Pytorch Tensor 常用操作
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html
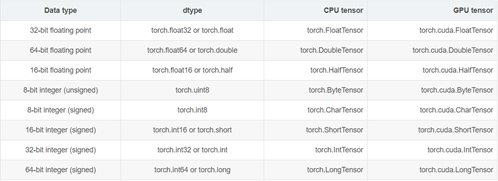
dtype: tessor的数据类型,总共有8种数据类型,其中默认的类型是torch.FloatTensor,而且这种类型的别名也可以写作torch.Tensor。
device: 这个参数表示了tensor将会在哪个设备上分配内存。它包含了设备的类型(cpu、cuda)和可选设备序号。如果这个值是缺省的,那么默认为当前的活动设备类型。
require_grad: 这个标志表明这个tensor的操作是否会被pytorch的自动微分系统(Autograd)记录其操作过程,以便后续自动求导。
layout: 表示了tensor的内存分布方式。目前,pytorch支持torch.strided方式以及实验性质地支持torch.sparse_coo。前者是目前普遍的使用方式。每一个strided tensor都关联一个torch.storage以保存其数据。
创建
典型的tensor构建方法:
torch.tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False)
从其他形式转换而来:
torch.as_tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None)
torch.from_numpy(ndarray)
创建特殊值组成的tensor:
torch.zeros(*sizes, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.zeros_like(input, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.ones(*sizes, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.ones_like(input, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.eye(n, m=None, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.empty(*sizes, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.empty_like(input, dtype=None, layout=None, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.full(size, fill_value, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.full_like(input, fill_value, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
按照步长或者区间创建tensor:
torch.arange(start=0, end, step=1, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.range(start=0, end, step=1, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.linspace(start, end, steps=100, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
torch.logspace(start, end, steps=100, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
索引,分块,组合,变形
组合--拼接
torch.cat(seq, dim=0, out=None):按照已经存在的维度进行concatenate。
在指定的维度dim上对序列seq进行连接操作。例如:
参数:
seq (sequence of Tensors) - Python序列或相同类型的张量序列
dim (int, optional) - 沿着此维度连接张量
out (Tensor, optional) - 输出参数
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
x
-0.5866 -0.3784 -0.1705
-1.0125 0.7406 -1.2073
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x3]
torch.cat((x, x, x), 0)
-0.5866 -0.3784 -0.1705
-1.0125 0.7406 -1.2073
-0.5866 -0.3784 -0.1705
-1.0125 0.7406 -1.2073
-0.5866 -0.3784 -0.1705
-1.0125 0.7406 -1.2073
[torch.FloatTensor of size 6x3]
torch.cat((x, x, x), 1)
-0.5866 -0.3784 -0.1705 -0.5866 -0.3784 -0.1705 -0.5866 -0.3784 -0.1705
-1.0125 0.7406 -1.2073 -1.0125 0.7406 -1.2073 -1.0125 0.7406 -1.2073
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x9]
torch.stack(seq, dim=0, out=None):按照新的维度进行concatenate。
在指定的维度dim上对序列seq进行连接操作。例如:
a = torch.IntTensor([[1,2,3],[11,22,33]])
b = torch.IntTensor([[4,5,6],[44,55,66]])
c = torch.stack([a,b],0)
d = torch.stack([a,b],1)
e = torch.stack([a,b],2)
c :tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[11, 22, 33]],
[[ 4, 5, 6],
[44, 55, 66]]], dtype=torch.int32)
d :tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[11, 22, 33],
[44, 55, 66]]], dtype=torch.int32)
e :tensor([[[ 1, 4],
[ 2, 5],
[ 3, 6]],
[[11, 44],
[22, 55],
[33, 66]]], dtype=torch.int32)
c, dim = 0时
c = [ a, b]
d, dim =1 时
d = [ [a[0] , b[0] ] , [a[1], b[1] ] ]
e, dim = 2 时
e=[[[a[0][0],b[0][0]],[a[0][1],b[0][1]],[a[0][2],b[0][2]]],[[a[1][0],b[1][0]],[a[1][1],b[0][1]],[a[1][2],b[1][2]]]]
分块
torch.chunk(tensor, chunks, dim=0):按照某个维度平均分块(最后一个可能小于平均值)
torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0):按照某个维度依照第二个参数给出的list或者int进行分割tensor。
索引
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None):沿给定轴 dim ,将输入索引张量 index 指定位置的值进行聚合输出tensor。输入与输出大小一致。
例如:
对一个 3 维张量,输出可以定义为:
out[i][j][k] = input[index[i][j][k]][j][k] # if dim == 0
out[i][j][k] = input[i][index[i][j][k]][k] # if dim == 1
out[i][j][k] = input[i][j][index[i][j][k]] # if dim == 2
- input (Tensor) – 源张量
- dim (int) – 索引的轴
- index (LongTensor) – 聚合元素的下标(index需要是torch.longTensor类型)
- out (Tensor, optional) – 目标张量
dim = 1
a = torch.randint(0, 30, (2, 3, 5))
print(a)
'''
tensor([[[ 18., 5., 7., 1., 1.],
[ 3., 26., 9., 7., 9.],
[ 10., 28., 22., 27., 0.]],
[[ 26., 10., 20., 29., 18.],
[ 5., 24., 26., 21., 3.],
[ 10., 29., 10., 0., 22.]]])
'''
index = torch.LongTensor([[[0,1,2,0,2],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[1,1,1,1,1]],
[[1,2,2,2,2],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[2,2,2,2,2]]])
print(a.size()==index.size())
b = torch.gather(a, 1,index)
print(b)
'''
True
tensor([[[ 18., 26., 22., 1., 0.],
[ 18., 5., 7., 1., 1.],
[ 3., 26., 9., 7., 9.]],
[[ 5., 29., 10., 0., 22.],
[ 26., 10., 20., 29., 18.],
[ 10., 29., 10., 0., 22.]]])
可以看到沿着dim=1,也就是列的时候。输出tensor第一页内容,
第一行分别是 按照index指定的,
input tensor的第一页
第一列的下标为0的元素 第二列的下标为1元素 第三列的下标为2的元素,第四列下标为0元素,第五列下标为2元素
index-->0,1,2,0,2 output--> 18., 26., 22., 1., 0.
'''
dim =2
c = torch.gather(a, 2,index)
print(c)
'''
tensor([[[ 18., 5., 7., 18., 7.],
[ 3., 3., 3., 3., 3.],
[ 28., 28., 28., 28., 28.]],
[[ 10., 20., 20., 20., 20.],
[ 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.],
[ 10., 10., 10., 10., 10.]]])
dim = 2的时候就安装 行 聚合了。参照上面的举一反三。
'''
dim = 0
index2 = torch.LongTensor([[[0,1,1,0,1],
[0,1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1,1]],
[[1,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[1,1,0,0,0]]])
d = torch.gather(a, 0,index2)
print(d)
'''
tensor([[[ 18., 10., 20., 1., 18.],
[ 3., 24., 26., 21., 3.],
[ 10., 29., 10., 0., 22.]],
[[ 26., 5., 7., 1., 1.],
[ 3., 26., 9., 7., 9.],
[ 10., 29., 22., 27., 0.]]])
这个有点特殊,dim = 0的时候(三维情况下),是从不同的页收集元素的。
这里举的例子只有两页。所有index在0,1两个之间选择。
输出的矩阵元素也是按照index的指定。分别在第一页和第二页之间跳着选的。
index [0,1,1,0,1]的意思就是。
在第一页选这个位置的元素,在第二页选这个位置的元素,在第二页选,第一页选,第二页选。
'''
torch.index_select(input, dim, index, out=None):选出一维度的一些slice组合成新的tensor。指定维度的大小与index大小一致。
torch.masked_select(input, mask, out=None):按照mask输出一个一维的tensor。
torch.take(input, indices):将输入看成1D tensor,按照索引得到输出。输出大小与index大小一致。
torch.nonzero(input, out=None):输出非0元素的坐标。
torch.where(condition, x, y):按照条件从x和y中选出满足条件的元素组成新的tensor。
变形
torch.reshape(input, shape)
torch.t(input):只针对2D tensor转置
torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1):交换两个维度
torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None):去除那些维度大小为1的维度,如果输入张量的形状为(A×1×B×C×1×D),那么输出张量的形状为(A×B×C×D)
torch.unbind(tensor, dim=0):去除某个维度
torch.unsqueeze(input, dim, out=None):在指定位置添加维度
数学运算
Pointwise Ops 逐点操作
torch.addcdiv(tensor, value=1, tensor1, tensor2, out=None)
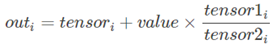
torch.addcmul(tensor, value=1, tensor1, tensor2, out=None)
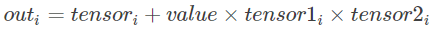
torch.ceil(input, out=None)
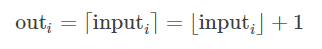
torch.clamp(input, min, max, out=None):max或者min可以用*代替,表示没有该项限制
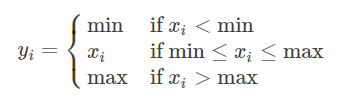
torch.erf(tensor, out=None)

