word2vec中文类似词计算和聚类的使用说明及c语言源代码
word2vec相关基础知识、下载安装參考前文:word2vec词向量中文文本相似度计算
文件夹:
官网C语言下载地址:http://word2vec.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/
执行 make 编译word2vec工具:
Makefile的编译代码在makefile.txt文件里,先改名makefile.txt 为Makefile,然后在当前文件夹下运行make进行编译,生成可运行文件(编译过程中报出非常出Warning,gcc不支持pthread多线程命令。凝视就可以)。
再执行演示样例脚本:./demo-word.sh 和 ./demo-phrases.sh:
a). 从http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip 在线下载了一个文件text8 ( 一个解压后不到100M的txt文件,可自己下载并解压放到同级文件夹下)。可替换为自己的语料
b). 运行word2vec生成词向量到 vectors.bin文件里
c). 假设运行 sh demo-word.sh 训练生成vectors.bin文件后,下次能够直接调用已经训练好的词向量,如命令 ./distance vectors.bin
语料是我使用Selenium爬取的三大百科(百度、互动、维基)文本信息。当中每一个百科有100个国家。总共300个国家(0001.txt~0300.txt),然后使用Jieba工具进行中文分词处理。
下图參数源自文章:Windows下使用Word2vec继续词向量训练 - 一仅仅鸟的天空
Java推荐參考文章:word2vec使用指导
-train Result_Country.txt 表示的是输入文件是Result_Country.txt
-output vectors.bin 输出文件是vectors.bin
-cbow 0 表示不使用cbow模型,默觉得Skip-Gram模型
-size 200 每一个单词的向量维度是200
-window 8 训练的窗体大小为8,就是考虑一个词前八个和后八个词语(实际代码中另一个随机选窗体的过程,窗体大小小于等于5)
-negative 0 表示是否使用NEG方,0表示不使用
-hs 1 是否使用HS方法,0表示不使用,1表示使用HS方法
-sample 指的是採样的阈值,假设一个词语在训练样本中出现的频率越大。那么就越会被採样
-binary 1 为1指的是结果二进制存储,为0是普通存储(普通存储的时候是能够打开看到词语和相应的向量的)
除了以上命令中的參数,word2vec还有几个參数对我们比較实用比方:
-alpha 设置学习速率。默认的为0.025
–min-count 设置最低频率,默认是5。假设一个词语在文档中出现的次数小于5。那么就会丢弃
-classes 设置聚类个数,看了一下源代码用的是k-means聚类的方法
要注意-threads 20 线程数也会对结果产生影响。
命令:sh demo-word.sh
demo-word.sh 中指令:
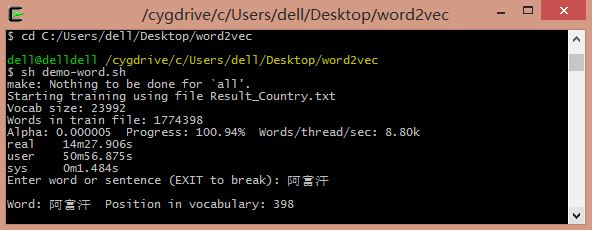
假设想要不训练调用上次训练的vectors.bin文件。则输入 ./distance vectors.bin
输入"阿富汗"输出相似次及相似距离,如"喀布尔"阿富汗首都,"坎大哈"阿富汗城市,类似中东国家"伊拉克"等。

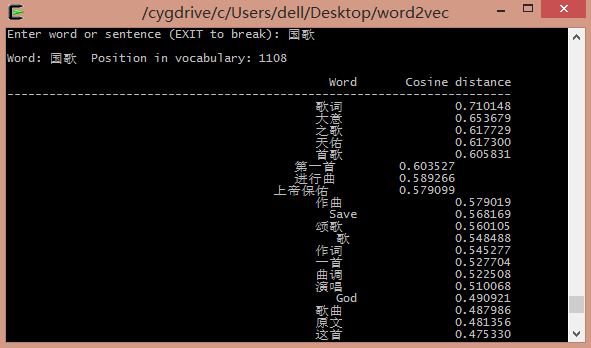
输入"国歌"输出相似词例如以下图所看到的:
不只名词能够获取相似词,动词也能够。如输入"位于",输出例如以下:

distance.c 源代码:
命令:sh demo-analogy.sh
demo-analogy.sh 中指令:
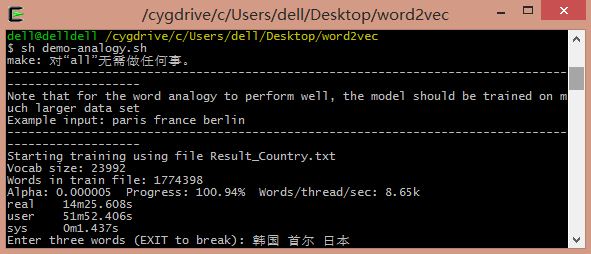
输入"韩国、首尔、日本"能够预測其首都"东京":
韩国的首都是首尔 <==> 日本的首都是东京

命令:sh demo-classes.sh
demo-classes.sh 中指令:
当中生词文件classes.txt和排序后的文件classes.sorted.txt:
聚类算法是Kmeans,类簇设置为100类。相应0~99,每类的关键词例如以下。可是怎样计算300行数据每行相应的类标。还不太清楚~
当中聚类代码见 word2vec.c 文件 void TrainModel() 函数:

demo-phrases.sh(word2phrase.c) 是就是将词语拼成短语。
希望文章对你有所帮助,尤其是正在学习word2vec基础文章的。
文件夹:
- word2vec使用说明及源代码介绍
- 1.下载地址
- 2.中文语料
- 3.參数介绍
- 4.计算相似词语
- 5.三个词预測语义语法关系
- 6.关键词聚类
1、下载地址
官网C语言下载地址:http://word2vec.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/
执行 make 编译word2vec工具:
Makefile的编译代码在makefile.txt文件里,先改名makefile.txt 为Makefile,然后在当前文件夹下运行make进行编译,生成可运行文件(编译过程中报出非常出Warning,gcc不支持pthread多线程命令。凝视就可以)。
再执行演示样例脚本:./demo-word.sh 和 ./demo-phrases.sh:
a). 从http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip 在线下载了一个文件text8 ( 一个解压后不到100M的txt文件,可自己下载并解压放到同级文件夹下)。可替换为自己的语料
b). 运行word2vec生成词向量到 vectors.bin文件里
c). 假设运行 sh demo-word.sh 训练生成vectors.bin文件后,下次能够直接调用已经训练好的词向量,如命令 ./distance vectors.bin
2、中文语料
