[Terraform] 02 - var, provider, state, etc
本篇大纲
- Open AWS account.
- Create IAM admin user.
- Create terraform file to spin up t2.micro instance.
- Run terraform apply.
通过创建一个ec2,来学习各个概念。
一、准备工作
手动地 在 界面环境下创建一个IAM用户。Manage access to AWS resources.
二、代码资源
Goto: https://github.com/AndrewProgramming/learn_terraform_from_scratch/tree/master/first-steps
三、概念分支图
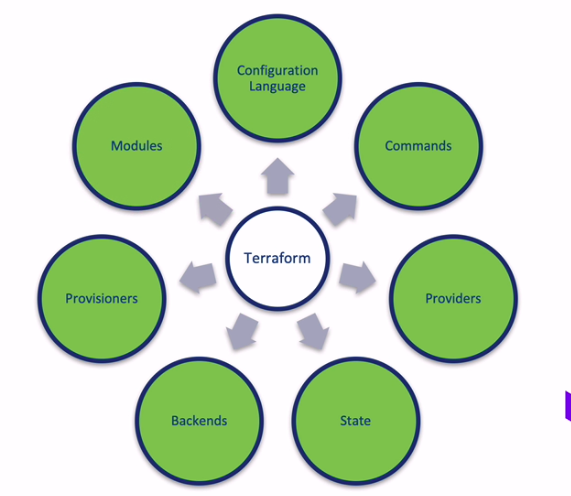
开始创建 EC2
一、简单案例
-
文件 instance.tf
provider "aws" { access_key = "todo" secret_key = "todo" region = "us-east-1" } # HCL定义的关键字resource
# 资源类型 + 名称
resource "aws_instance" "example" { ami = "ami-0d729a60" # 使用的操作系统的镜像,去哪里找? ----> instance_type = "t2.micro" }
-
文件 versions.tf
terraform { required_version = ">= 0.12" }
-
-
AMI 的 ID 查找
-
by http://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/locator/ec2/
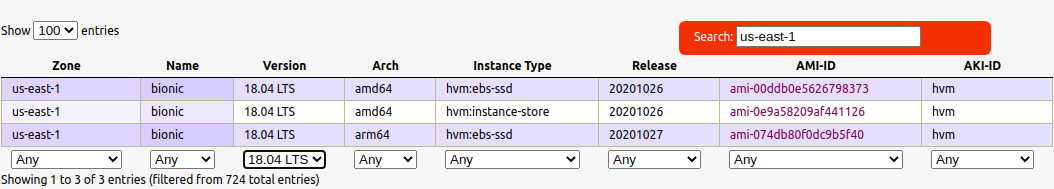
二、基础命令
$ terraform init
使用aws的provider,所以执行命令,下载该provider。
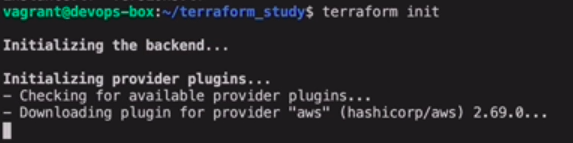
-
-
terraform init 做了什么
-
在 ./terraform/plugins/ 目录下,有 terraform init 后的配置文件,可以share。
如下,就 不用再反复输入:yes 去确认 了。
terraform apply -help
terraform apply -auto-approve
$ terraform plan
记得先配置aws的key。
$ terraform apply
具体执行。
$ terraform destroy
及时的销毁掉。
概念进阶
一、变量
Ref: https://github.com/AndrewProgramming/learn_terraform_from_scratch/tree/master/demo-1【作者提供的代码地址】
-
变量的使用
instance.tf 中的内容本地通过 var 在其他文件中去寻找。“使用” 和 “定义” 相分离。
resource "aws_instance" "example" { ami = var.AMIS[var.AWS_REGION] instance_type = var.INSTANCE_TYPE }
-
变量的定义
vars.tf
# define variable "AWS_ACCESS_KEY" { # 敏感信息的处理 } variable "AWS_SECRET_KEY" { } variable "AWS_REGION" { default = "eu-west-1" } variable "AMIS" { type = map(string) default = { us-east-1 = "ami-13be557e" us-west-2 = "ami-06b94666" eu-west-1 = "ami-089cc16f7f08c4457" } } variable INSTANCE_TYPE { default = "t2.micro" }
-
