java_NIO
1.Java_第一季_JAVASE_自增、单例模式、类与实例初始化过程、方法参数传递机制、递归和迭代、成员变量与局部变量2.Java_第一季_SSM_Spring Bean的作用域、Spring事务的传播行为、Spring MVC的执行流程、3.Java_第一季_java高级_Redis持久化、MySql何时建立索引4.java_JUC、volatile5.java_CAS6.java_阻塞队列(FIFO先进先出)7.JUC下countDownLatch、CyclicBarrier、Semaphore以及枚举的常见使用方法8.java_锁9.java_集合不安全10.Spring循环依赖11.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer---AQS12.LockSuport13.java_线程池7大参数_底层运行原理14.java_线程池三个常用方式15.Java_Callable<V>的基本使用16.java_锁_synchronized与Lock的区别17.java_强、软、弱、虚四大引用18.java_OOM19.JAVA-interview
20.java_NIO
21.java_JVM之GC22.java_JVM23.单例模式设计24.netty服务端、客户端简单搭建25.java使用webSocket与前端通讯26.java串口通讯27.用Java读取文件文字并语音播报28.Proguard-混淆29.Spring Security30.MQ31.spring相关面试题32.执行jar包33.Spring34.SpringBoot数据访问35.Java Stream(流)基本使用36.java集合工具类 Collections基本使用37.LocalDateTime、LocalDate、Date、String相互转化38.java8新特性39.java设计模式40.java springboot使用定时器41.MQ根据正常队列、死信队列来实现延迟队列的场景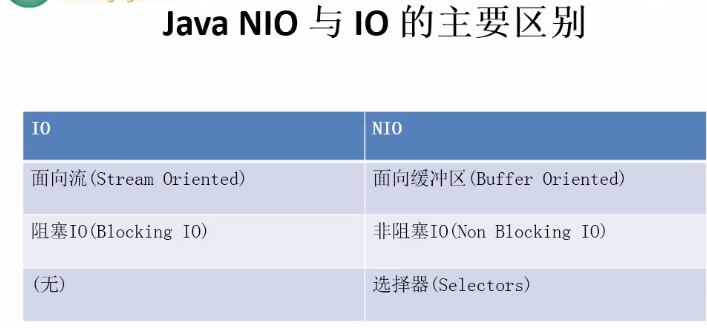

/** * 缓冲区(Buffer):在java NIO 中负责存储数据;缓冲区就是数组,存储不同类型的数据; * * 根据不同的类型(boolean类型除外),提供了相应类型的缓冲区; * ByteBuffer * CharBuffer * ShortBuffer * IntBuffer * LongBuffer * FloatBuffer * DoubleBuffer * * 上述缓冲区的管理方式几乎一致,都是使用 allocate();获取缓冲区 * * 缓冲区中存储数据的核心 * put();存入数据到缓存区中 * get();获取缓冲区中的数据 * * 缓冲区的四大核心属性: * capacity:容量、表示缓冲区中最大存储数据的容量、一旦声明不能更改; * limit:界限、表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小;(limit 后数据不能进行读写); * position:位置、表示缓冲区中正在操作数据的位置; * * mark:标记、表示记录当前 position 的位置;可以通过 reset() 将恢复 position 到 mark记录的位置; * * mark <= position <= limit <= capacity */ public class TestBuffer { public static void main(String[] args) { test01(); } public static void test01(){ //一个大小为 5 个字节的字符串 String str = "abcde"; //1、分配一个指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println("--------allocate()--------"); //查看当前缓冲区、正在操作数据的位置(当前缓冲区未写入数据、因此 position指向第一个位置、也就是起始位置、下标为 0) System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //查看当前缓冲区、可操作数据最大位置(当前是写入模式、最多可以写入 1024 字节) System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //查看当前缓冲区、容量(当前缓冲区容量为 1024 字节) System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); //2、利用 put() 将数据存入到缓冲区 System.out.println("---------put()------------"); //将字符串转换为字节并存储到缓冲区 byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes()); //当前缓冲区存入了5个字节、下标 0-4、因此 position 指向下标为 5; System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //当前缓冲区可存入的最大位置为 1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //当前缓冲区的容量是 1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); //3、切换到读取数据的模式 System.out.println("---------flip()------------"); byteBuffer.flip(); //当前是读取数据模式、当前 position在起始位置、下标为 0 System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //当前缓冲区存入了 5字节、下标 0-4、limit指向 下标 5(表示当前缓冲区最多可操作 5个字节、下标0-4) System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //当前缓冲区容量为 1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); //4、利用 get() 读取缓冲区中的数据 System.out.println("---------get()------------"); //创建一个字节数组、5 个长度 byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.limit()]; //获取缓冲区的所有数据、并存入到字节数组中 byteBuffer.get(bytes); //创建一个字符串(当前字节数组从 下标 0开始、5个长度)并输出 System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,bytes.length)); //当前取出了所以数据、下标 