语料是我使用Selenium爬取的三大百科(百度、互动、维基)文本信息。当中每一个百科有100个国家。总共300个国家(0001.txt~0300.txt),然后使用Jieba工具进行中文分词处理。
最后输出Result_Country.txt文件。它把全部文本合并。共300行,每行相应一个国家的分词文本信息。
3、參数介绍
下图參数源自文章:Windows下使用Word2vec继续词向量训练 - 一仅仅鸟的天空
Java推荐參考文章:word2vec使用指导
make #if [ ! -e text8 ]; then # wget http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip -O text8.gz # gzip -d text8.gz -f #fi time ./word2vec -train Result_Country.txt -output vectors.bin -cbow 1 -size 200 -window 8 -negative 25 -hs 0 -sample 1e-4 -threads 20 -binary 1 -iter 15 ./distance vectors.bin详细命令解释例如以下:
-train Result_Country.txt 表示的是输入文件是Result_Country.txt
-output vectors.bin 输出文件是vectors.bin
-cbow 0 表示不使用cbow模型,默觉得Skip-Gram模型
-size 200 每一个单词的向量维度是200
-window 8 训练的窗体大小为8,就是考虑一个词前八个和后八个词语(实际代码中另一个随机选窗体的过程,窗体大小小于等于5)
-negative 0 表示是否使用NEG方,0表示不使用
-hs 1 是否使用HS方法,0表示不使用,1表示使用HS方法
-sample 指的是採样的阈值,假设一个词语在训练样本中出现的频率越大。那么就越会被採样
-binary 1 为1指的是结果二进制存储,为0是普通存储(普通存储的时候是能够打开看到词语和相应的向量的)
除了以上命令中的參数,word2vec还有几个參数对我们比較实用比方:
-alpha 设置学习速率。默认的为0.025
–min-count 设置最低频率,默认是5。假设一个词语在文档中出现的次数小于5。那么就会丢弃
-classes 设置聚类个数,看了一下源代码用的是k-means聚类的方法
要注意-threads 20 线程数也会对结果产生影响。
4、计算相似词语
命令:sh demo-word.sh
demo-word.sh 中指令:
make #if [ ! -e text8 ]; then # wget http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip -O text8.gz # gzip -d text8.gz -f #fi time ./word2vec -train Result_Country.txt -output vectors.bin -cbow 1 -size 200 -window 8 -negative 25 -hs 0 -sample 1e-4 -threads 20 -binary 1 -iter 15 ./distance vectors.bin执行结果例如以下图所看到的:
假设想要不训练调用上次训练的vectors.bin文件。则输入 ./distance vectors.bin
输入"阿富汗"输出相似次及相似距离,如"喀布尔"阿富汗首都,"坎大哈"阿富汗城市,类似中东国家"伊拉克"等。
输入"国歌"输出相似词例如以下图所看到的:
不只名词能够获取相似词,动词也能够。如输入"位于",输出例如以下:
distance.c 源代码:
// Copyright 2013 Google Inc. All Rights Reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <malloc.h>
const long long max_size = 2000; // max length of strings
const long long N = 40; // number of closest words that will be shown
const long long max_w = 50; // max length of vocabulary entries
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
FILE *f;
char st1[max_size];
char *bestw[N];
char file_name[max_size], st[100][max_size];
float dist, len, bestd[N], vec[max_size];
long long words, size, a, b, c, d, cn, bi[100];
char ch;
float *M;
char *vocab;
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: ./distance <FILE>\nwhere FILE contains word projections in the BINARY FORMAT\n");
return 0;
}
strcpy(file_name, argv[1]);
f = fopen(file_name, "rb");
if (f == NULL) {
printf("Input file not found\n");
return -1;
}
fscanf(f, "%lld", &words);
fscanf(f, "%lld", &size);
vocab = (char *)malloc((long long)words * max_w * sizeof(char));
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestw[a] = (char *)malloc(max_size * sizeof(char));
