3.2 Hive 基本操作(Hadoop3.0)
3.2 Hive 基本操作(Hadoop3.0)
【实验目的】
1.了解Hive的基本操作
2.了解Hive的外部表与普通表的区别
【实验原理】
Hive定义了一套自己的SQL,简称HQL,它与关系型数据库的SQL略有不同,但支持了绝大多数的语句如DDL、DML以及常见的聚合函数、连接查询、条件查询。
DDL操作(数据定义语言)包括:Create、Alter、Show、Drop等。
(1)create database- 创建新数据库
(2)alter database - 修改数据库
(3)drop database - 删除数据库
(4)create table - 创建新表
(5)alter table - 变更(改变)数据库表
(6)drop table - 删除表
(7)create index - 创建索引(搜索键)
(8)drop index - 删除索引
(9)show table - 查看表
DML操作(数据操作语言)包括:Load 、Insert、Update、Delete、Merge。
(1)load data - 加载数据
①insert into - 插入数据
②insert overwrite - 覆盖数据(insert ... values从Hive 0.14开始可用。)
(2)update table - 更新表(update在Hive 0.14开始可用,并且只能在支持ACID的表上执行)
(3)delete from table where id = 1; - 删除表中ID等于1的数据(delete在Hive 0.14开始可用,并且只能在支持ACID的表上执行)
(4)merge - 合并(MERGE在Hive 2.2开始可用,并且只能在支持ACID的表上执行)
注意:频繁的update和delete操作已经违背了Hive的初衷。不到万不得已的情况,还是使用增量添加的方式最好。
【实验环境】
AnolisOS8.8
Java 1.8.0
Hadoop-3.0.0
Eclipse-JEE 2022.03
HBase 1.4.10
mysql-8.0.26
Pycharm
apache-hive-2.3.5
【实验内容】
1.数据库的创建与删除。
2.表的创建、修改、删除。
3.表中数据的导入导出。
【实验步骤】
一、实验环境准备
切换到vmuser用户下,密码(vm123456)
su vmuser
1.首先在Linux本地新建/data/hive2目录。
mkdir -p /data/hive2
2.切换到/data/hive2目录下,使用wget命令,下载cat_group和goods文件。
cd /data/hive2
wget http://hive2/cat_group
wget http://hive2/goods
3.切换到/apps/hadoop/sbin目录下,启动Hadoop
cd /apps/hadoop/sbin
./start-all.sh
输入jps检查Hadoop相关进程
jps
4.开启Hive,首先,需要保证MySQL启动。执行以下命令,查看MySQL的运行状态。(sudo命令密码:vmuser)
sudo systemctl status mysqld
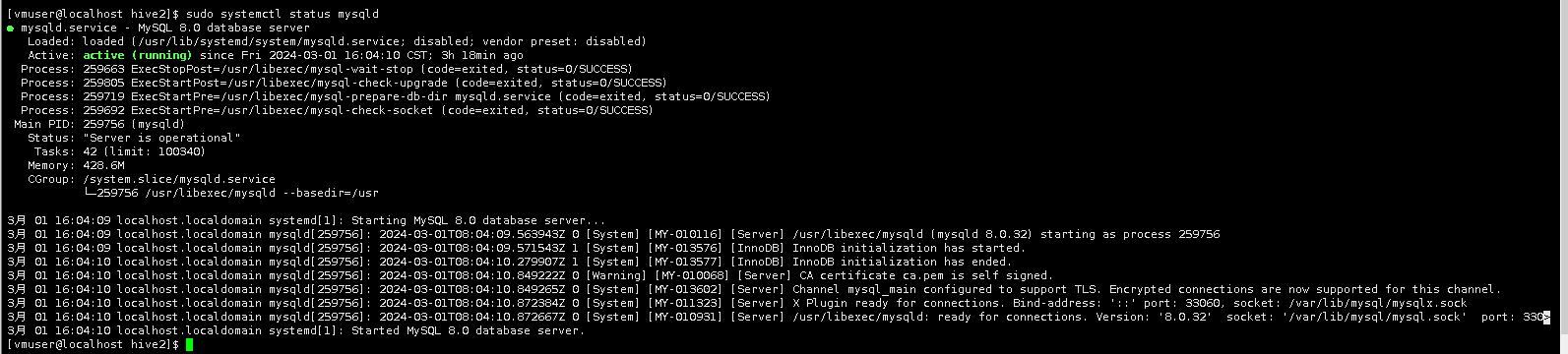
按“q”退出
输出显示MySQL已经启动。
