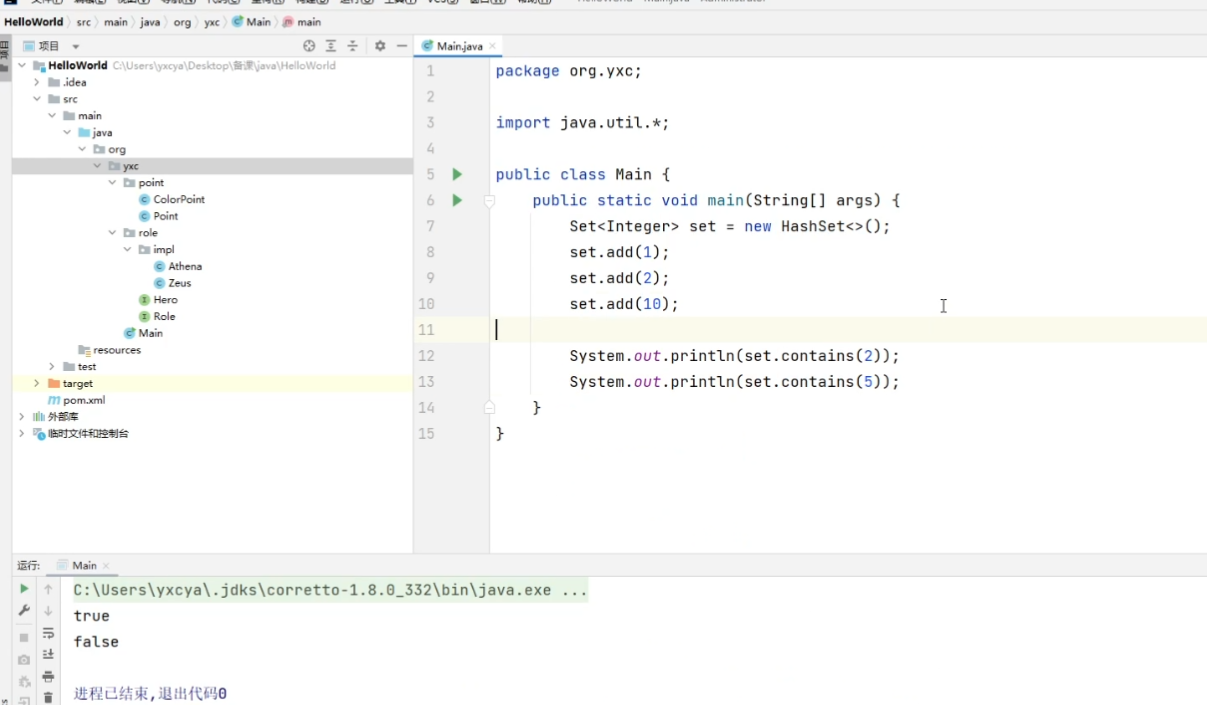
接口:java.util.Set<K>
实现:
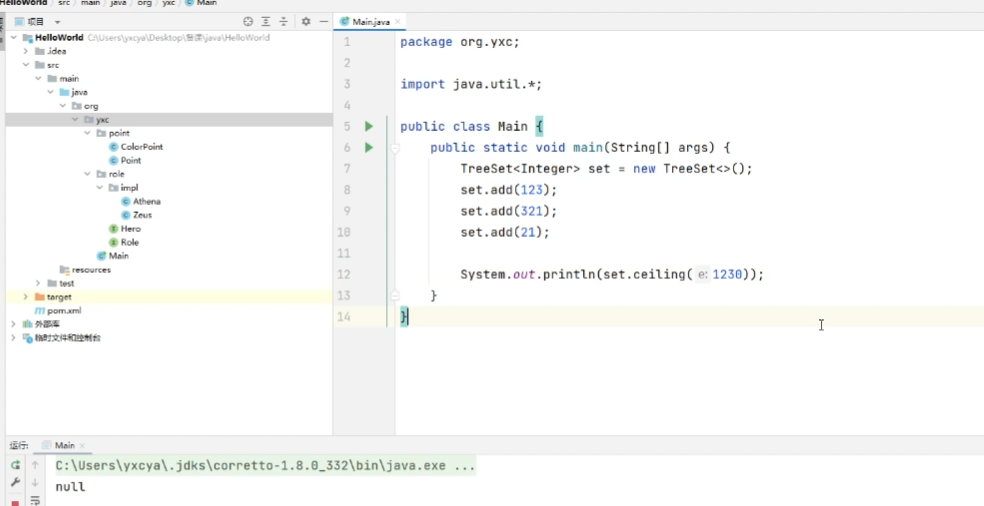
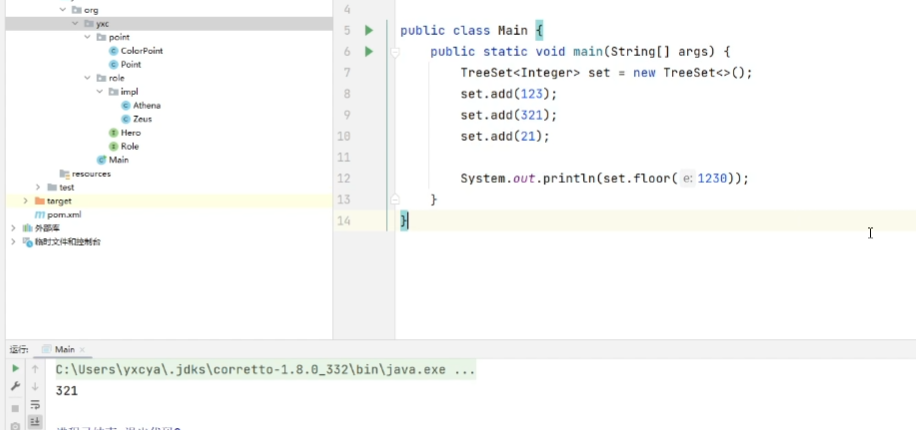
java.util.HashSet<K>:哈希表java.util.TreeSet<K>:平衡树
函数:
add():添加元素contains():是否包含某个元素remove():删除元素size():返回元素数isEmpty():是否为空clear():清空
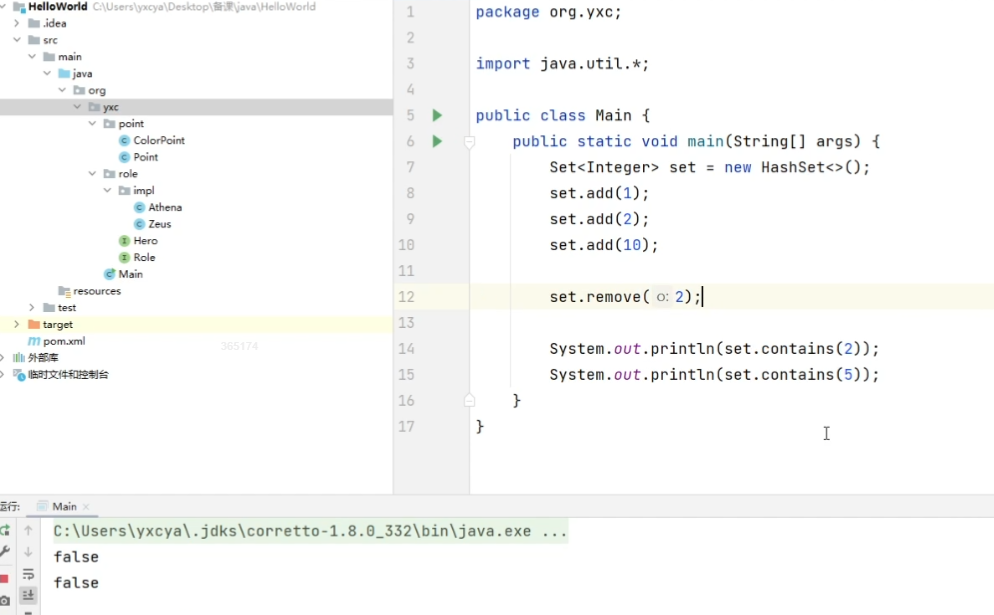
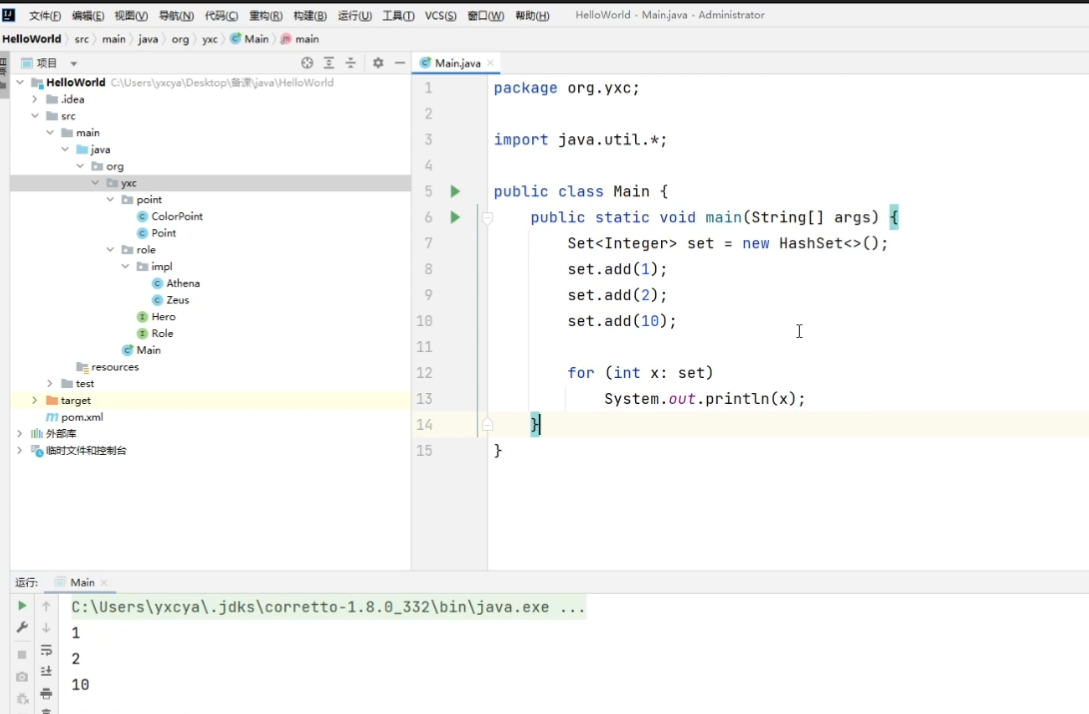
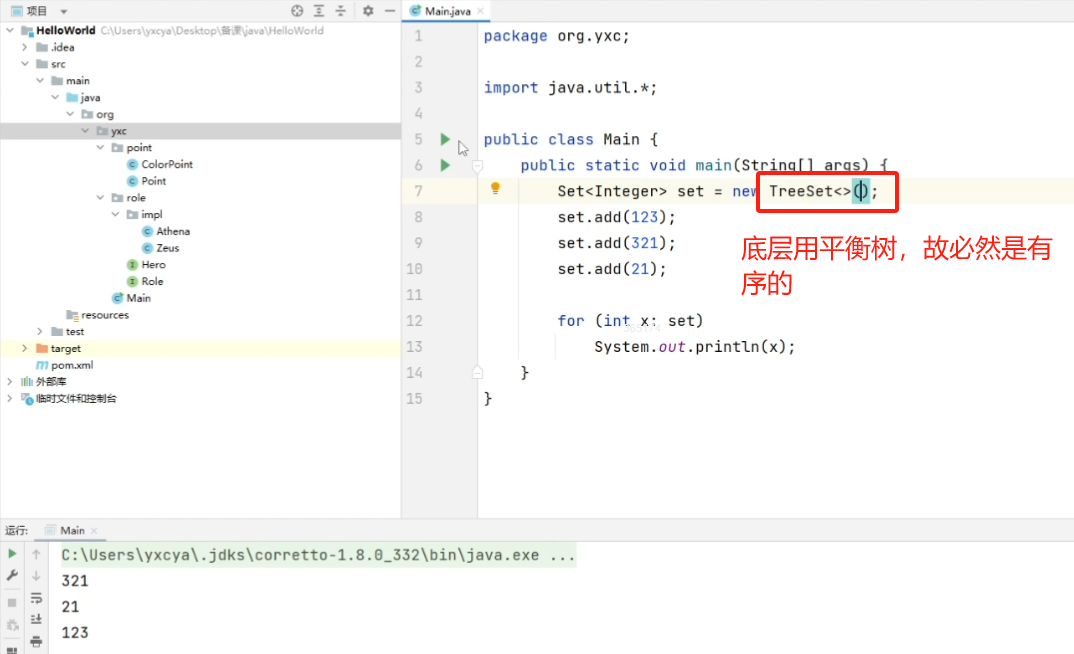
java.util.TreeSet多的函数:
ceiling(key):返回大于等于key的最小元素,不存在则返回nullfloor(key):返回小于等于key的最大元素,不存在则返回null
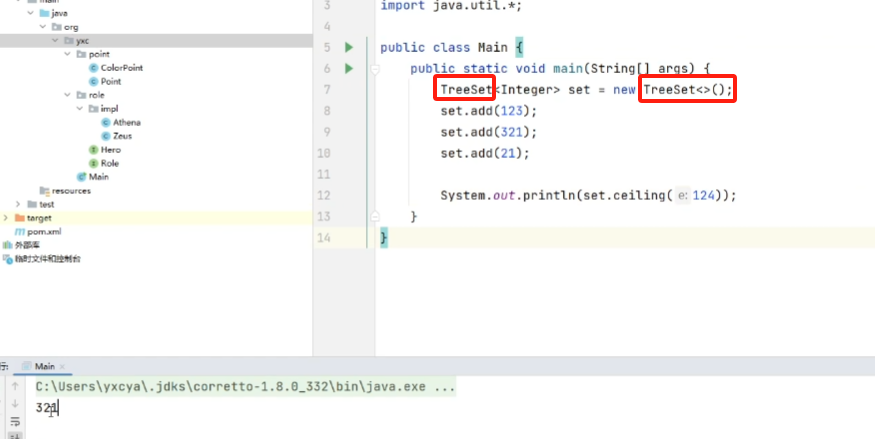