0-4、因此 position指向 5 System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //当前可操作的数据是 5个长度 System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //容量 1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); //5、利用 rewind() 可重复读取缓冲区中的数据 System.out.println("---------rewind()------------"); //将当前缓冲区的 position 置为起始位置处 下标 0 //并且将 mark 置为默认值 -1 byteBuffer.rewind(); //0 System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //5 System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); System.out.println("---------mark()------------"); //6、利用 mark()记录当前 position的位置 byte[] byteArr = new byte[10]; //从 byteBuffer缓冲区中取出 2个元素、下标 从 0开始 即 0、1 byteBuffer.get(byteArr,0,2); //输出 System.out.println(new String(byteArr,0,10)); //当前 position下标 指向 2 System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //当前 limit下标 指向 5 System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //容量 1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); //使用 mark()记录当前 position byteBuffer.mark(); //当前从缓冲区再取出一个字节、若当前 position指向 limit(最大可操作数量)、再次取出数据时会抛出异常 byteBuffer.get(); //当前 position下标 指向 3 System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //当前 limit下标 指向 5 System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //容量 1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); //使用reset()复原 position、基于 mark的记录、如果 mark 为默认值 -1、则会抛出异常 byteBuffer.reset(); //当前 position下标 指向 2 System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); //当前 limit下标 指向 5 System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); //容量 1024 System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); System.out.println("----------------------"); //判断缓冲区是否还有剩余数据 if (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()){ //返回缓冲区剩余数据的数量 System.out.println(byteBuffer.remaining()); } //10、利用 clear() 清空缓冲区、缓冲区中的数据依然存在、处于一个 ”被遗忘“的状态; System.out.println("---------clear()------------"); //将 position 置为起始位置处 下标 0 //将 limit 置为 容量值 capacity //并且将 mark 置为默认值 -1 byteBuffer.clear(); System.out.println(byteBuffer.position()); System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit()); System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity()); } }
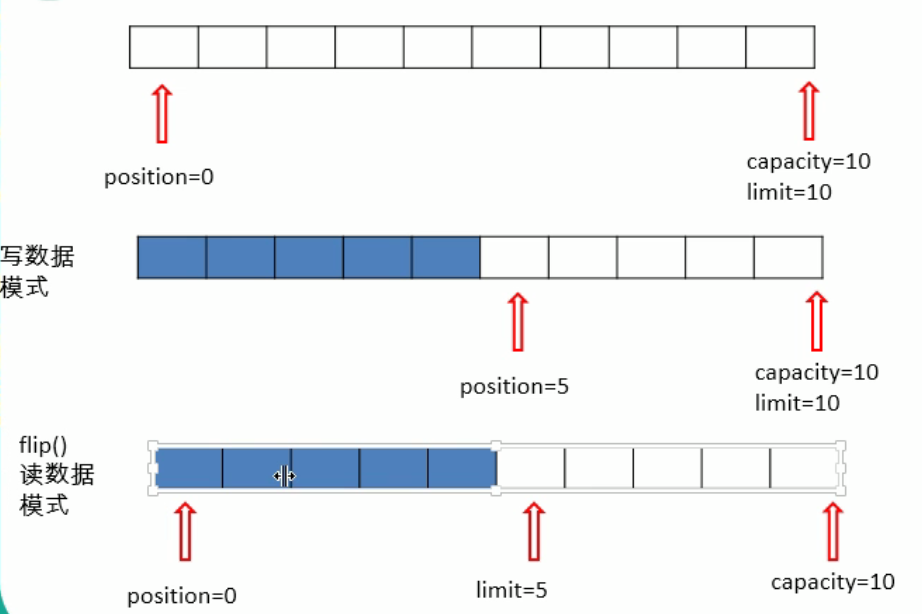
直接缓冲区和非直接缓冲区
非直接缓冲区:通过 allocate(int size);分配的缓冲区、将缓冲区建立在 JVM 内存中;
直接缓冲区:通过 allocateDirect(int size);分配的缓冲区、将缓冲区建立在操作系统的物理内存之中;可以提高效率
public static void test02(){ //创建一个非直接缓冲区 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //byteBuffer.isDirect() 返回true:直接缓冲区、false:非直接缓冲区 System.out.println(byteBuffer.isDirect());//false ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024); System.out.println(byteBuffer2.isDirect());//true }


通道之间的数据传输与内存映射文件