然后切换到/apps/hive/bin目录下,开启Hive。
cd /apps/hive/bin
./hive

二、Hive数据仓库的操作
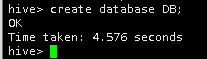
1.在Hive中创建一个数据仓库,名为DB。
create database DB;
2.以上简单创建了一个DB库,但是这条sql可以更进一步的优化,我们可以加上if not exists。
create database if not exists DB;
解析:在创建库时,应避免新建的库名与已有库名重复。如果库名重复将会报出以下错误(如下,在已有DB库的前提下,再次创建了DB库)。
错误提示数据仓库DB已经存在, 那么加入的if not exists就起了作用,如下(在已有DB库的前提下,再次创建DB库,提示成功不会报错)
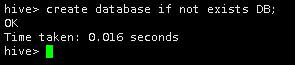
加入if not exists的意思是如果没有DB库就创建,如果已有就不再创建。
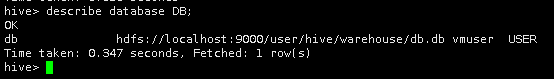
3.查看数据仓库DB的信息及路径。
describe database DB;
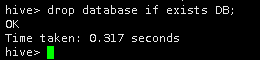
4.删除名为DB的数据仓库。
drop database if exists DB;
三、Hive数据表的操作
Hive的数据表分为两种:内部表和外部表。
Hive创建内部表时,会将数据移动到数据仓库指向的路径;若创建外部表,仅记录数据所在的路径, 不对数据的位置做任何改变。在删除表的时候,内部表的元数据和数据会被一起删除, 而外部表只删除元数据,不删除数据。这样外部表相对来说更加安全些,数据组织也更加灵活,方便共享源数据,生产中常使用外部表。
下面详细介绍对表操作的命令及使用方法:
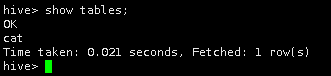
即将创建的表,表名不能和已有表名重复,否则会报错,现在我们show tables一下,查看已存在的表。
show tables;
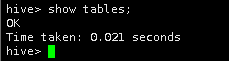
现在库中没有表。
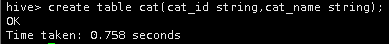
1创建一个名为cat的内部表,有两个字段为cat_id和cat_name,字符类型为string。
create table cat(cat_id string,cat_name string);
查看是否创建成功。
show tables;
下面我们再次创建一个与刚才表名相同的表,看一下报错。
create table cat(cat_id string,cat_name string);

查看是否创建成功。
show tables;

外部表较内部表而言,只是在create后加了一个external。
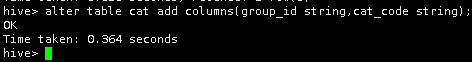
3.修改cat表的表结构。对cat表添加两个字段group_id和cat_code。
alter table cat add columns(group_id string,cat_code string);
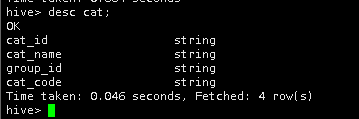
