[c++] Algorithms in STL
[Link] 105 STL Algorithms in Less Than an Hour
作者的官网:STL Learning Resource
[Link] http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/
类似的总结笔记:https://izualzhy.cn/stl-algorithms
有必要,根据逻辑层面,根据使用和需求的策略再整理一次.
for_each
heap
sort
partial_sort
nth_element
在一个无序表中快速得到第K小的元素
在当前区间[L,R]上,找一个基准位置mid
通过线性的扫描交换,
使得[L,mid)的元素都比mid小,(mid,R]的元素都比mid大
此时mid上的元素就是第mid小的
然后判断k在哪半边,继续递归处理
所以这样就达到了期望的O(N)O(N)复杂度
sort_heap
inplace_merge
在一个容器中进行归并。
rotate
shuffle
next_permutation(start,end),和prev_permutation(start,end)
这两个函数作用是一样的,区别就在于前者求的是当前排列的下一个排列,后一个求的是当前排列的上一个排列。
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;
int main() { int num[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
// 打印出所有的排列组合 do { cout<<num[0]<<" "<<num[1]<<" "<<num[2]<<endl; } while (next_permutation(num,num+5));
return 0; }
stable_sort
stable_partition
int main() { std::vector<double> temperatures {65, 75, 56, 48, 31, 28, 32, 29, 40, 41, 44, 50}; int average = std::accumulate(std::begin(temperatures),std::end(temperatures), 0.0)/temperatures.size(); std::cout << "Average temperature: "<< average << std::endl; std::partition(std::begin(temperatures), std::end(temperatures), [average](double t) { return t < average; }); std::copy(std::begin(temperatures), std::end(temperatures),std::ostream_iterator<double>{std::cout, " "}); std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }
is_sorted
sort是快速排序实现,因此是不稳定的;stable_sort是归并排序实现,因此是稳定的;
对于相等的元素sort可能改变顺序,stable_sort保证排序后相等的元素次序不变;
如果提供了比较函数,sort不要求比较函数的参数被限定为const,而stable_sort则要求参数被限定为const,否则编译不能通过。
is_partitioned
is_heap
is_sorted_until
is_partitioned_until
is_heap_until
count
inner_product
// inner_product example #include <iostream> // std::cout #include <functional> // std::minus, std::divides #include <numeric> // std::inner_product int myaccumulator (int x, int y) {return x-y;} int myproduct (int x, int y) {return x+y;} int main () { int init = 101; int series1[] = {10,20,30}; int series2[] = {1,1,2}; std::cout << "using default inner_product: "; std::cout << std::inner_product(series1,series1+3,series2,init); std::cout << '\n'; std::cout << "using functional operations: "; std::cout << std::inner_product(series1,series1+3,series2,init, std::minus<int>(),std::divides<int>()); std::cout << '\n'; std::cout << "using custom functions: "; std::cout << std::inner_product(series1,series1+3,series2,init, myaccumulator,myproduct); std::cout << '\n'; return 0; }
------------ output ------------
using default inner_product: 191
using functional operations: 56
using custom functions: 37
accumulate/transform_reduce
transfom类似与python中的map函数,与for_each有点类似,但for_each不会save结果.
transform_reduce支持不太好.
// transform algorithm example #include <iostream> // std::cout #include <algorithm> // std::transform #include <vector> // std::vector #include <functional> // std::plus int op_increase (int i) { return ++i; } int main () {
std::vector<int> foo; std::vector<int> bar; // set some values: for (int i=1; i<6; i++) foo.push_back (i*10); // foo: 10 20 30 40 50 bar.resize(foo.size()); // allocate space std::transform (foo.begin(), foo.end(), bar.begin(), op_increase); // bar: 11 21 31 41 51 // std::plus adds together its two arguments: std::transform (foo.begin(), foo.end(), bar.begin(), foo.begin(), std::plus<int>()); // foo: 21 41 61 81 101 std::cout << "foo contains:"; for (auto it=foo.begin(); it!=foo.end(); ++it) std::cout << ' ' << *it; std::cout << '\n'; return 0; }
adjacent_difference
用来计算容器相邻元素的关系,除了相邻元素之差,或自定义相邻元素操作.
与transform相对应的类似"reduce"的函数.
int main() { // Default implementation - the difference b/w two adjacent items std::vector<int> v{2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20}; std::adjacent_difference(v.begin(), v.end(), v.begin()); for (auto n : v) { std::cout << n << ' '; } std::cout << '\n'; // Fibonacci // Notice, next item on the list is the result of the current iteration std::vector<int> v2 = std::vector<int>(10); for (auto n : v2) { std::cout << n << ' '; } std::cout << '\n'; v2[0] = 1; std::adjacent_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end()-1, v2.begin()+1, std::plus<int>()); for (auto n : v2) { std::cout << n << ' '; } std::cout << '\n'; }
partial_sum
std::vector<int> data {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19}; std::cout << "Partial sums: "; std::partial_sum(std::begin(data), std::end(data),std::ostream_iterator<int>{std::cout, " "}); std::cout << std::endl; // Partial sums: 2 5 10 17 28 41 58 77 std::cout << "Partial sums:"; std::partial_sum (std::begin (data) , std::end (data),std::ostream_iterator<int>{std::cout, " "}, std::minus<int>()); std::cout << std::endl; // Partial sums: 2 -1 -6 -13 -24 -37 -54 -73 // 这里使用了减法运算符,所以值是 2、2-3、2-3-5、2-3-5-7 的结果,以此类推。
transform_inclusive_scan (c++17)
transform_exclusive_scan (c++17)
sample
all_of
any_of
none_of
equal, mismatch
语句 equal(first1,last1,first2) 和 mismatch(first1,last1,first2).first==last1 是等价的.