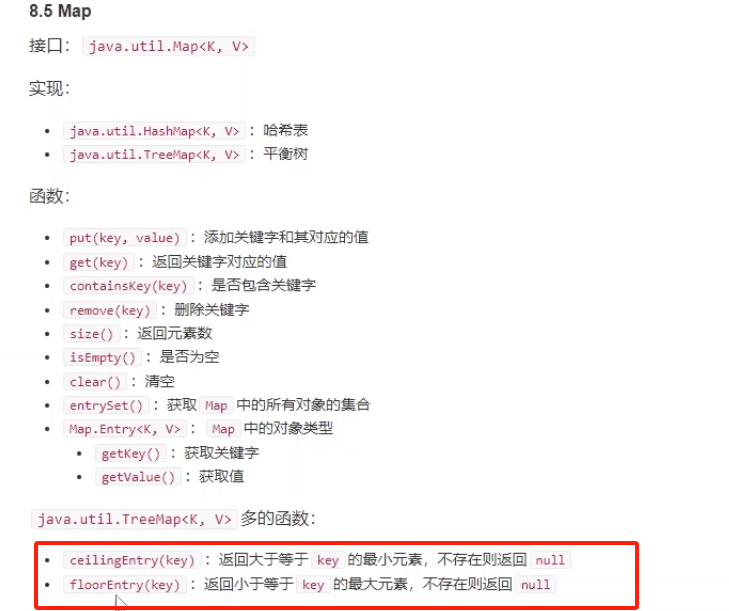
8.5 Map
接口:java.util.Map<K, V>
实现:
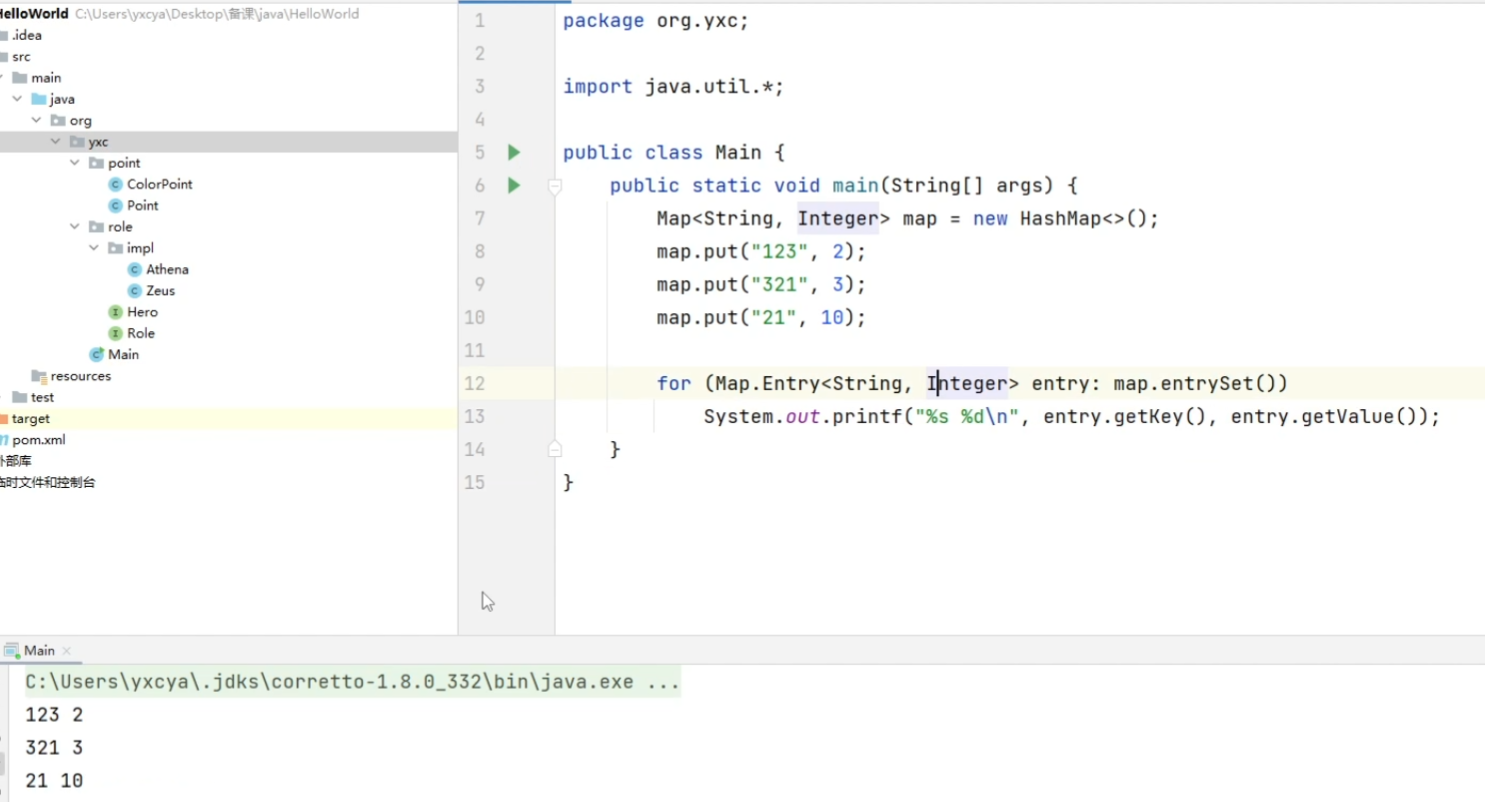
java.util.HashMap<K, V>:哈希表java.util.TreeMap<K, V>:平衡树
函数:
put(key, value):添加关键字和其对应的值get(key):返回关键字对应的值containsKey(key):是否包含关键字remove(key):删除关键字size():返回元素数isEmpty():是否为空clear():清空entrySet():获取Map中的所有对象的集合Map.Entry<K, V>:Map中的对象类型getKey():获取关键字getValue():获取值
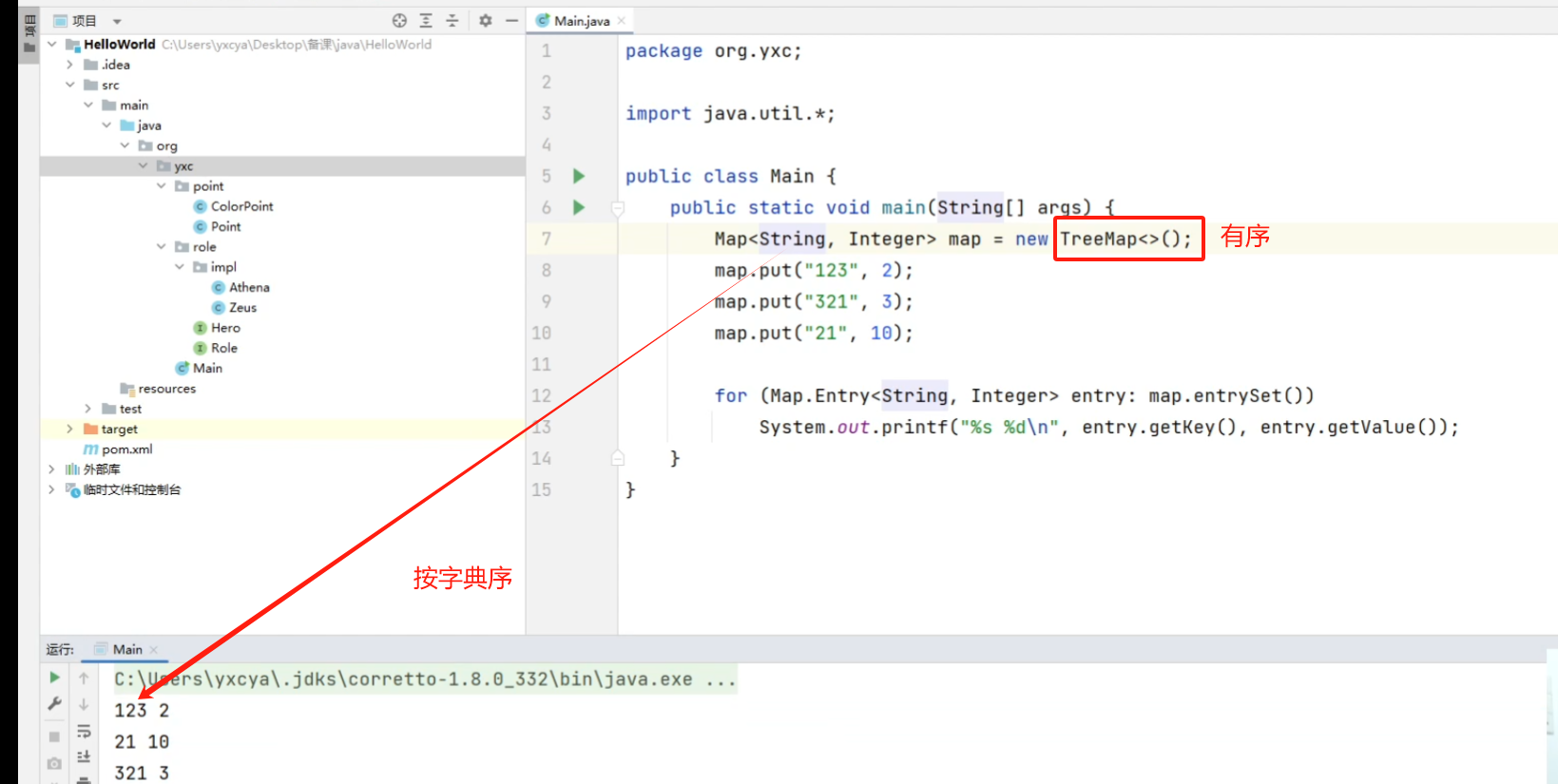
java.util.TreeMap<K, V>多的函数:
ceilingEntry(key):返回大于等于key的最小元素,不存在则返回nullfloorEntry(key):返回小于等于key的最大元素,不存在则返回null