使用desc命令查看一下加完字段后的cat表结构 。
desc cat;
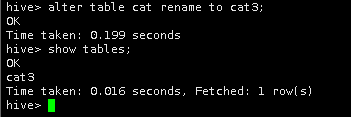
4.修改cat2表的表名。把cat2表重命名为cat3,并查看操作结果 。
alter table cat rename to cat3;
show tables;
这个命令可以让用户为表更名,数据所在的位置和分区名并不改变。
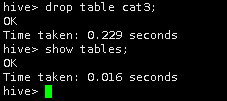
5.删除名为cat3的表并查看。
drop table cat3;
show tables;
6.创建与已知表相同结构的表,创建一个与cat表结构相同的表,名为cat4,这里要用到like关键字。
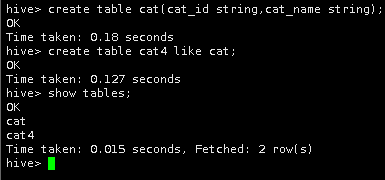
create table cat(cat_id string,cat_name string);
create table cat4 like cat;
show tables;
四、Hive中数据的导入导出
以下介绍四种常见的数据导入方式:
1.从本地文件系统中导入数据到Hive表。
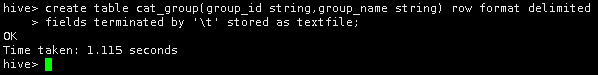
首先,在Hive中创建一个cat_group表,包含group_id和group_name两个字段,字符类型为string,以“\t”为分隔符
create table cat_group(group_id string,group_name string) row format delimited
fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile;
[row format delimited]关键字,是用来设置创建的表在加载数据的时候,支持的列分隔符。
[stored as textfile]关键字,是用来设置加载数据的数据类型,默认是TEXTFILE,如果文件数据是纯文本,就是使用 [stored as textfile],然后从本地直接拷贝到HDFS上,Hive直接可以识别数据。
查看结果。
show tables;

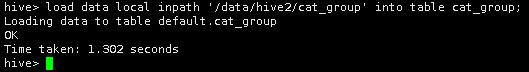
然后,将Linux本地/data/hive2目录下的cat_group文件导入到Hive中的cat_group表中。
load data local inpath '/data/hive2/cat_group' into table cat_group;
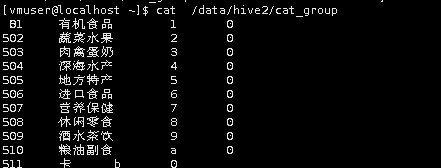
通过select语句查看cat_group表中是否成功导入数据,由于数据量大,使用limit关键字限制输出10条记录。
select * from cat_group limit 10;
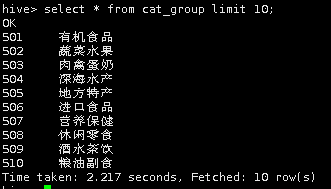
导入成功。
2.将HDFS上的数据导入到Hive中。
首先,另外开启一个操作窗口,切换到vmuser用户,密码vm123456
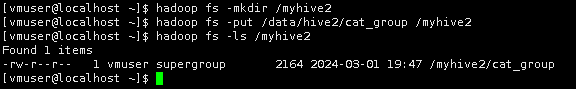
在HDFS上创建/myhive2目录。
hadoop fs -mkdir /myhive2
然后,将本地/data/hive2/下的cat_group表上传到HDFS的/myhive2上,并查看是否创建成功。
