[Distributed ML] Application Driven
背景介绍
Academic skills
一、Itemset Mining
例如:啤酒和尿布的关系
研究怎么样的 itemset 的 support 出现的次数。
二、Frequent itemset mining
FP-growth by Jiawei Han, 1663 citations. Hundreds of variants.
Ref: 获得数据频繁集的神器:FP Tree算法
Ref: 数据挖掘 FP-tree 算法
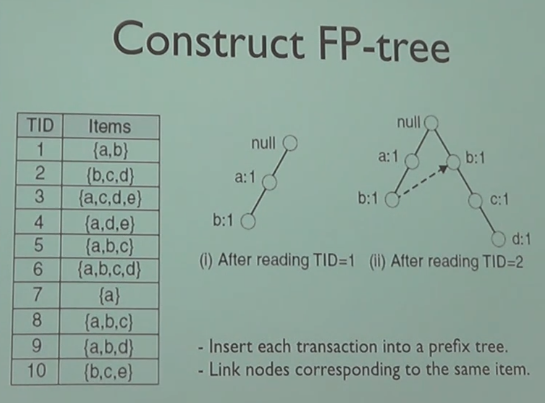
对大内存的要求比较高,取决于树的深度。
三、Infrequent itemset mining
Long-tail data analysis sould focus on infrequency
PFP, 168 citations
No variant..., but implemented in Mahout.
Mahout & MLib
Mahout一开始基于MapReduce,目前已基于Spark。
Mahout和Spark ML并不是竞争关系,Mahout是MLlib的补充。
四、结论
有用,但工业界不是很需要。
PFP穷举了所有的情况,但在”实际需求“中,有什么用呢?没遇到过。
也就引出下面的话题,Data-driven的学习策略才不是弯路。
Data-driven.
Ref: 分布式机器学习系列讲座 - 02: Application Driven
一、Aim before fire!
1). Recommender systems
2). Search engine
3). Online advertising
语义理解 Semantics = commonalities = co-occurrences 找共性
a). Unsupervised: collaborative filterin 协同过滤, matrix factorization, probabilistic latent semantic analysis.
b). Supervised: categorization and classification
c). Human labor: tags.
二、Unsupervised
Frequent itemset mining
Collaborative filtering
LSA - SVD decomposition of text matrix.
NMF - constraint SVD
pLSA - probabilistic version of LSA (来新数据就傻眼了)
LDA - smoothed pLSA (可实时,加了prior)
GaP - A re-modeling of LDA
RBM - A re-modeling of LDA (dnn)
HDP - extending LDA to infinite (#semantics, 不用预先制定语义个数,比如”中餐馆模型“)
三、优化策略
算法的间接等价性,所以不是很在意;大数据重在工程性。

四、Business Analysis
Relevance: information retrieval
Ranking: click-through rate prediction (supervised model --> deep learning)
概率统计:Entropy
商业分析:基尼系数
Unsupervised models 与 倒排表;
模型更新了,倒排表结构不用更新;
广告关键词变化,倒排表如何实时更新,模型如何训练;
/* implement */



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号