8.6 习题
8.6.1 模拟栈

- 输入样例:
10
push 5
query
push 6
pop
query
pop
empty
push 4
query
empty
- 输出样例:
5
5
YES
4
NO
- 题解
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @author ljm
* @create 2024-02-20 18:33
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int m=sc.nextInt();
Stack<Integer> stk=new Stack<>();
while(m-->0){
String op=sc.next();
if(op.equals("push")){
int x=sc.nextInt();
stk.push(x);
} else if (op.equals("pop")) {
stk.pop();
} else if (op.equals("empty")) {
if(stk.empty()){
System.out.println("YES");
}else {
System.out.println("NO");
}
} else if (op.equals("query")) {
System.out.println(stk.peek());
}
}
}
}
8.6.2 0到n-1中缺失的数字
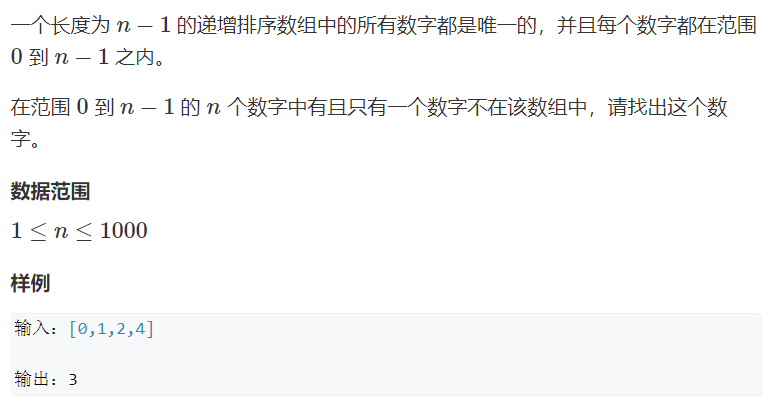
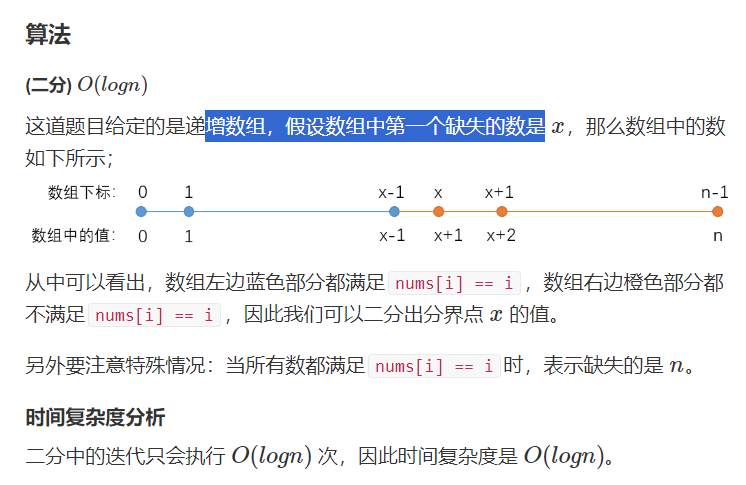
- 题解
class Solution {
public:
int getMissingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.empty()) return 0;
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (nums[mid] != mid) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
if (nums[r] == r) r ++ ;
return r;
}
};
