[Mobilar] 06 - DRF: Token
一些复杂的页面,还是使用vue, react开发会好一些,但会涉及到一个permission的问题,也就是接下来我们要关注的部分。
Goto: Django Rest-framework

一、基础回顾
Ref: [Django] 02 - Django REST Framework (DRF) 【打基础】
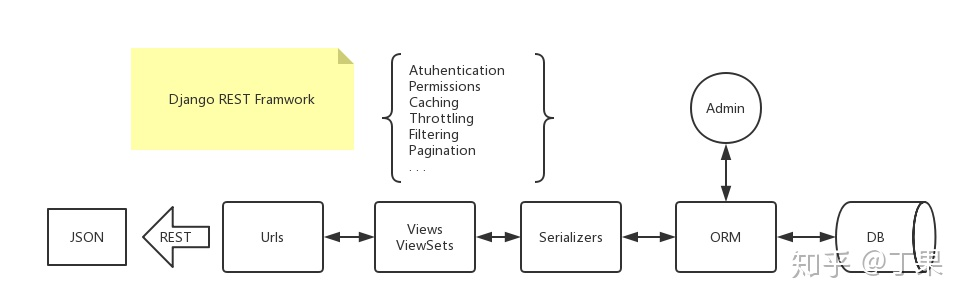
二、Token
Ref: REST API Token Authentication for Mobile Apps
Ref: Register a New User (Django Rest framework)
REST API 的代码单独放在了 ./api 文件夹中。
-
模型 account/
文件 Models.py
class Account(AbstractBaseUser):
email = models.EmailField(verbose_name="email", max_length=60, unique=True) username = models.CharField(max_length=30, unique=True) date_joined = models.DateTimeField(verbose_name='date joined', auto_now_add=True) last_login = models.DateTimeField(verbose_name='last login', auto_now=True) is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False) is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) is_staff = models.BooleanField(default=False) is_superuser = models.BooleanField(default=False) USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['username'] objects = MyAccountManager() # ----> def __str__(self): return self.email # For checking permissions. to keep it simple all admin have ALL permissons def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None): return self.is_admin # Does this user have permission to view this app? (ALWAYS YES FOR SIMPLICITY) def has_module_perms(self, app_label): return True
文件 modes.py
class MyAccountManager(BaseUserManager): # # 创建普通用户 # def create_user(self, email, username, password=None): if not email: raise ValueError('Users must have an email address') if not username: raise ValueError('Users must have a username') user = self.model( email=self.normalize_email(email), username=username, ) user.set_password(password) user.save(using=self._db) return user # # 创建超级用户 # def create_superuser(self, email, username, password): user = self.create_user( email=self.normalize_email(email), password=password, username=username, ) user.is_admin = True user.is_staff = True user.is_superuser = True user.save(using=self._db) return user
文件 modes.py
@receiver(post_save, sender=settings.AUTH_USER_MODEL) def create_auth_token(sender, instance=None, created=False, **kwargs): if created: Token.objects.create(user=instance) # <---- 对应了一个db中单独的一个表。
数据存储的方式,样例如下。
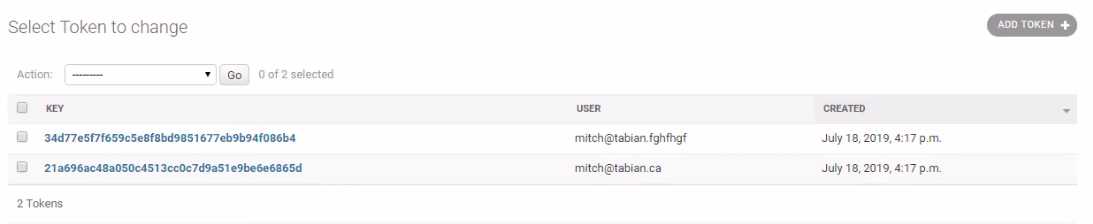
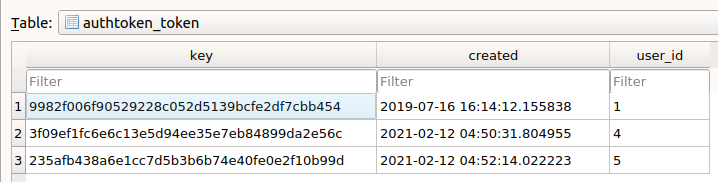
Ref: https://www.django-rest-framework.org/api-guide/authentication/#tokenauthentication
根据链接中内容,修改authentication的方式。
REST_FRAMEWORK = { # 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [ # 'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication', # 'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication', # ], 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.authentication.TokenAuthentication', ), 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated', ), 'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.PageNumberPagination', 'PAGE_SIZE': 10, }
-
REST API account/api/
文件 api/urls.py
urlpatterns = [ path('check_if_account_exists/', does_account_exist_view, name="check_if_account_exists"), path('change_password/', ChangePasswordView.as_view(), name="change_password"), path('properties', account_properties_view, name="properties"), path('properties/update', update_account_view, name="update"), path('login', ObtainAuthTokenView.as_view(), name="login"), path('register', registration_view, name="register"), # <---- ]
文件 api/views.py
@api_view(['POST', ]) @permission_classes([]) @authentication_classes([]) def registration_view(request): if request.method == 'POST': data = {} email = request.data.get('email', '0').lower() if validate_email(email) != None: data['error_message'] = 'That email is already in use.' data['response'] = 'Error' return Response(data) username = request.data.get('username', '0') if validate_username(username) != None: data['error_message'] = 'That username is already in use.' data['response'] = 'Error' return Response(data) # ?? serializer = RegistrationSerializer(data=request.data) if serializer.is_valid(): # # { # "response": "successfully registered new user.", # "email": "test1223@tabian.ca", # "username": "test1232", # "pk": 1, # "token": "c2f020e5d8a88d888d2da67e08098f5113f753a5" # } # account = serializer.save() data['response'] = 'successfully registered new user.' data['email'] = account.email data['username'] = account.username data['pk'] = account.pk data['token'] = Token.objects.get(user=account).key # <---- 将要返回给 client 的token else: data = serializer.errors return Response(data)
文件 api/serializers.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from account.models import Account
class RegistrationSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): password2 = serializers.CharField(style={'input_type': 'password'}, write_only=True) class Meta: model = Account fields = ['email', 'username', 'password', 'password2'] extra_kwargs = { 'password': {'write_only': True}, } def save(self): account = Account( email=self.validated_data['email'], username=self.validated_data['username'] ) password = self.validated_data['password'] password2 = self.validated_data['password2'] if password != password2: raise serializers.ValidationError({'password': 'Passwords must match.'})
account.set_password(password) account.save() return account
三、客户端的 Token
直接在 request 中包含 token 发送出去,安全嚒?
Token 是浏览器共享么?
-
服务端 token 验证
加一个装饰器,就自动验证了呢。查看 username 与 当前的 token 是否都回答正确。但token是无状态的。
文件 views.py
@api_view(['GET', ]) @permission_classes((IsAuthenticated, )) def account_properties_view(request): try: account = request.user except Account.DoesNotExist: return Response(status=status.HTTP_404_NOT_FOUND) if request.method == 'GET': serializer = AccountPropertiesSerializer(account) return Response(serializer.data)
-
token 和 session 的区别
详见: [Wagtail] Topic: REST API Token
End.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号