Spring IOC 初始化刷新流程
Spring Web 环境下(存在父子容器),注解驱动容器实例为:AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext,XML 配置驱动容器实例为:XmlWebApplicationContext
SpringBoot Web 环境下容器实例为(单一容器):AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
一、调试环境
只是研究 IOC 启动刷新流程,其实不管什么方式启动 IOC,都是用的一样的代码(一个父类,主要启动流程在这个父类里)
非 Web 环境:https://gitee.com/jhxxb/MySpringBoot/tree/master/Spring-Base/src/test/java
Web 环境:https://gitee.com/jhxxb/MySpringBoot/tree/master/Spring-Base-Web/mvc-ssm-annotation
图中这两个类,是非 web 环境下注解驱动启动和 xml 配置启动的实例类,可以看到它们有共同的父类 AbstractApplicationContext
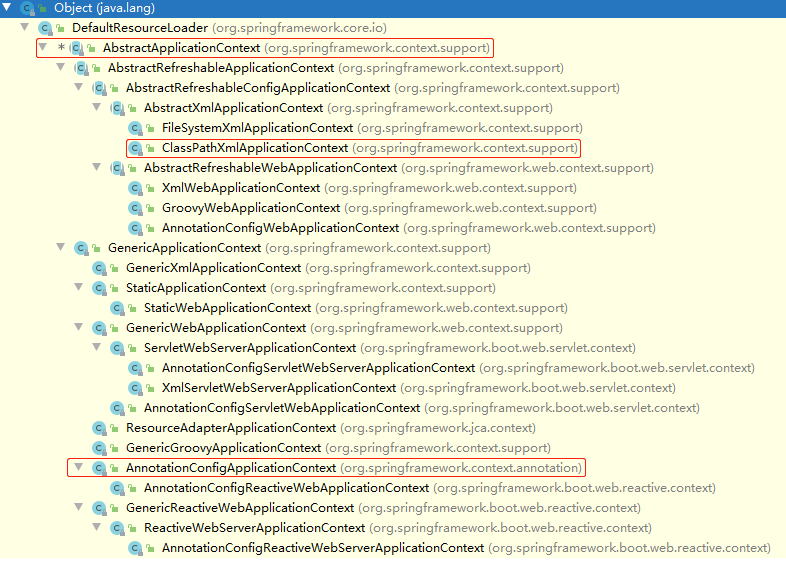
其中 StaticApplicationContext 一般用于测试,几乎不使用
再看 AbstractApplicationContext 的接口
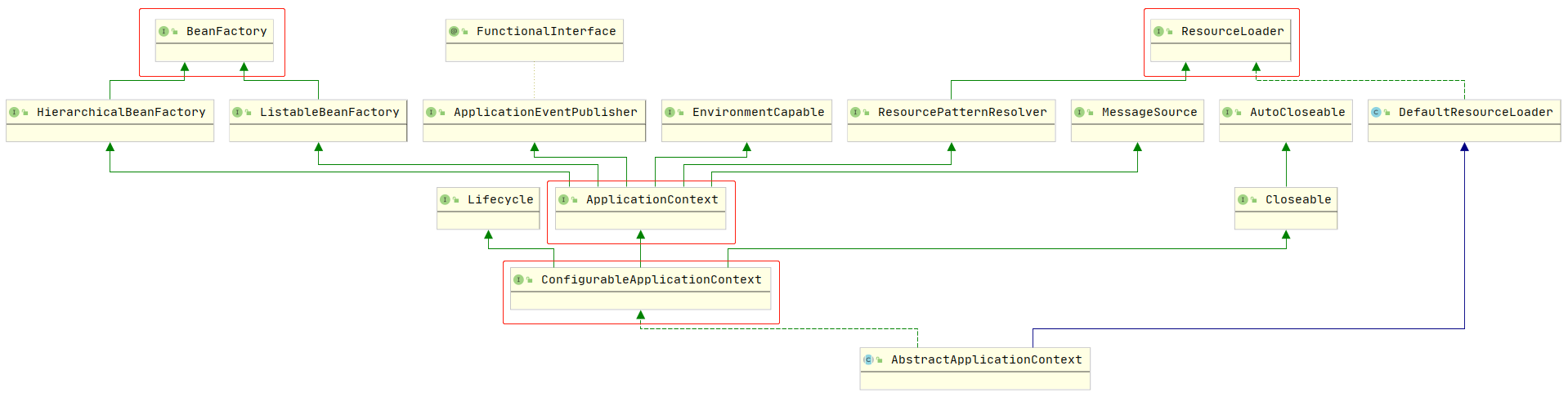
refresh() 方法所有的 ApplicationContext 子类都没重写,只有 AbstractApplicationContext 里有实现过(接口定义在 ConfigurableApplicationContext)
二、开始源码
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry { public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) { this(); register(componentClasses); // 把配置类(们)注册进来 refresh(); // 容器启动核心方法 } public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() { // AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 是一个读取注解的 Bean 读取器,这里将 this 传了进去。 this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); // 从上面这个构造函数可以顺便提一句:如果你仅仅是这样 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() // 容器是不会启动的(也就是不会执行refresh()的),这时候需要自己之后再手动启动容器 } @Override public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) { Assert.notEmpty(componentClasses, "At least one component class must be specified"); this.reader.register(componentClasses); }
refresh()
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext { @Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. // 容器刷新前的准备,设置上下文状态,获取属性,验证必要的属性等 prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. // 获取新的 beanFactory,销毁原有 beanFactory、为每个 bean 生成 BeanDefinition 等。注意,此处是获取新的,销毁旧的,这就是刷新的意义 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. // 配置标准的 beanFactory,设置 ClassLoader,设置 SpEL 表达式解析器等 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. // 模板方法,允许在子类中对 beanFactory 进行后置处理。 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. // 实例化并调用所有注册的 beanFactory 后置处理器(实现接口 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 bean)。 // 在 beanFactory 标准初始化之后执行 例如:PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(处理占位符) invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. // 实例化和注册 beanFactory 中扩展了 BeanPostProcessor 的 bean。 // 例如: // AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理被 @Autowired 注解修饰的 bean 并注入) // RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理被 @Required 注解修饰的方法) // CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理 @PreDestroy、@PostConstruct、@Resource 等多个注解的作用)等。 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. // 初始化国际化工具类 MessageSource initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. // 初始化事件广播器 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. // 模板方法,在容器刷新的时候可以自定义逻辑(子类自己去实现逻辑),不同的 Spring 容器做不同的事情 onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. // 注册监听器,并且广播 early application events,也就是早期的事件 registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. // 非常重要。。。实例化所有剩余的(非懒加载)单例 Bean。(也就是我们自己定义的那些 Bean 们) // 比如 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法中根据各种注解解析出来的类,在这个时候都会被初始化 扫描的 @Bean 之类的 // 实例化的过程各种 BeanPostProcessor 开始起作用~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. // refresh 做完之后需要做的其他事情 // 清除上下文资源缓存(如扫描中的 ASM 元数据) // 初始化上下文的生命周期处理器,并刷新(找出 Spring 容器中实现了 Lifecycle 接口的 bean 并执行 start() 方法)。 // 发布 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件告知对应的 ApplicationListener 进行响应的操作 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. // 如果刷新失败那么就会将已经创建好的单例 Bean 销毁掉 destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. // 重置 context 的活动状态 告知是失败的 cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. // 抛出异常 throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... // 失败与否,都会重置 Spring 内核的缓存。因为可能不再需要 metadata 给单例 Bean 了 resetCommonCaches(); } } }
三、具体步骤
一、prepareRefresh()
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13650829.html
二、obtainFreshBeanFactory()
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13950058.html
三、prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13953664.html
四、postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13953816.html
五、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13955154.html
六、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13957928.html
七八九十、initMessageSource()、initApplicationEventMulticaster()、onRefresh()、registerListeners()
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13960012.html
十一、finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13960276.html
十二、finishRefresh()
https://www.cnblogs.com/jhxxb/p/13985589.html
https://blog.csdn.net/f641385712/article/details/88041409
https://blog.csdn.net/f641385712/article/details/88118288
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html#spring-core