8.6.3 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面

- 解题思路


交换
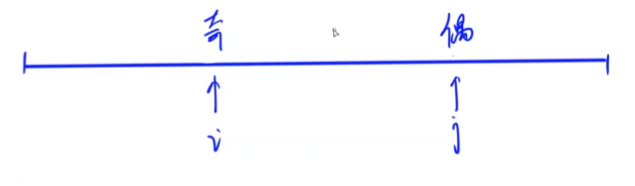
- 题解
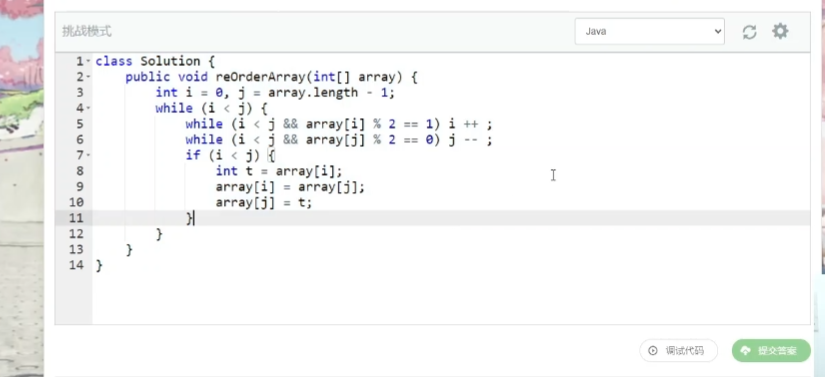
本人复杂题解
class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int[] array) {
int[] res=new int[array.length];
int s1=0,s2=0;
for (int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
if(array[i]%2!=0) s1++;
else s2++;
res[i]=array[i];
}
int p=0,q=s1;
for (int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
if(res[i]%2!=0){
array[p++]=res[i];
}else {
array[q++]=res[i];
}
}
}
}