hadoop fs -put /data/hive2/cat_group /myhive2
hadoop fs -ls /myhive2
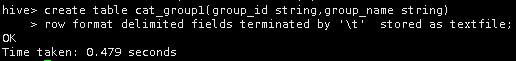
接着,在Hive中创建名为cat_group1的表,创表语句如下。
create table cat_group1(group_id string,group_name string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile;
最后,将HDFS下/myhive2中的表cat_group导入到Hive中的cat_group1表中 ,并查看结果。
load data inpath '/myhive2/cat_group' into table cat_group1;
select * from cat_group1 limit 10;
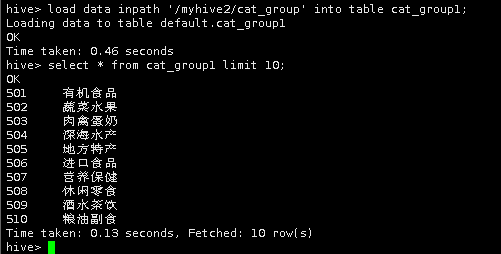
导入成功。
提示:HDFS中数据导入到Hive中与本地数据导入到hive中的区别是load data后少了local。
3.从别的表中查询出相应的数据并导入到Hive中。
首先在Hive中创建一个名为cat_group2的表。
create table cat_group2(group_id string,group_name string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile;
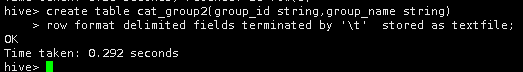
用下面两种方式将cat_group1表中的数据导入到cat_group2表中。
insert into table cat_group2 select * from cat_group1;
或者
insert overwrite table cat_group2 select * from cat_group1;
(insert overwrite 会覆盖数据)。

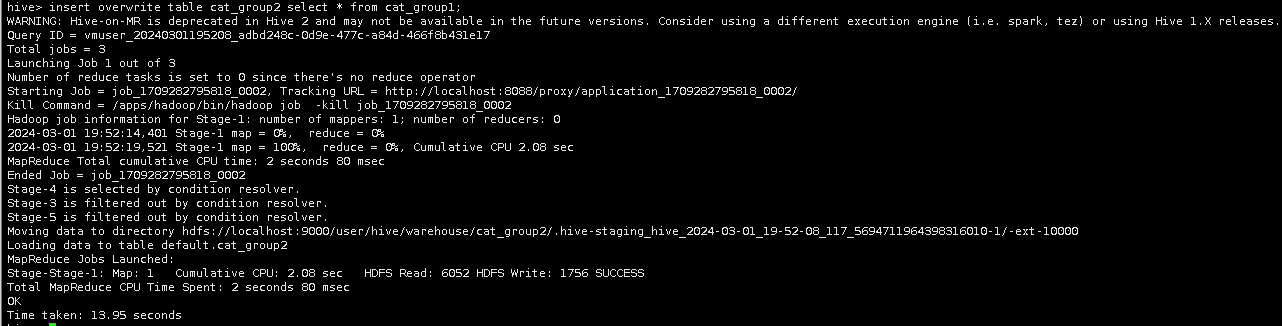
导入完成后,用select语句查询cat_group2表。
select * from cat_group2 limit 10;

4.在创建表的时候从别的表中查询出相应数据并插入到所创建的表中。
Hive中创建表cat_group3并直接从cat_group2中获得数据。
create table cat_group3 as select * from cat_group2;
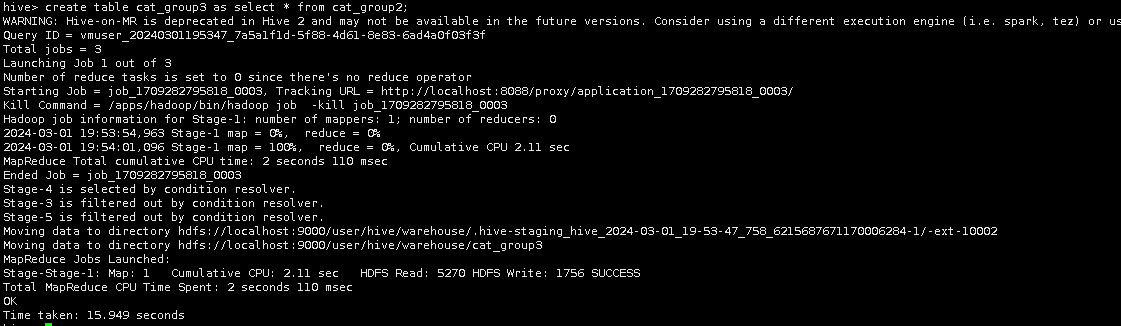
创建并导入完成,用select语句查询实验结果。
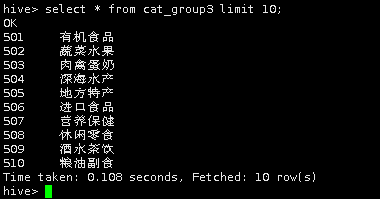
select * from cat_group3 limit 10;
五、三种常见的数据导出方式
1.导出到本地文件系统。
首先,切换到vmuser用户,密码vm123456
将Hive中的cat_group表导出到本地文件系统/data/hive2/out中。
注意:方法和导入数据到Hive不一样,不能用insert into来将数据导出。