M = (float *)malloc((long long)words * (long long)size * sizeof(float));
if (M == NULL) {
printf("Cannot allocate memory: %lld MB %lld %lld\n", (long long)words * size * sizeof(float) / 1048576, words, size);
return -1;
}
for (b = 0; b < words; b++) {
a = 0;
while (1) {
vocab[b * max_w + a] = fgetc(f);
if (feof(f) || (vocab[b * max_w + a] == ' ')) break;
if ((a < max_w) && (vocab[b * max_w + a] != '\n')) a++;
}
vocab[b * max_w + a] = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) fread(&M[a + b * size], sizeof(float), 1, f);
len = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) len += M[a + b * size] * M[a + b * size];
len = sqrt(len);
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) M[a + b * size] /= len;
}
fclose(f);
while (1) {
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestd[a] = 0;
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestw[a][0] = 0;
printf("Enter word or sentence (EXIT to break): ");
a = 0;
while (1) {
st1[a] = fgetc(stdin);
if ((st1[a] == '\n') || (a >= max_size - 1)) {
st1[a] = 0;
break;
}
a++;
}
if (!strcmp(st1, "EXIT")) break;
cn = 0;
b = 0;
c = 0;
while (1) {
st[cn][b] = st1[c];
b++;
c++;
st[cn][b] = 0;
if (st1[c] == 0) break;
if (st1[c] == ' ') {
cn++;
b = 0;
c++;
}
}
cn++;
for (a = 0; a < cn; a++) {
for (b = 0; b < words; b++) if (!strcmp(&vocab[b * max_w], st[a])) break;
if (b == words) b = -1;
bi[a] = b;
printf("\nWord: %s Position in vocabulary: %lld\n", st[a], bi[a]);
if (b == -1) {
printf("Out of dictionary word!\n");
break;
}
}
if (b == -1) continue;
printf("\n Word Cosine distance\n------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) vec[a] = 0;
for (b = 0; b < cn; b++) {
if (bi[b] == -1) continue;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) vec[a] += M[a + bi[b] * size];
}
len = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) len += vec[a] * vec[a];
len = sqrt(len);
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) vec[a] /= len;
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestd[a] = -1;
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestw[a][0] = 0;
for (c = 0; c < words; c++) {
a = 0;
for (b = 0; b < cn; b++) if (bi[b] == c) a = 1;
if (a == 1) continue;
dist = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) dist += vec[a] * M[a + c * size];
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) {
if (dist > bestd[a]) {
for (d = N - 1; d > a; d--) {
bestd[d] = bestd[d - 1];
strcpy(bestw[d], bestw[d - 1]);
}
bestd[a] = dist;
strcpy(bestw[a], &vocab[c * max_w]);
break;
}
}
}
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) printf("%50s\t\t%f\n", bestw[a], bestd[a]);
}
return 0;
}
5、三个词预測语义语法关系
命令:sh demo-analogy.sh
demo-analogy.sh 中指令:
make #if [ ! -e text8 ]; then # wget http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip -O text8.gz # gzip -d text8.gz -f #fi echo ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- echo Note that for the word analogy to perform well, the model should be trained on much larger data set echo Example input: paris france berlin echo ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- time ./word2vec -train Result_Country.txt -output vectors.bin -cbow 1 -size 200 -window 8 -negative 25 -hs 0 -sample 1e-4 -threads 20 -binary 1 -iter 15 ./word-analogy vectors.bin执行结果例如以下图所看到的:
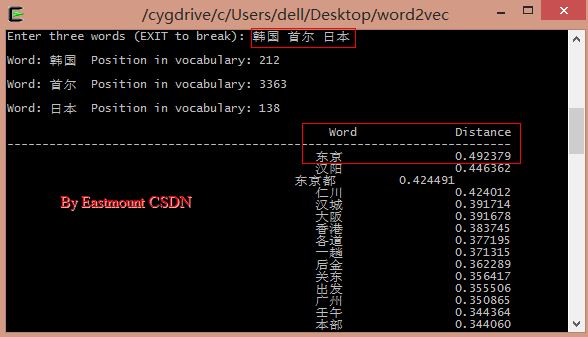
输入"韩国、首尔、日本"能够预測其首都"东京":
韩国的首都是首尔 <==> 日本的首都是东京
输入"中国 亚洲 德国"能够预測语义语法关系"欧洲":
中国位于亚洲 <==> 德国位于欧洲
中国位于亚洲 <==> 德国位于欧洲
假设输入只2个词体会提示错误。同一时候输入"EXIT"可推出继续输入。
word-analogy.c 源代码:
// Copyright 2013 Google Inc. All Rights Reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <malloc.h>
const long long max_size = 2000; // max length of strings
const long long N = 40; // number of closest words that will be shown
const long long max_w = 50; // max length of vocabulary entries
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
FILE *f;
char st1[max_size];
char bestw[N][max_size];
char file_name[max_size], st[100][max_size];
float dist, len, bestd[N], vec[max_size];
long long words, size, a, b, c, d, cn, bi[100];
char ch;
float *M;
char *vocab;
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: ./word-analogy <FILE>\nwhere FILE contains word projections in the BINARY FORMAT\n");
return 0;
}
strcpy(file_name, argv[1]);
f = fopen(file_name, "rb");
if (f == NULL) {
printf("Input file not found\n");
return -1;
}
fscanf(f, "%lld", &words);
fscanf(f, "%lld", &size);
vocab = (char *)malloc((long long)words * max_w * sizeof(char));
M = (float *)malloc((long long)words * (long long)size * sizeof(float));
if (M == NULL) {
printf("Cannot allocate memory: %lld MB %lld %lld\n", (long long)words * size * sizeof(float) / 1048576, words, size);
return -1;
}
for (b = 0; b < words; b++) {
a = 0;
while (1) {
vocab[b * max_w + a] = fgetc(f);
if (feof(f) || (vocab[b * max_w + a] == ' ')) break;
if ((a < max_w) && (vocab[b * max_w + a] != '\n')) a++;
}
vocab[b * max_w + a] = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) fread(&M[a + b * size], sizeof(float), 1, f);
len = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) len += M[a + b * size] * M[a + b * size];
len = sqrt(len);
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) M[a + b * size] /= len;
}
fclose(f);
while (1) {
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestd[a] = 0;
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestw[a][0] = 0;
printf("Enter three words (EXIT to break): ");
a = 0;
while (1) {