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.CharBuffer; import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.*; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder; import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import java.util.SortedMap; /** * 一、Channel:通道、用于源节点与目标节点的连接、在 Java NIO 中负责缓冲区数据的传输、Channel本身不存储数据、因此需要配合缓冲区进行传输; * <p> * 二、通道的主要实现类: * java.nio.channels.Channel接口: * FileChannel * SocketChannel * ServerSocketChannel * DatagramChannel * <p> * 三、获取通道 * 1、在java中针对通道的类提供了 getChannels() 方法 * 本地 IO * FileInputStream/FileOutStream * RandomAccessFile * <p> * 网络 IO * Socket * ServerSocket * DatagramSocket * <p> * 2、在 java中的 NIO针对各个通道提供了静态 open()方法; * 2、在 java中的 NIO的 Files工具类的 newByteChannel(); * <p> * 四、通道之间的数据传输 * transferTo() * transferFrom() * <p> * 五、分散与聚集 * 分散读取(Scattering Reads):将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中去 * 聚集写入(Gathering Writes):将多个缓冲区中的数据聚集到通道中去 * <p> * 六、字符集 Charset * 编码:字符串 -> 字节数组 * 解码:字节数组 -> 字符串 */ public class TestChannel { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { test6(); } //字符集、编码与解码 public static void test6() throws Exception { //通过名称获取字符集 Charset charsetUTF8 = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); //通过当前字符集获取一个编码器 CharsetEncoder ce = charsetUTF8.newEncoder(); //通过当前字符集获取解码器 CharsetDecoder cd = charsetUTF8.newDecoder(); //创建一个1024个长度的 字符非直接缓冲区 CharBuffer charBuffer = CharBuffer.allocate(1024); //为改字符非直接缓冲区存储数据 charBuffer.put("汪洋大海!"); //将该字符非直接缓冲区转换为读取模式 charBuffer.flip(); /** * 通过当前编码器进行编码操作(字符串 -> 字节数组) * 传入一个需要进行编码操作的字符缓冲区、返回一个字节缓冲区 */ ByteBuffer bBuf = ce.encode(charBuffer); //遍历 for (int i = 0; i < bBuf.limit(); i++) { System.out.println(bBuf.get()); } //通过当前解码器进行解码操作 //将需要进行解码操作的字节缓冲区转换成读取模式 bBuf.flip(); //传入一个需要进行解码操作的字节缓冲区、返回一个字符缓冲区 CharBuffer cBuf2 = cd.decode(bBuf); System.out.println(cBuf2.toString()); } //支持的字符集 public static void test5() { Map<String, Charset> map = Charset.availableCharsets(); Set<Map.Entry<String, Charset>> set = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry entry : set) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue()); } } //分散读取和聚集写入 public static void test4() throws Exception { /** * 创建一个随机访问文件 * rw:读写模式 */ RandomAccessFile raf1 = new RandomAccessFile("d://分散读取.txt", "rw"); //获取通道 FileChannel channel1 = raf1.getChannel(); //分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(100); ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); ByteBuffer[] bufs = {buf1, buf2}; //分散读取、传入一个 ByteBuffer数组 //将通道中的数据分散读取到 bufs数组中去 channel1.read(bufs); for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bufs) { //将 bufs数组中的 buf缓冲区切换到读取模式 byteBuffer.flip(); } //将 bufs数组中的缓冲区转换重字符串打印到控制台 System.out.println(new String(bufs[0].array(), 0, bufs[0].limit())); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------"); System.out.println(new String(bufs[1].array(), 0, bufs[1].limit())); //聚集写入 RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile("d://聚集写入.txt", "rw"); //获取通道 FileChannel channel2 = raf2.getChannel(); //聚集写入、将 bufs数组中的缓冲区数据写入到通道中 channel2.write(bufs); //关闭 channel2.close(); channel1.close(); raf2.close(); raf1.close(); } //通道之间的数据传输(直接缓冲区) public static void test3() throws Exception { FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d://卡比兽.png"), StandardOpenOption.READ); FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d://憨憨.png"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //将 inChannel 通道的字节(从下标 0开始 inChannel.size()结束)传输到 outChannel通道 inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel); //关闭通道 inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); } //使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件) public static void test2() throws Exception { //创建一个通道、读取 d盘下的 卡比兽.png、StandardOpenOption.READ:读取模式(枚举) FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d://卡比兽.png"), StandardOpenOption.READ); /** * 创建一个通道、输出到 d盘下、名称为 憨憨.png; * StandardOpenOption.WRITE:写模式(枚举) * StandardOpenOption.CREATE:如果目标文件存在、则覆盖,不存在:则创建; * StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW:如果目标文件存在、则抛出异常,不存在:则创建; */ FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d://憨憨.png"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //内存映射文件 MappedByteBuffer inMapBuf = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size()); MappedByteBuffer outMapBuf = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size()); //直接对缓冲区的数据进行读写操作 byte[] dst = new byte[inMapBuf.limit()]; //将 inMapBuf 内存映射文件中的数据读取到 dst字节数组中去 inMapBuf.get(dst); //将 dst字节数组中的数据 写入到 outMapBuf 内存映射文件中去 outMapBuf.put(dst); //关闭通道 outChannel.close(); inChannel.close(); } //利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区) public static void test1() throws Exception { //创建一个文件输入流、读取 d盘下的 卡比兽.png FileInputStream fls = new FileInputStream("d://卡比兽.png"); //创建一个文件输出流、写出到 d盘下、名称为 憨憨.png FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d://憨憨.png"); //①、获取通道 FileChannel inChannel = fls.getChannel(); FileChannel outChannel = fos.getChannel(); //②、分配一个指定大小的非直接缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //③、将通道 inChannel 中的数据存入到 buf 缓冲区中( != -1:代表当前通道获取到了数据) while (inChannel.read(buf) != -1) { //将缓冲区切换到读取数据的模式 buf.flip(); //④、将缓冲区中的数据写入通道 outChannel.write(buf); //清空 buf 缓冲区 buf.clear(); } //关闭通道 outChannel.close(); inChannel.close(); //关闭流 fos.close(); fls.close(); } }
客户端与服务端交互(阻塞式)
import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; /** * 一、使用 NIO完成网络通信的三个核心 * 1、通道:Channel、负责连接; * 2、缓冲区:Buffer、负责数据的存储; * 3、选择器:Selector、是SelectableChannel的多路复用器,用于监控 SelectableChannel 的IO状况; */ public class TestBlockingClient { public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{ client(); } //客户端 public static void client() throws Exception { System.out.println("------client start------"); //1、获取通道 //获取一个Socket通道、用来向服务端发送数据、传入一个 ip地址和 端口 SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9898)); //获取一个文件通道、读取 d 盘下的 卡比兽.png、读取模式 FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d://卡比兽.png"), StandardOpenOption.READ); //2、分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //3、读取本地文件、并发送到服务器 //从 inChannel 通道中读取数据、若等于 -1则代表未读取到数据 while (inChannel.read(buf) != -1){ //将缓冲区转换成读取模式 buf.flip(); //将缓冲区的数据 sChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } //关闭连接以进行写入,而不关闭通道。 