8.6.4 用两个栈实现队列
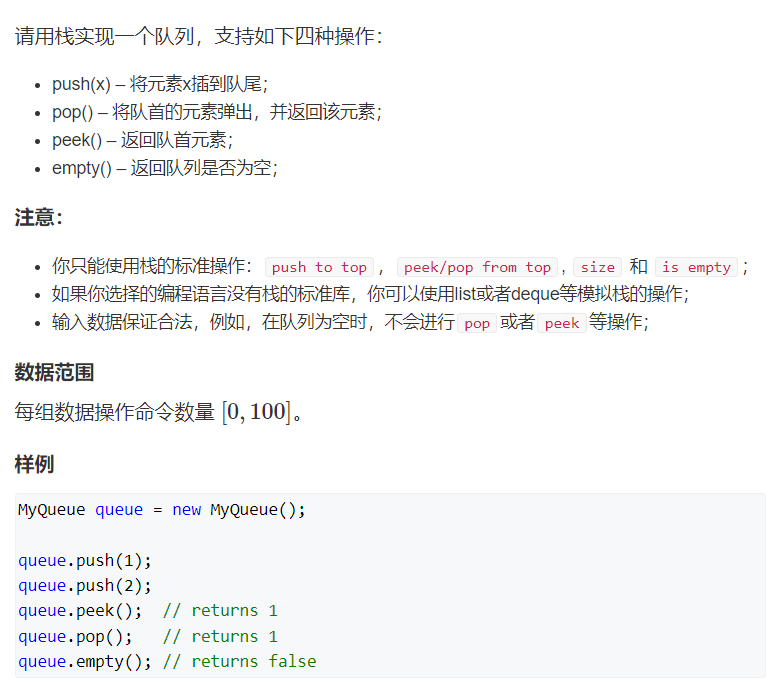
- 本人题解
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stk1=new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stk2=new Stack<>();
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stk1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if(!stk2.empty()){
return stk2.pop();
}else{
while(!stk1.empty()){
stk2.push(stk1.pop());
}
return stk2.pop();
}
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if(!stk2.empty()){
return stk2.peek();
}else{
while(!stk1.empty()){