st1[a] = fgetc(stdin);
if ((st1[a] == '\n') || (a >= max_size - 1)) {
st1[a] = 0;
break;
}
a++;
}
if (!strcmp(st1, "EXIT")) break;
cn = 0;
b = 0;
c = 0;
while (1) {
st[cn][b] = st1[c];
b++;
c++;
st[cn][b] = 0;
if (st1[c] == 0) break;
if (st1[c] == ' ') {
cn++;
b = 0;
c++;
}
}
cn++;
if (cn < 3) {
printf("Only %lld words were entered.. three words are needed at the input to perform the calculation\n", cn);
continue;
}
for (a = 0; a < cn; a++) {
for (b = 0; b < words; b++) if (!strcmp(&vocab[b * max_w], st[a])) break;
if (b == words) b = 0;
bi[a] = b;
printf("\nWord: %s Position in vocabulary: %lld\n", st[a], bi[a]);
if (b == 0) {
printf("Out of dictionary word!\n");
break;
}
}
if (b == 0) continue;
printf("\n Word Distance\n------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) vec[a] = M[a + bi[1] * size] - M[a + bi[0] * size] + M[a + bi[2] * size];
len = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) len += vec[a] * vec[a];
len = sqrt(len);
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) vec[a] /= len;
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestd[a] = 0;
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) bestw[a][0] = 0;
for (c = 0; c < words; c++) {
if (c == bi[0]) continue;
if (c == bi[1]) continue;
if (c == bi[2]) continue;
a = 0;
for (b = 0; b < cn; b++) if (bi[b] == c) a = 1;
if (a == 1) continue;
dist = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) dist += vec[a] * M[a + c * size];
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) {
if (dist > bestd[a]) {
for (d = N - 1; d > a; d--) {
bestd[d] = bestd[d - 1];
strcpy(bestw[d], bestw[d - 1]);
}
bestd[a] = dist;
strcpy(bestw[a], &vocab[c * max_w]);
break;
}
}
}
for (a = 0; a < N; a++) printf("%50s\t\t%f\n", bestw[a], bestd[a]);
}
return 0;
}
6、关键词聚类
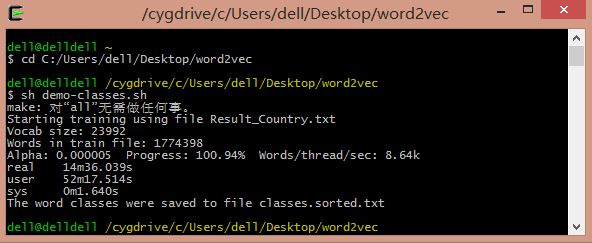
命令:sh demo-classes.sh
demo-classes.sh 中指令:
make #if [ ! -e text8 ]; then # wget http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip -O text8.gz # gzip -d text8.gz -f #fi time ./word2vec -train Result_Country.txt -output classes.txt -cbow 1 -size 200 -window 8 -negative 25 -hs 0 -sample 1e-4 -threads 20 -iter 15 -classes 100 sort classes.txt -k 2 -n > classes.sorted.txt echo The word classes were saved to file classes.sorted.txt执行结果例如以下图所看到的:
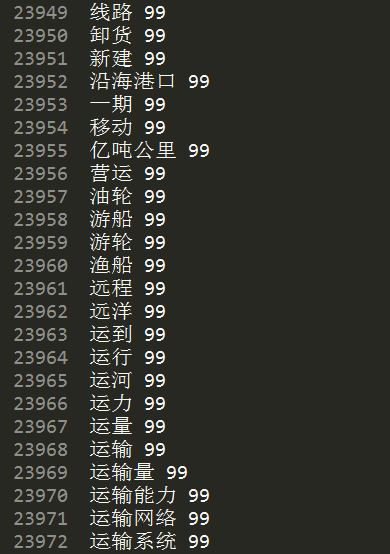
当中生词文件classes.txt和排序后的文件classes.sorted.txt:
聚类算法是Kmeans,类簇设置为100类。相应0~99,每类的关键词例如以下。可是怎样计算300行数据每行相应的类标。还不太清楚~
当中聚类代码见 word2vec.c 文件 void TrainModel() 函数:
demo-phrases.sh(word2phrase.c) 是就是将词语拼成短语。
希望文章对你有所帮助,尤其是正在学习word2vec基础文章的。
推荐文章:文本深度表示模型Word2Vec - 小唯THU大神
利用中文数据跑Google开源项目word2vec - hebin大神
Word2vec在事件挖掘中的调研 - 热点事件推荐 (思路不错)
(By:Eastmount 2016-02-20 深夜2点 http://blog.csdn.net/eastmount/ )