lexicographical_compare
find, adjacent_find
find() : 在序列中找某个值的第一个出现
find_if() : 在序列中符合某谓词的第一个元素
find_first_if : 在两个序列中找匹配元素
adjacent_find : 用于查找相等或满足条件的邻近元素对
#include <algorithm> #include <list> #include <iostream> using namespace std; //判断X和y是否奇偶同性 bool parity_equal(int x, int y) { return (x - y) % 2 == 0 ? 1 : 0; } int main() { //初始化链表 list<int> iList; iList.push_back(3); iList.push_back(6); iList.push_back(9); iList.push_back(11); iList.push_back(11); iList.push_back(18); iList.push_back(20); iList.push_back(20); //输出链表 list<int>::iterator iter; for(iter = iList.begin(); iter != iList.end(); ++iter) { cout << *iter << " "; } cout << endl; //查找邻接相等的元素 list<int>::iterator iResult = adjacent_find(iList.begin(), iList.end()); if (iResult != iList.end()) { cout << "链表中第一对相等的邻近元素为:" << endl; cout << *iResult++ << endl; cout << *iResult << endl; } //查找奇偶性相同的邻近元素 iResult = adjacent_find(iList.begin(), iList.end(), parity_equal); if (iResult != iList.end()) { cout << "链表中第一对奇偶相同的元素为:" << endl; cout << *iResult++ << endl; cout << *iResult << endl; } return 0; }
equal_range
返回值是个pair对象,pair的first是左边界的迭代器,pair的second是右边界的迭代器。
区间是左闭右开的,[左边界,右边界)。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> bool mygreater (int i,int j) { return (i>j); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20}; std::vector<int> v(myints,myints+8); // 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20 std::pair<std::vector<int>::iterator,std::vector<int>::iterator> bounds; // using default comparison: std::sort (v.begin(), v.end()); // 10 10 10 20 20 20 30 30 bounds=std::equal_range (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^ ^ std::cout << "bounds at positions " << (bounds.first - v.begin()); std::cout << " and " << (bounds.second - v.begin()) << '\n'; // using "mygreater" as comp: std::sort (v.begin(), v.end(), mygreater); // 30 30 20 20 20 10 10 10 bounds=std::equal_range (v.begin(), v.end(), 20, mygreater); // ^ ^ std::cout << "bounds at positions " << (bounds.first - v.begin()); std::cout << " and " << (bounds.second - v.begin()) << '\n'; return 0; }
lower_bound, upper_bound, binary_search
lower_bound( )和upper_bound( )都是利用二分查找的方法在一个排好序的数组中进行查找的。
lower_bound( begin, end, num):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于或等于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
upper_bound( begin, end, num):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
search, find_end
在查找序列的子序列方面,search() 算法和 find_end() 算法相似,但它所查找的是第一个匹配项而不是最后一个。
find_first_of
返回值是第一个与指定字符串中任何字符匹配的字符位置;如果没有找到匹配的内容,就返回 string::npos 。
max_element
minmax_element
min_element
都是返回iterator
std::set_difference
std::set_union
std::set_intersection
std::set_symmetric_difference
std::includes
std:merge
std::copy(first, last, out);
std::move(first, last, out);
std::copy_backward
std::move_backward
相对于普通的从第一个元素开始复制的 copy() 算法,copy_backward() 提供了哪些优势。
一个回答是,在序列重叠时,可以用 copy() 将元素复制到重叠的目的序列剩下的位置——也就是目的序列第一个元素之前的位置。如果想尝试用 copy() 算法将元素复制到同一个序列的右边,这个操作不会成功,因为被复制的元素在复制之前会被重写。如果想将它们复制到右边,可以使用 copy_backward(),只要目的序列的结束迭代器在源序列的结束迭代器的右边。
std::fill(first, last, 42);
std::generate(first, last, f);
std::iota(first, last, 42);
std::replace(first, last, 42, 43);
std::remove(begin(collection), end(collection), 99);
std::remove(begin(collection), end(collection), 99);
erase
std::unique(begin(collection), end(collection));
remove_copy
remove是移除而并非删除,利用快慢指针+数据前移。
如果将结果存于另外一个空间,就是remove_copy算法。
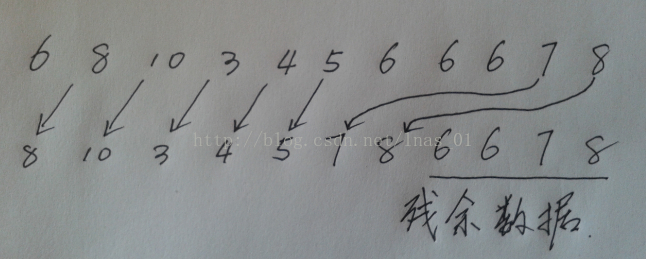
unique_copy
reverse_copy
rotate_copy
replace_copy
partition_copy
partial_sort_copy
find_if, find_if_not
和 find() 函数相同,find_if() 函数也用于在指定区域内执行查找操作。
不同的是,前者需要明确指定要查找的元素的值,而后者则允许自定义查找规则。
count_if
remove_if, remove_copy_if
replace_if, replace_copy_if
copy_if
transform
for_each
uninitialized_fill
uninitialized_copy
uninitialized_move
destory
使我们将内存配置与对象构造行为分离开来
copy_n
fill_n
generate_n
search_n
for_each_n
uninitialized_copy
uninitialized_fill
uninitialized_move
uninitialized_default_construct_n
uninitialized_value_construct_n
destroy_n
End.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号