-
敏感信息
-
从 vars.tf 中分离出来,单独保存在了 terraform.tfvars,防止git commit上去。
在 vars.tf 中只是定义了一下。
发现 .tfvars,会自动将其中的内容作为后补 去匹配。
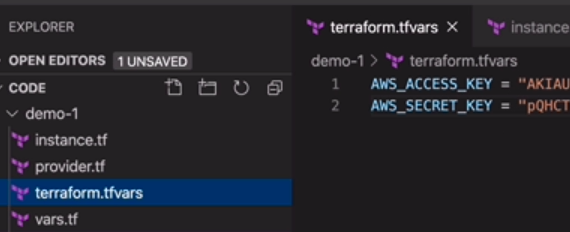
二、provider & state
-
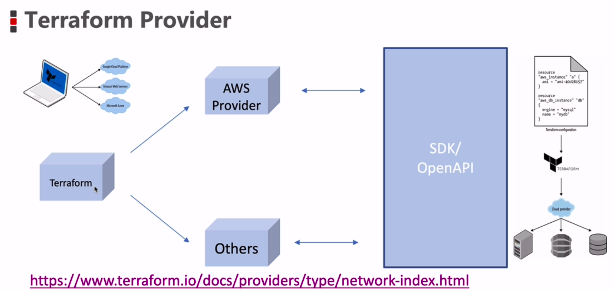
terraform provide r
Goto: https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/index.html
面向接口编程,支持了不同平台的接口。
-
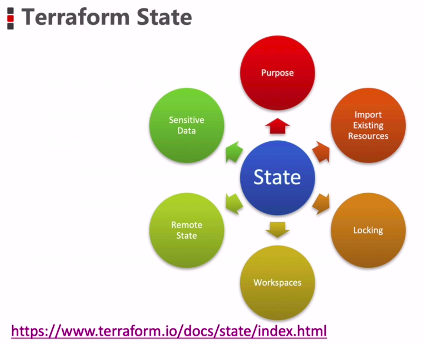
terraform state
Goto: https://www.terraform.io/docs/state/index.html
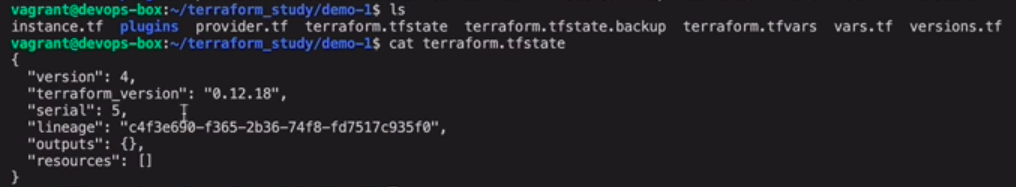
存储在本地 - terraform.tfstate
存储在远程 - 结合 “锁” 即可多人协作
-- Pre-request: Backend
-- Store in Terraform Cloud, AWS S3, Consul, etc.
存储的位置可以有多种选择,S3就是其中的一个option。
-
-
Local State file
-
-
-
Remote State on S3
-
Goto: https://www.terraform.io/docs/state/remote.html
一个人的话,backend的意义不大。
1. Working in a team.
2. Keeping sensitive information off disk.
3. Remote operations.
Ref: https://github.com/AndrewProgramming/learn_terraform_from_scratch/tree/master/demo-2-remote_state
(1) On S3, we create a bucket.
(2) 略,不是团队开发,不需要共享,暂时忽略。
三、OUTPUT
代码实例:注意对应关系。
resource "aws_instance" "example" { # a.这里做了定义 ami = var.AMIS[var.AWS_REGION] instance_type = "t2.micro"
provisioner"local-exec" { command = "echo ${aws_instance.example.private_ip} >> private_ips.txt""ip" { value = aws_instance.example.public_ip # b.这里便能如此使用 description = "demo for output" sensitive = true }
-
-
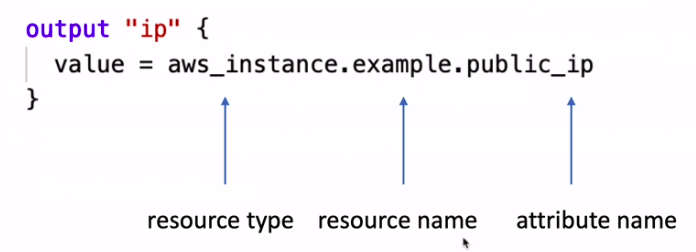
output 的格式定义
-
Ref: https://www.terraform.io/docs/configuration/outputs.html
四、Provisioner
Ref: https://www.terraform.io/docs/language/resources/provisioners/syntax.html
Provisioners can be used to model specific actions on the local machine or on a remote machine in order to prepare servers or other infrastructure objects for service.
