Reference: 《谈谈C++的智能指针与自动资源管理(包括自动垃圾回收)》[1] ,《我的C++实践(16):引用计数实现》[2],《C++沉思录》[3]
最近写的C++项目由于起初设计的时候缺乏考虑,一大堆的指针乱指,容易出现悬空指针的情况,为彻底解决这一问题,决定实现引用计数和智能指针(小Boss不让用别人库……)
目标描述:
实现带引用计数的智能指针,不影响现有项目中的继承和多态性,小Boss不让用template……WTF
模仿项目现有结构写了一个小的Demo,记录如下:
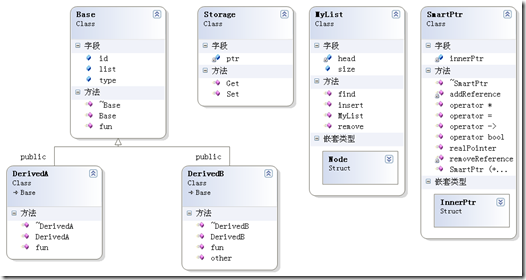
Base.h 中(包含基类和智能指针)
#ifndef BASE_H#define BASE_Hclass Base{public:int id;int type;MyList* list; //模拟项目中Base的链表Base(int i,int t);virtual ~Base(){}virtual void fun(){cout<<"Base:"<<id<<endl;cout<<"Type:"<<type<<endl;}};class SmartPtr{private:struct InnerPtr{Base* pointee;int refCount;InnerPtr(Base* p):refCount(1),pointee(p){}~InnerPtr(){delete pointee;}};InnerPtr* innerPtr;void addReference(){if(innerPtr)innerPtr->refCount++;}void removeReference(){if(innerPtr && --innerPtr->refCount==0){delete innerPtr;}}public:SmartPtr(){innerPtr=NULL;} //与 operator bool() const 共同完成空指针的概念SmartPtr(Base* p):innerPtr(new InnerPtr(p)){cout<<"SmartPtr(Base* p) is called"<<endl;}SmartPtr(const SmartPtr& rhs):innerPtr(rhs.innerPtr){addReference();}~SmartPtr(){cout<<"~SmartPtr is called"<<endl;removeReference();}SmartPtr& operator=(const SmartPtr& rhs){cout<<"SmartPtr::operator= is called"<<endl;if(innerPtr==rhs.innerPtr){return *this;}removeReference();//减少自己的innerPtr=rhs.innerPtr; //换成别人的addReference();return *this;}operator bool()const{if(innerPtr)return true;elsereturn false;}Base* operator->()const{return innerPtr->pointee;}Base& operator*()const{return *innerPtr->pointee;}Base* realPointer()const{return innerPtr->pointee; //提供无引用计数的裸指针,慎用}};#endif
MyList.h 一个简单的链表作为存储结构,注意其
#ifndef MYLIST_H#define MYLIST_Hclass MyList{public:struct Node{SmartPtr value;Node* next;Node(SmartPtr &p= SmartPtr(),Node* n=NULL):value(p),next(n){}};MyList(){size=0;}void insert(Base* p){head.next=new Node(SmartPtr(p),head.next);size++;}int remove(int id){Node* last=&head;for(Node* itr=head.next;itr!=NULL;itr=itr->next){if(itr->value->id==id){last->next=itr->next;delete itr;size--;}last=itr;}}SmartPtr& find(int id){for(Node* itr=head.next;itr!=NULL;itr=itr->next){if(itr->value->id==id)return itr->value;}return head.value;//head对外显示为空指针}int size;private:Node head;};#endif
MyList.cpp 仅仅是为了保持项目风格
#include "header.h"
header.h
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Base;class SmartPtr;class MyList;#include "Base.h"#include "MyList.h"
main.cpp
#include "header.h"class DerivedA:public Base{public:DerivedA(int i):Base(i,1){}~DerivedA(){}void fun(){cout<<"Derived A:"<<id<<endl;}};class DerivedB:public Base{public:DerivedB(int i):Base(i,2){}~DerivedB(){}void fun(){cout<<"Derived B:"<<id<<endl;}void other(){cout<<"Derived B:"<<"Other"<<endl;};};class Storage{private:SmartPtr ptr;public:void Set(Base* p){ptr=p; //会调用隐式转换}SmartPtr& Get(){return ptr;}};SmartPtr func(Storage* s,Base* a){s->Set(a);s->Get()->fun();SmartPtr p=s->Get();p->fun();return p;}void main(){Storage* s=new Storage();DerivedA* a=new DerivedA(10);DerivedB* b=new DerivedB(20);DerivedB* bb=new DerivedB(30);SmartPtr p=func(s,b);SmartPtr* pp=new SmartPtr(s->Get());delete pp;//delete s;p->fun();(static_cast<DerivedB*> (p.realPointer()))->other();s->Set(a);cout<<"start insert"<<endl;s->Get()->list->insert(b);s->Get()->list->insert(bb);cout<<"end insert"<<endl;p=s->Get()->list->find(40);if(p)p->fun();}
做了一些存取测试,确保不会想过去那样出现悬空指针,测试了一下“空指针”用来代替原来裸指针使用时的NULL的概念。
小Demo很成功。
======= Let’s GO 项目重构!===========
心酸历程……记录要点和感想
1. 原来所有使用裸指针的地方都要换成智能指针,尽量不要再项目中使用裸指针(除了new原始对象的时候),否则有可能无法保证“一个对象只有一个内存空间”
2. 原来对象中的交叉引用(A类中绑定B类的指针,B类也绑定A类指针),可以通过在析构函数中解除绑定并删除引用的对象,但采用带引用计数的智能指针后,由于对象的析构函数只有在所有引用都已经被删除的情况下才会被调用,所以原来只需要delete A就可以达到的A和B一起被删除的效果现在只能显式的完成,即delete A之前先清空其所有的绑定对象,再delete A。所以要真正释放一个对象的空间必须手动显式地删除其所有的引用位置。
3. 引用的智能指针使用时应使用RAII手法 resource acquisition is initialization(资源获取就是初始化)的类似思想,尽量在栈上开辟空间,尽量避免出现new一个智能指针的情况。
最后大赞博文 [1],讲的而很透彻清晰!