torch.fmod(input, divisor, out=None): 计算余数
torch.frac(tensor, out=None)
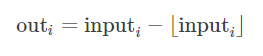
torch.lerp(start, end, weight, out=None)

torch.neg(input, out=None)
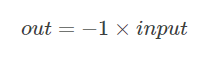
torch.pow(base, input, out=None)
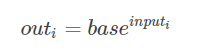
torch.reciprocal(input, out=None)

torch.remainder(input, divisor, out=None):计算余数
torch.rsqrt(input, out=None)
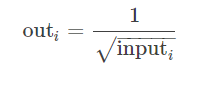
torch.sign(input, out=None):取符号
torch.trunc(input, out=None):截取整数部分
Reduction Ops 归约操作
torch.dist(input, other, p=2) 计算p范数
torch.norm() 计算2范数
torch.prod() 计算所有元素的积
torch.unique(input, sorted=False, return_inverse=False) 以1D向量保存张量中不同的元素。
Comparison Ops 比较操作
torch.isfinite(tensor)/torch.isinf(tensor)/torch.isnan(tensor):返回一个标记元素是否为 finite/inf/nan 的mask 张量。
torch.kthvalue(input, k, dim=None, keepdim=False, out=None) -> (Tensor, LongTensor):返回最小的第k个元素,如果为指定维度,则默认为最后一个维度。
torch.sort(input, dim=None, descending=False, out=None):沿着某一维度对张量进行升序排列。
torch.topk(input, k, dim=None, largest=True, sorted=True, out=None):返回最大的k个元素。
Other Operations 其他操作
torch.bincount(self, weights=None, minlength=0):返回每个值得频数。
torch.cross(input, other, dim=-1, out=None):按照维度计算叉积。
torch.diag(input, diagonal=0, out=None):如果输入时1D,则返回一个相应的对角矩阵;如果输入时2D,则返回相应对角线的元素。
torch.flip(input, dims):按照给定维度翻转张量
torch.histc(input, bins=100, min=0, max=0, out=None):计算张量的直方图。
torch.meshgrid(seq):生成网格(可以生成坐标)。
查看张量单个元素的字节数
torch.Tensor.element_size() → int
查看某类型张量单个元素的字节数。
例如:
torch.FloatTensor().element_size()
4




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号