数据库(三):存储引擎
进击のpython
数据库——存储引擎
上一节在表的操作的最后一点,提到了一个设置存储引擎
那什么是存储引擎呢?存储引擎能用来干什么?
这就是本小节所要研究的问题了
存储引擎
库就是创建了一个文件夹,在文件夹里存储的文件就叫表
那根据生活常识应该知道,不同的文件的格式是不一样的
文字的就是txt,视频的就是MP4,音乐的就是MP3... ...
那对于表来说也应该有不同的类型用以存储不同的信息
那这个搜索引擎,就是表的类型
MySQL支持的引擎
有个语句可以帮助你知道有什么引擎
show engines \G
mysql> show engines \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Engine: FEDERATED
Support: NO
Comment: Federated MySQL storage engine
Transactions: NULL
XA: NULL
Savepoints: NULL
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Engine: MRG_MYISAM
Support: YES
Comment: Collection of identical MyISAM tables
Transactions: NO
XA: NO
Savepoints: NO
*************************** 3. row ***************************
Engine: MyISAM
Support: YES
Comment: MyISAM storage engine
Transactions: NO
XA: NO
Savepoints: NO
*************************** 4. row ***************************
Engine: BLACKHOLE
Support: YES
Comment: /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears)
Transactions: NO
XA: NO
Savepoints: NO
*************************** 5. row ***************************
Engine: CSV
Support: YES
Comment: CSV storage engine
Transactions: NO
XA: NO
Savepoints: NO
*************************** 6. row ***************************
Engine: MEMORY
Support: YES
Comment: Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables
Transactions: NO
XA: NO
Savepoints: NO
*************************** 7. row ***************************
Engine: ARCHIVE
Support: YES
Comment: Archive storage engine
Transactions: NO
XA: NO
Savepoints: NO
*************************** 8. row ***************************
Engine: InnoDB
Support: DEFAULT
Comment: Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys
Transactions: YES
XA: YES
Savepoints: YES
*************************** 9. row ***************************
Engine: PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA
Support: YES
Comment: Performance Schema
Transactions: NO
XA: NO
Savepoints: NO
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
那现在就进行简单的介绍,只是了解!!!!!!
create table e1(id int) engine= innodb;
create table e2(id int) engine= memory;
create table e3(id int) engine= blackhole;
create table e4(id int) engine= myisam;
mysql> create table e1(id int) engine= innodb;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.72 sec)
mysql>
mysql> create table e2(id int) engine= memory;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec)
mysql>
mysql> create table e3(id int) engine= blackhole;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.13 sec)
mysql>
mysql> create table e4(id int) engine= myisam;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.14 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+-------------+
| Tables_in_e |
+-------------+
| e1 |
| e2 |
| e3 |
| e4 |
+-------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
创建了之后,我们就去文件夹里找一下我们刚才创建的文件
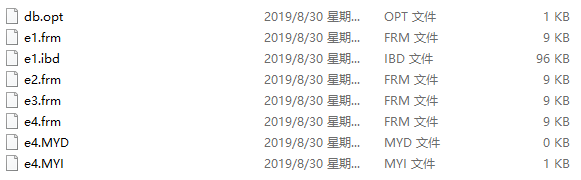
frm后缀的是表结构,ibd 就是 innodb的缩写,所以我们就看出来不是一个表就对应一个文件,那只是你的意淫
e2的搜索引擎是memory,特点是存在内存里的,而不是硬盘,所以没有数据存储,只有表结构
e3的搜索引擎是blackhole,特点是放进去数据就没了,所以也不需要数据存储,只有表结构
e4的搜索引擎是myisam,特点是支持索引,所以除了表结构,数据以外,还多了个索引文件
还是这句话,只是简单了解就行!
那现在就来试试每个引擎下的表的特点
引擎实例展示
首先先给上面的表格赋值
insert into e1 values(1);
insert into e2 values(1);
insert into e3 values(1);
insert into e4 values(1);
只验证两个具有代表性的引擎:
blackhole
mysql> select * from e1;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
mysql> select * from e2;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
mysql>
mysql> select * from e3;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
mysql> select * from e4;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
我们可以看出来e3里面的数据不见了,所以是不是丢进去就没有了~
memory
这是将数据放在内存中,也就是将内存清理后数据就不见了
那怎么办才是将内存进行清理呢?关掉服务再开启就ok了
C:\Users\Administrator>net stop mysql
MySQL 服务正在停止.
MySQL 服务已成功停止。
C:\Users\Administrator>net start mysql
MySQL 服务正在启动 ...
MySQL 服务已经启动成功。
C:\Users\Administrator>mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1
Server version: 5.6.45 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use e
Database changed
mysql> select * from e1;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.08 sec)
mysql> select * from e2;
Empty set (0.03 sec)
mysql> select * from e3;
Empty set (0.03 sec)
mysql> select * from e4;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
所以说可以确定memory引擎是将表存在内存的


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号