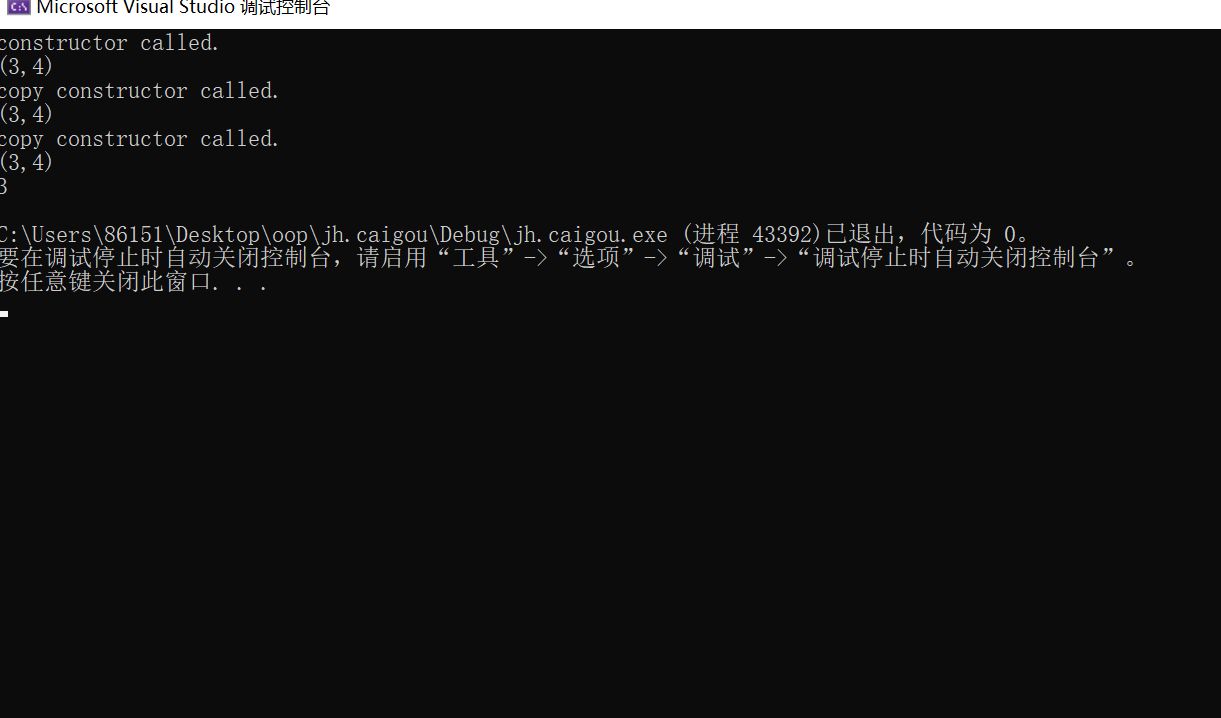
实验一 类和对象
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Point { public: Point(int x0=0,int y0=0); Point(const Point&p ); ~Point() = default; int get_x() const {return x;} int get_y() const{return y;} void show () const; private: int x,y; }; Point::Point (int x0,int y0):x{x0},y{y0} { cout<<"constructor called."<<endl; } Point::Point(const Point& p):x{p.x},y{p.y} { cout<<"copy constructor called."<<endl; } void Point::show()const { cout<<"("<<x<<","<<y<<")"<<endl; } int main() { Point p1(3,4); p1.show(); Point p2=p1; p2.show(); Point p3{p2}; p3.show(); cout<<p3.get_x()<<endl; }
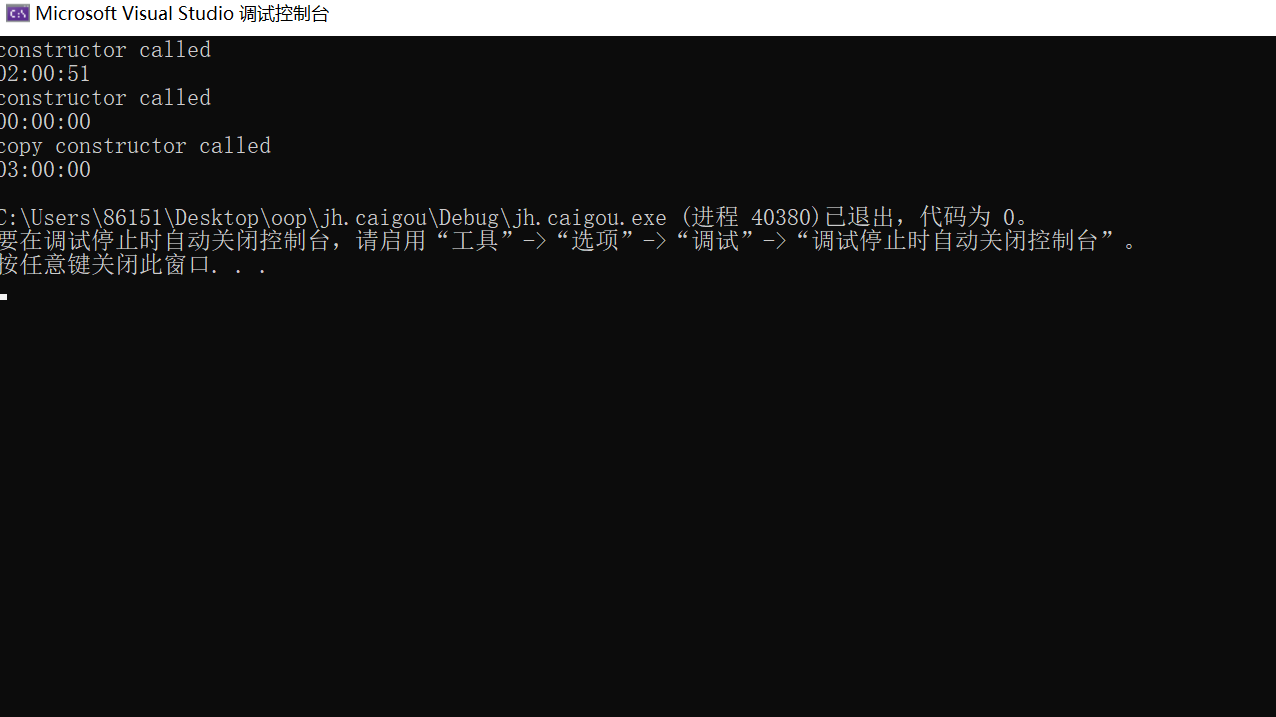
实验3
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Clock { public: Clock(int h = 0, int m = 0, int s = 0); Clock(const Clock& t); ~Clock() = default; void set_time(int h, int m = 0, int s = 0); void show_time() const; private: int hour, minute, second; }; Clock::Clock(int h, int m, int s): hour{h}, minute{m}, second{s} { cout << "constructor called" << endl; } Clock::Clock(const Clock& t): hour{t.hour}, minute{t.minute}, second{t.second} { cout << "copy