insert overwrite local directory '/data/hive2/out' select * from cat_group;
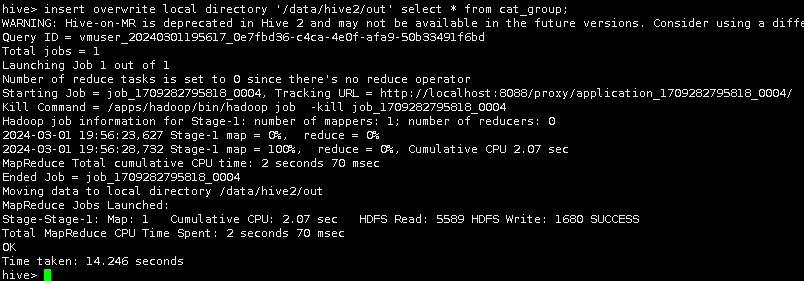
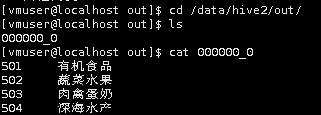
导出完成后,在Linux本地切换到/data/hive2/out目录,通过cat命令查询导出文件的内容。
cd /data/hive2/out
ls
cat 000000_0
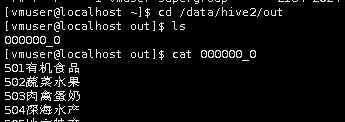
通过上图可以看到导出的数据,字段之间没有分割开,所以我们使用下面的方式,将输出字段以“\t”键分割。
insert overwrite local directory '/data/hive2/out' select group_id,concat('\t',group_name) from cat_group;
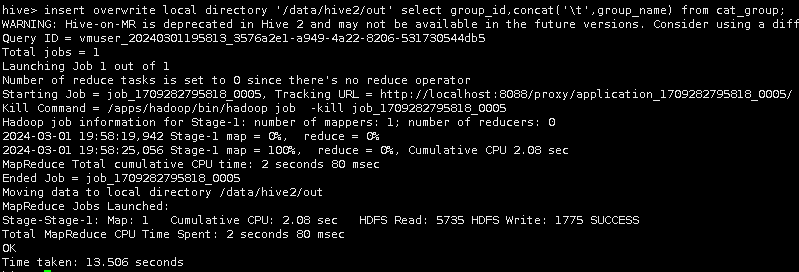
通过cat命令查询/data/hive2/out目录下的导出文件。
cd /data/hive2/out/
ls
cat 000000_0
2.Hive中数据导出到HDFS中
在HDFS上创建/myhive2/out目录。
hadoop fs -mkdir -p /myhive2/out
并将Hive中的表cat_group中的数据导入到HDFS的/myhive2/out目录里。
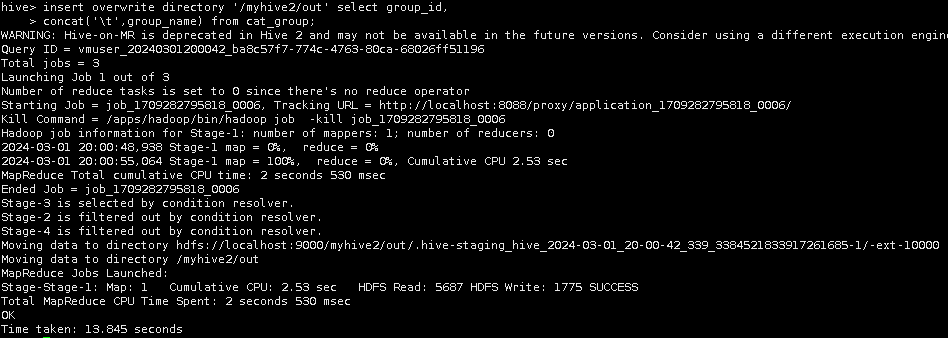
导入完成后,在HDFS上的/myhive2/out目录下查看结果。
hadoop fs -ls /myhive2/out
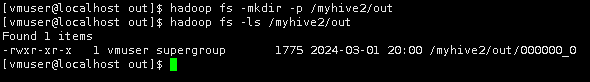
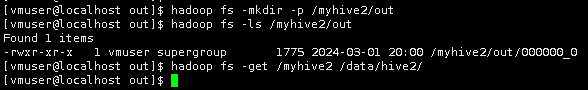
将HDFS上的输出结果下载到本地。
hadoop fs -get /myhive2 /data/hive2/
3.导出到Hive的另一个表中。
将Hive中表cat_group中的数据导入到cat_group4中(两表字段及字符类型相同)。
首先在Hive中创建一个表cat_group4,有group_id和group_name两个字段,字符类型为string,以‘\t’为分隔符。
create table cat_group4(group_id string,group_name string) row format delimited
fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile;
然后将cat_group中的数据导入到cat_group4中。
insert into table cat_group4 select * from cat_group;
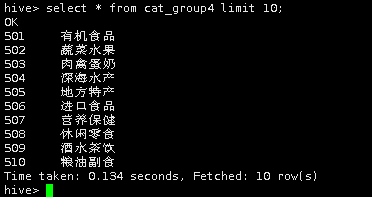
导入完成后,查看cat_group4表中数据。
select * from cat_group4 limit 10;
六、Hive分区表的操作
Hive中创建分区表没有什么复杂的分区类型(范围分区、列表分区、hash 分区,混合分区等)。分区列也不是表中的一个实际的字段,而是一个或者多个伪列。意思是说,在表的数据文件中实际并不保存分区列的信息与数据。