sChannel.shutdownOutput(); //接收服务端的反馈 int len = 0; while ((len = sChannel.read(buf)) != -1){ buf.flip(); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len)); } //4、关闭通道 inChannel.close(); sChannel.close(); System.out.println("------client end------"); } } class TestBlockingServer{ public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { server(); } //服务端 public static void server()throws Exception{ System.out.println("-----server start-------"); //1、获取通道 //获取一个Socket通道、用来接收客户端发送的数据 ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //将该通道绑定 9898 端口 ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); //获取客户端连接的通道 SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); //获取一个文件通道、将数据写入到 d 盘下 憨憨.png FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d://憨憨.png"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //2、分配一直指定的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //3、接收客户端的数据 //将客户端通道中的数据读取到缓冲区中 while (sChannel.read(buf) != -1){ //将缓冲区转换为读取模式 buf.flip(); //将缓冲区中的数据写入到 outChannel中 outChannel.write(buf); //清空缓冲区 buf.clear(); } //发送反馈给客户端 buf.put("服务器接收数据成功".getBytes()); buf.flip(); sChannel.write(buf); //4、关闭通道 sChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); ssChannel.close(); System.out.println("-----server end-------"); } }
客户端与服务端交互(非阻塞式)SocketChannel(TCP)
import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.*; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Scanner; /** * 非阻塞式 * SocketChannel 使用的是 TCP协议 * 一、使用 NIO完成网络通信的三个核心 * 1、通道:Channel、负责连接; * 2、缓冲区:Buffer、负责数据的存储; * 3、选择器:Selector、是SelectableChannel的多路复用器,用于监控 SelectableChannel 的IO状况; */ public class TestNonBlockClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { client(); } public static void client() throws Exception { //1、获取通道、该通道用于连接客户端与服务端 SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898)); //2、设置当前通道为非阻塞模式、false:非阻塞、true:阻塞 sChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3、分配一个指定的缓冲区大小 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //5、发送数据给服务器 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (scanner.hasNext()) { String next = scanner.nextLine(); //将数据存入到缓冲区中 buf.put((new Date().toString() + "\n" + next).getBytes()); buf.flip(); //读取缓冲区的数据并写入到 sChannel通道中 sChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } //6、关闭通道 sChannel.close(); } } class TestNonBlockServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { server(); } public static void server() throws Exception { //1、获取通道 ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2、切换到非阻塞模式 ssChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3、绑定连接 ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); //4、获取选择器 Selector selector = Selector.open(); /** * 5、将通道注册到选择器上、并且指定 “监听接收事件” * selector:选择器 * * SelectionKey的四个静态常量 * static final int OP_ACCEPT:操作集位用于插座接受操作。(接收) * static final int OP_CONNECT:用于套接字连接操作的操作集位。(连接) * static final int OP_READ:读操作的操作位。(读) * static final int OP_WRITE:写操作的操作位。(写) */ ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //6、轮询的获取选择器上已经“准备就绪”的事件 while (selector.select() > 0) { //7、获取当前选择器中所有注册的选择键(已就绪的监听事件) Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { //8、获取 “准备就绪”的事件 SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); //9、判断具体是什么事件 //如果当前是接收事件 if (sk.isAcceptable()) { //10、若 “接收就绪”,则获取客户端连接 SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); //11、将客户端通道切换成非阻塞模式 sChannel.configureBlocking(false); //12、将客户端通道注册到选择器上、并监控 “读数据” 操作 sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //如果当前是 读取事件 } else if (sk.isReadable()) { //13、获取当前选择器上 “读就绪” 状态的通道 SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel(); //分配一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //14、读取数据 int len = 0; /** * 将当前客户端通道中的数据读取到 buf 缓冲区中 * 当前若 sChannel.read(buf) == -1 :当前未读取到数据 * 当前若 sChannel.read(buf) == 0 :当前读取到了数据、数据为 “” */ while ((len = sChannel.read(buf)) > 0) { //避免当前读取的数据为 “” buf.flip(); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len)); buf.clear(); } } //15、取消选择键 iterator.remove(); } } } }