constructor called" << endl; } void Clock::set_time(int h, int m, int s) { hour = h; minute = m; second = s; } void Clock::show_time() const { using std::setw; using std::setfill; cout << setfill('0') << setw(2) << hour << ":" << setw(2) << minute << ":" << setw(2) << second << endl; } Clock reset() { return Clock(0, 0, 0); } int main() { Clock c1(2, 0, 51); c1.show_time(); c1 = reset(); c1.show_time(); Clock c2(c1); c2.set_time(3); c2.show_time(); }
实验四
#include <iostream> class X{ public: X(); ~X(); X(int m); X(const X& obj); X(X&& obj) noexcept; void show() const; private: int data; }; X::X(): data{42} { std::cout << "default constructor called.\n"; } X::~X() { std::cout << "destructor called.\n"; } X::X(int m): data{m} { std::cout << "constructor called.\n"; } X::X(const X& obj): data{obj.data} { std::cout << "copy constructor called.\n"; } X::X(X&& obj) noexcept: data{obj.data} { std::cout << "move constructor called.\n"; } void X::show() const { std::cout << data << std::endl; }int main() { X x1; x1.show(); X x2{2049}; x2.show(); X x3{x1}; x3.show(); X x4{ std::move(x2) }; x4.show(); }
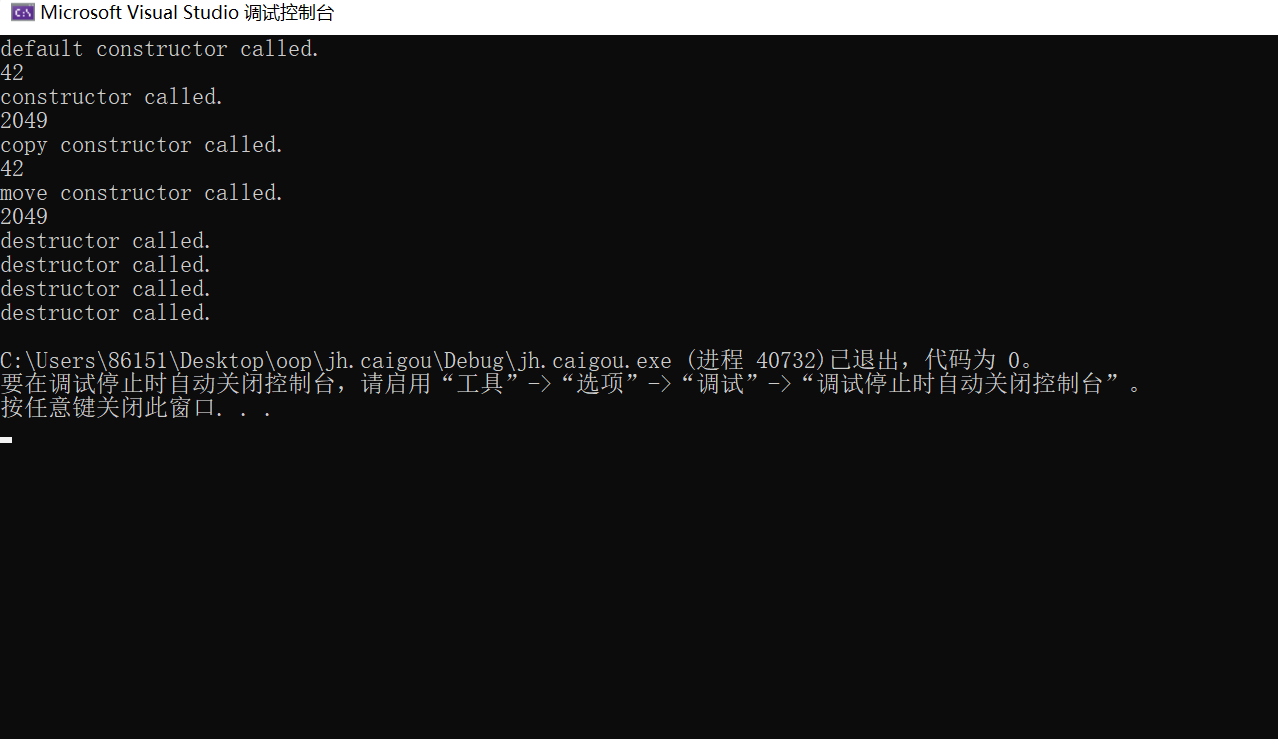