1创建表分区,在Hive中创建一个分区表goods,包含goods_id和goods_status两个字段,字符类型为string,分区为cat_id,字符类型为string,以“\t“为分隔符。
create table goods(goods_id string,goods_status string) partitioned by (cat_id string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
查看表goods表结构。
desc goods;
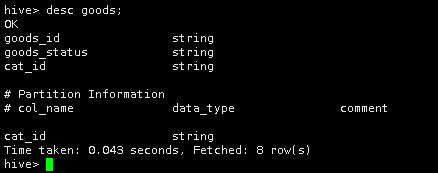
这样一个分区表就建好了。
2.向分区表插入数据,将本地/data/hive2下的表goods中数据,插入到分区表goods中。
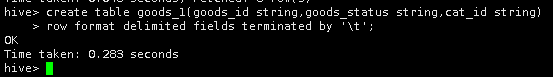
首先,在Hive中创建一个非分区表goods_1表,用于存储本地/data/hive2下的表goods中数据。
create table goods_1(goods_id string,goods_status string,cat_id string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
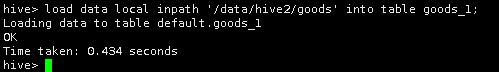
将本地/data/hive2下的表goods中数据导入到Hive中的goods_1表中。
load data local inpath '/data/hive2/goods' into table goods_1;
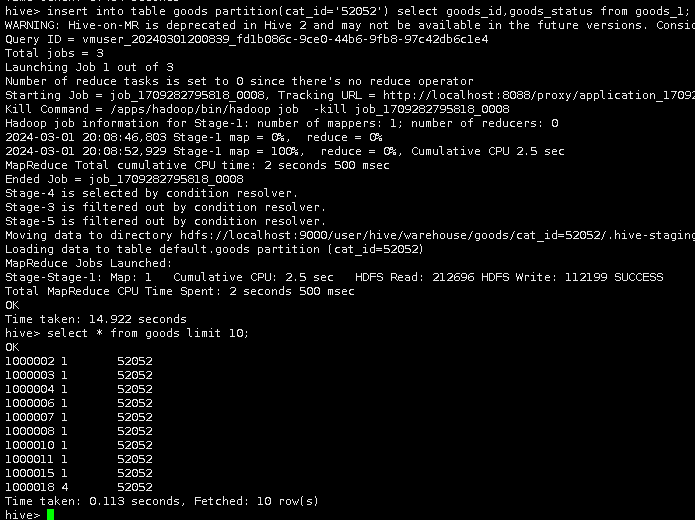
再将表goods_1中的数据导入到分区表goods中。
insert into table goods partition(cat_id='52052') select goods_id,goods_status from goods_1;
插入数据完成后,用select语句查看实验结果。
select * from goods limit 10;
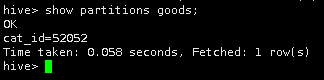
4.查看表goods中的分区。
show partitions goods;
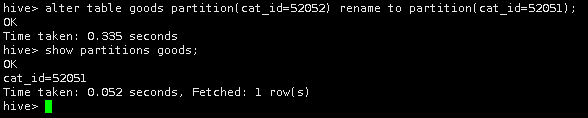
5.修改表分区,将分区表goods中的分区列cat_id=52052改为cat_id=52051,并查看修改后的分区名。
alter table goods partition(cat_id=52052) rename to partition(cat_id=52051);
show partitions goods;
6.删除表分区。
在删除goods分区表之前,先将goods表备份出一个goods_2表。
create table goods_2(goods_id string,goods_status string) partitioned by (cat_id string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
insert into table goods_2 partition(cat_id='52052') select goods_id,goods_status from goods_1;