供应商可用于对本地计算机或远程计算机上的 特定操作 进行建模,以准备服务器或其他基础结构对象以进行服务。
-
provisioner 的 类型
boot standardized AMIs, and then install the software on it.
就需要上传“预安装脚本”,再远程执行。

-
provisioner 的 使用
1. 生成公钥和私钥,有了两个文件:mykey 和 mykey.pub
ssh-keygen -f mykey
2. 自动创建EC2,并搭建好SSH。
resource "aws_key_pair" "mykey" { key_name = "mykey" public_key = file(var.PATH_TO_PUBLIC_KEY) # file()是个函数 } resource "aws_instance" "example" { ami = var.AMIS[var.AWS_REGION] instance_type = "t2.micro" key_name = aws_key_pair.mykey.key_name
# 先上传文件 provisioner"file" { source = "script.sh" destination = "/tmp/script.sh" }
# 再远程执行 provisioner"remote-exec" { inline = [ "chmod +x /tmp/script.sh", "sudo sed -i -e 's/\r$//' /tmp/script.sh", # Remove the spurious CR characters. "sudo /tmp/script.sh", ] }
connection { host = coalesce(self.public_ip, self.private_ip) # 内置函数,返回第一个不为空的参数 type = "ssh" user = var.INSTANCE_USERNAME private_key = file(var.PATH_TO_PRIVATE_KEY) } }
output "ip" { value = aws_instance.example.public_ip description = "demo for output" }
创建完毕后,通过以下命令远程登录EC2。
ssh -i mykey ubuntu@13.124.66.135
五、Modules
避免重复造轮子。
-
local 方式
Ref: https://github.com/AndrewProgramming/learn_terraform_from_scratch/tree/master/demo-5b_local_modules
把source指定的module为己用,名字自定义为 "consul"。
属性在这里都是consul已有的,user则根据需求自定义赋值。
module "consul" { source = "./module/consul-cluster" key_name = aws_key_pair.mykey.key_name key_path = var.PATH_TO_PRIVATE_KEY region = var.AWS_REGION
vpc_id = aws_default_vpc.default.id subnets = { "0" = aws_default_subnet.default_az1.id "1" = aws_default_subnet.default_az2.id "2" = aws_default_subnet.default_az3.id } } output "consul-output" { value = module.consul.server_address }
-
remote 方式
Ref: https://github.com/AndrewProgramming/learn_terraform_from_scratch/tree/master/demo-5_remote_modules
module "consul" { source = "github.com/AndrewProgramming/terraform_tutrial_code_modules" # 与本地时的代码一样,只是上传到了github key_name = aws_key_pair.mykey.key_name key_path = var.PATH_TO_PRIVATE_KEY region = var.AWS_REGION vpc_id = aws_default_vpc.default.id subnets = { "0" = aws_default_subnet.default_az1.id "1" = aws_default_subnet.default_az2.id "2" = aws_default_subnet.default_az3.id } } output "consul-output" { value = module.consul.server_address }
另外,执行命令,下载module到./terraform中。
$ terraform get
六、Data Source
定义了一个数据源。获得 计算 结果(右)的示范如下:返回结果(数组)的第一个元素中的属性id的值。
Instance_type=${alicloud_instance_types.1c1g.instance_types.0.id}
解释:在阿里云中查找 core:1, mem size:1 的实例,结果保存在 instance_type.json 中。(右)结果,符合的instance 类型。
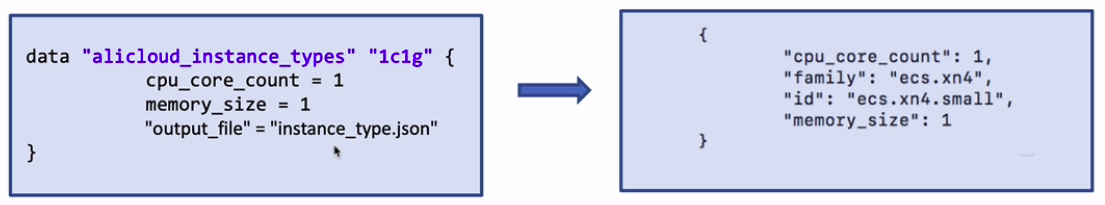
Goto: TERRAFORM中DATASOURCE的深度分析
Goto: 当Terraform遇上ECS(一)——DataSource篇
先列出来instance的列表,然后按照数组的方式选择一个。
七、Terraform Registry
Ref: https://registry.terraform.io/
Ref: https://registry.terraform.io/browse/modules?provider=aws
可以下载使用:providers and modules。
End.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号