客户端与服务端交互(非阻塞式)DatagramChannel(UDP)
import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.*; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Scanner; /** * 非阻塞式 * DatagramChannel 是一个能收发 UDP 包的通道 */ public class TestNonBlockSend { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { send(); } //发送端 public static void send() throws Exception { //创建一个通道 DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); //转换为 非阻塞 模式 dc.configureBlocking(false); //创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //监听键盘信息输入 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); //如果输入了信息 while (scanner.hasNext()) { //获取输入的一行信息 String nextLine = scanner.nextLine(); //将当前输入的信息存入到缓冲区中 buf.put((new Date().toString() + "\n" + nextLine).getBytes()); //将缓冲区转换成读取模式 buf.flip(); //使用 DatagramChannel通道将信息发送指定的目的地 dc.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898)); buf.clear(); } //关闭通道 dc.close(); } } class TestNonBlockReceive { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { receive(); } //接收端 public static void receive() throws Exception { //1、获取通道 DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); //2、切换到非阻塞模式 dc.configureBlocking(false); //3、绑定连接 dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); //4、获取选择器 Selector selector = Selector.open(); //5、将通道注册到选择器上、并且指定 “读取事件” dc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //6、轮询的获取选择器上已经“准备就绪”的事件 while (selector.select() > 0) { //7、获取当前选择器中所有注册的选择键(已就绪的监听事件) Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { //8、获取 “准备就绪”的事件 SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); if (sk.isReadable()) { //9、创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //10、将当前接收的数据存入到缓冲区红 dc.receive(buf); //将缓冲区转换为读取模式 buf.flip(); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,buf.limit())); buf.clear(); } } //11、取消选择键 iterator.remove(); } } }
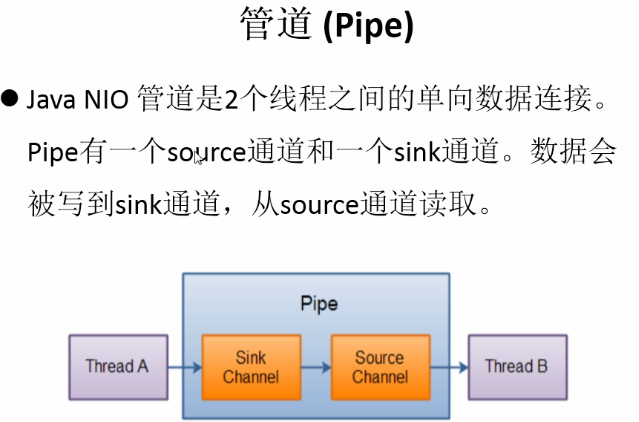
import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.Pipe; /** * java nio 管道中是两个线程之间的单向数据连接,Pipe有source、sink两个通道; * 数据会被写入到 sink通道中、从source通道中读取 */ public class TestPipe { public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { test(); } public static void test()throws Exception { //1、获取管道 Pipe pipe = Pipe.open(); //创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buf.put("通过单向管道发送数据".getBytes()); //2、将缓冲区的数据写入到管道中 //获取 Pipe 中的 sink通道 Pipe.SinkChannel sink = pipe.sink(); //将缓冲区转换为读取模式 buf.flip(); //将缓冲区的数据写入 sink 通道中 sink.write(buf); //3、读取缓冲区中的数据 //获取 Pipe 中的 source通道 Pipe.SourceChannel source = pipe.source(); buf.flip(); //将source通道中读取数据到缓冲区中 source.read(buf); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,buf.limit())); source.close(); sink.close(); } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?