stk2.push(stk1.pop());
}
return stk2.peek();
}
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
if(stk1.empty()&&stk2.empty()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
8.6.5 最小的k个数
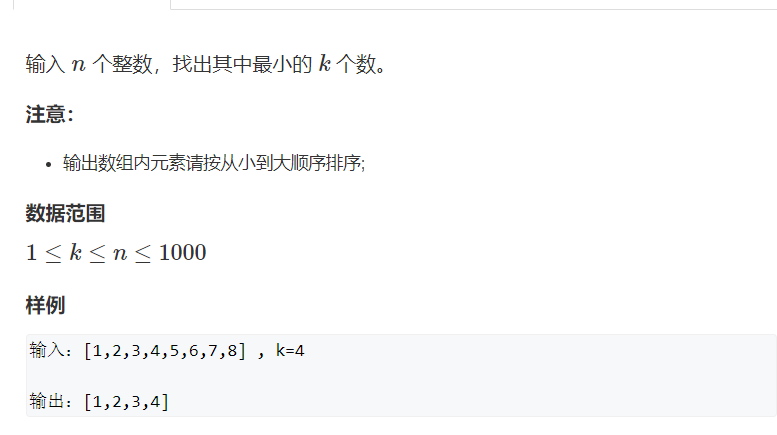
- 题解
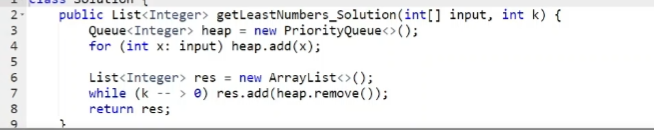
8.6.6 和为S的两个数字
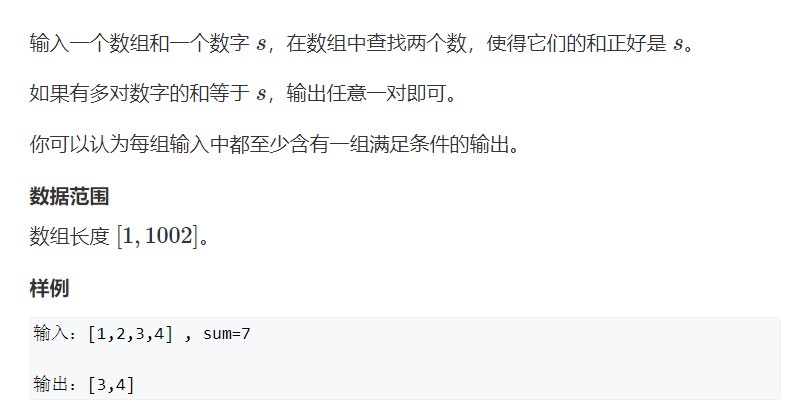
- 本人题解
class Solution {
public int[] findNumbersWithSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
int[] res=new int[2];
for(int x:nums) set.add(x);