32行:调用默认构造函数
35行:调用构造函数
38行:调用复制构造函数
41行:调用移动构造函数
析构函数在对象被销毁时被调用
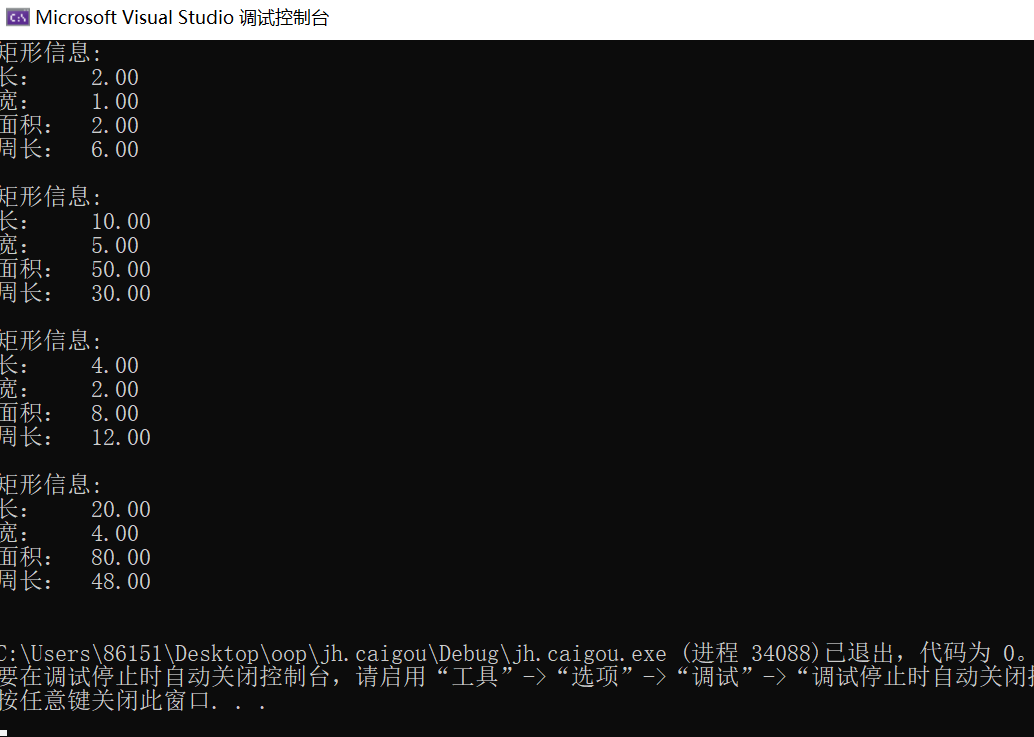
实验五
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; class Rectangle { public: Rectangle(double l = 2.0, double w = 1.0) : length(l), width(w) {} Rectangle(const Rectangle& rect) : length(rect.length), width(rect.width){} ~Rectangle() {}; double len() { return length; } double wide() { return width; } double area() { return length * width; } double circumference() const { return (length + width) * 2; } void resize(int times) { length *= times; width *= times; } void resize(int l_times, int w_times) { length *= l_times; width *= w_times; } private: double length, width; }; void output(const Rectangle& rect) { using namespace std; cout << "矩阵信息:\n"; cout << fixed << setprecision(2); cout << "长:" << rect.len() << endl; cout << "宽:" << rect.wide() << endl; cout << "面积:" << rect.area() << endl; cout << "周长:" << rect.circumference() << endl; } int main() { Rectangle rect1; output(rect1); Rectangle rect2(10, 5); output(rect2); Rectangle rect3(rect1); rect3.resize(2); output(rect3); rect3.resize(5, 2); output(rect3); }