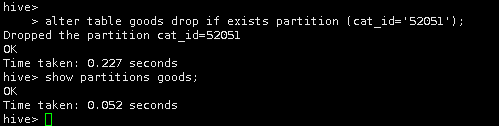
删除goods表中的cat_id分区,并查看操作结果。
alter table goods drop if exists partition (cat_id='52051');
show partitions goods;
七、Hive桶的操作
1.桶的定义及用途
Hive还可以把表或分区,组织成桶。将表或分区组织成桶有以下几个目的:
(1)是为使取样更高效。在处理大规模的数据集时,在开发、测试阶段将所有的数据全部处理一遍可能不太现实,如果能在数据集的一小部分数据上试运行查询,会带来很多方便。
(2)是为了获得更好的查询处理效率。
桶为表提供了额外的结构,Hive在处理某些查询时利用这个结构,能够有效地提高查询效率。
具体而言,连接两个在(包含连接列的)相同列上划分了桶的表,可以使用Map端连接(Map-side join)高效的实现。比如JOIN操作。对于JOIN操作两个表有一个相同的列,如果对这两个表都进行了桶操作。那么将保存相同列值的桶进行JOIN操作就可以,可以大大较少JOIN的数据量。在建立桶之前,需要设置hive.enforce.bucketing属性为true,使得Hive能识别桶。
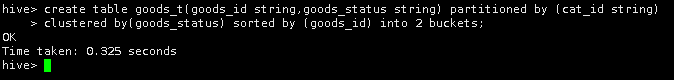
2.创建桶
创建一个名为goods_t的表,包含两个字段goods_id和goods_status,字符类型都为string,按cat_id string做分区,按goods_status列聚类和goods_id列排序,划分成两个桶
create table goods_t(goods_id string,goods_status string) partitioned by (cat_id string)
clustered by(goods_status) sorted by (goods_id) into 2 buckets;
设置环境变量
set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
3.向goods_t表中插入goods_2表中的数据。
from goods_2 insert overwrite table goods_t partition(cat_id='52063') select goods_id,goods_status;
查看结果
select * from goods_t tablesample(bucket 1 out of 2 on goods_id);
tablesample 是抽样语句,语法如下:
tablesample(bucket x out of y)
其中,y必须是table总bucket数的倍数或者因子。hive根据y的大小,决定抽样的比例。例如,table总共分了64份,当y=32时,抽取(64/32=)2个bucket的数据,当y=128时,抽取(64/128=)1/2个bucket的数据。x表示从哪个bucket开始抽取。例如,table总bucket数为32,tablesample(bucket 3 out of 16),表示总共抽取(32/16=)2个bucket的数据,分别为第3个bucket和第(3+16=)19个bucket的数据。
至此,实验结束!