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
int leave=target-nums[i];
if(set.contains(leave)){
res[0]=nums[i];
res[1]=leave;
}
}
return res;
}
}
- 题解
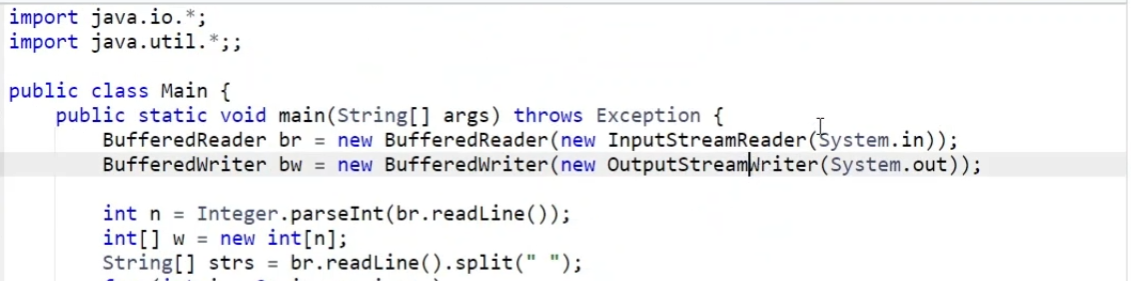
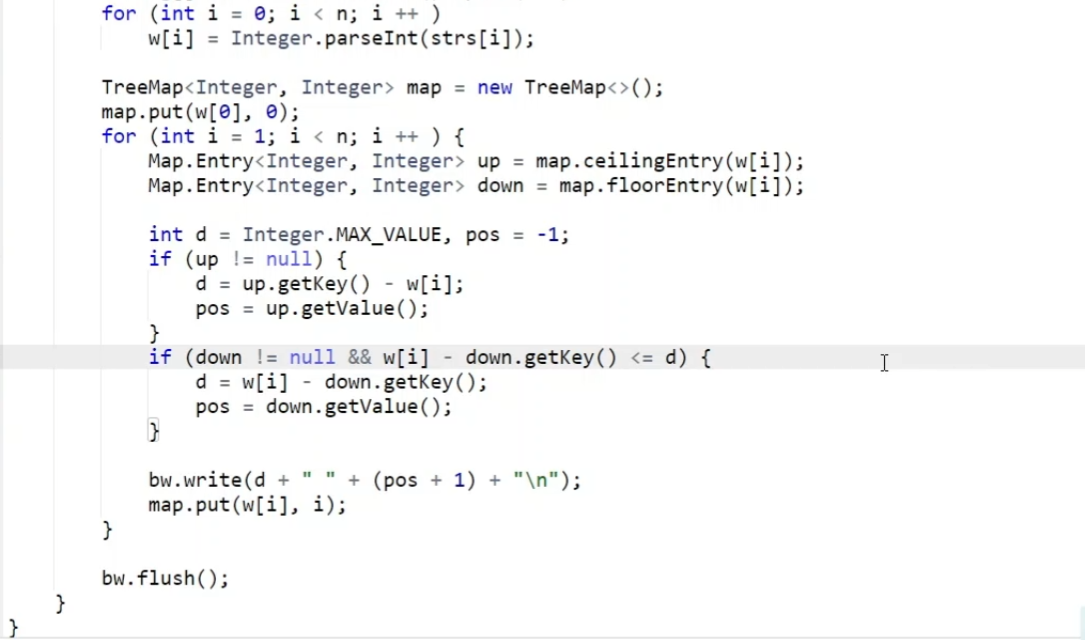
8.6.7 邻值查找

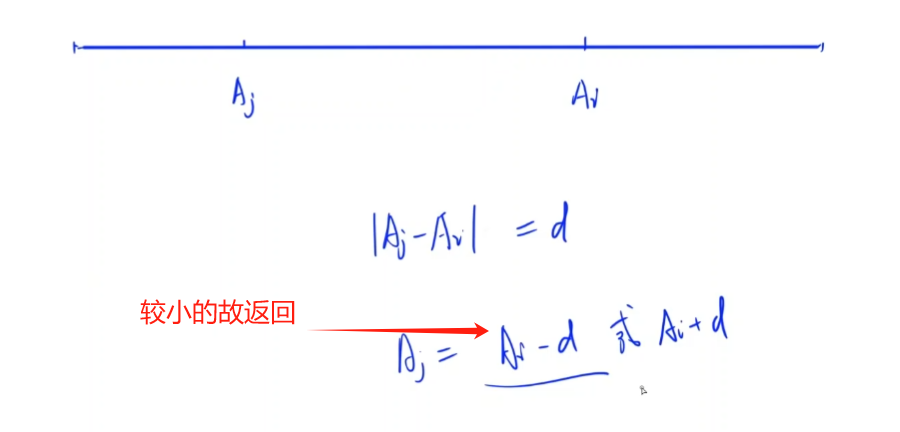
- 找所有
>Ai的数当中最小的一个,即最接近Ai的 - 找所有
<Ai的数当中最大的一个
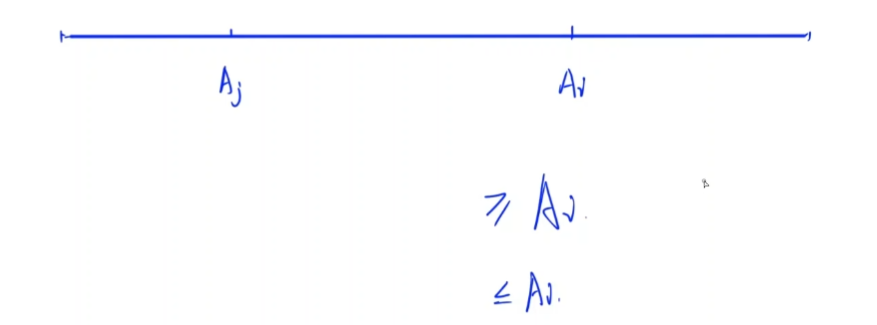
- 故考虑
Set,又由于本题要返回坐标,故选择也有类似api的Map
- 题解
8.6.8 二进制中1的个数
负数用补码来存,负数中会有会多个1

左移<< 乘2 右移>>除2


也可移动若干位

- 题解
右移若干位 与(&)上1
000...1 前面所有数与0都会变成0,最后一位若是0,与1则为0;最后一位若是1,与1则为1