使用Thread类创建线程
前面一段时间,一直在看<<C#高级编程>>第七版线程、任务和同步这一章的知识。创建线程,除了前面介绍的使用委托创建线程之外,创建线程的第二种方式是使用Thread类创建线程。
1.创建线程
使用Thread类可以创建和控制线程。下面的代码是创建和启动一个新线程的简单例子。
1: using System;
2: using System.Collections.Generic;
3: using System.Linq;
4: using System.Text;
5: using System.Threading;
6:
7: namespace Threading
8: {
9: class Program
10: {
11: static void Main(string[] args)
12: {
13: //Thread类的构造函数重载为接受ThreadStart和ParameterizedThreadStart类型的委托参数
14: var t1 = new Thread(ThreadMain);
15: t1.Start();
16: Console.WriteLine("This is the main thread");
17: }
18:
19: //ThreadStart委托定义了一个返回类型为void的无参数方法
20: static void ThreadMain()
21: {
22: Console.WriteLine("running in a thread.");
23: }
24: }
25: }
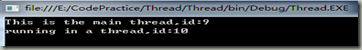
运行这个程序时,得到两个线程的输出:
不能保证哪个结果先输出,线程由操作系统调度,每次哪个线程在前面可以不同。
前面探讨了Lamda表达式如何与异步委托一起使用。Lamda表达式还可以与Thread类一起使用,将线程方法的实现代码传递给Thread构造函数的实参。
1: using System;
2: using System.Collections.Generic;
3: using System.Linq;
4: using System.Text;
5: using System.Threading;
6:
7: namespace Threading
8: {
9: class Program
10: {
11: static void Main(string[] args)
12: {
13: var t1=new Thread(()=>Console.WriteLine("running in a thread,id:{0}",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId));
14: t1.Start();
15: Console.WriteLine("This is the main thread,id:{0}",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
16: }
17: }
18: }
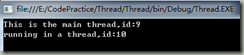
运行这个应用程序,现在可以看到线程名和ID。
2、给线程传递数据
1)、使用带ParameterizedThreadStart委托参数给Thread构造函数。
1: using System;
2: using System.Collections.Generic;
3: using System.Linq;
4: using System.Text;
5: using System.Threading;
6:
7: namespace Threading
8: {
9: class Program
10: {
11: //要给线程传递数据,需要某个存储数据的类或者结构。这里定义了包含字符串的Data结构,但可以传递任意对象
12: public struct Data
13: {
14: public string Message;
15: }
16:
17: //如果使用了ParameterizedThreadStart委托,线程的入口点必须有一个object类型的参数,且返回类型为void。对象可以强制转换为任意数据类型,这里是把消息写入控制台
18: static void ThreadMainWithParameters(object o)
19: {
20: Data d = (Data)o;
21: Console.WriteLine("running in a thread,receive {0}", d.Message);
22: }
23: static void Main(string[] args)
24: {
25: var d = new Data { Message = "info" };
26: //通过Thread类的构造函数,可以将新的入口点赋予ThreadMainWithParameters,传递变量d,以此调用Start()方法。
27: var t2 = new Thread(ThreadMainParameters);
28: t2.Start(d);
29: }
30: }
31: }
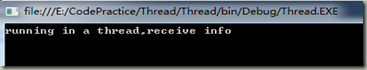
运行结果如下所示:
2)、定义一个类(参见MyThread类),在其中定义需要的字段,将线程的主方法定义为类的一个实例方法:
MyThead.cs:
1: using System;
2: using System.Collections.Generic;
3: using System.Linq;
4: using System.Text;
5:
6: namespace Threading
7: {
8: public class MyThead
9: {
10: private string data;
11:
12: public MyThead(string data)
13: {
14: this.data = data;
15: }
16: //定义成实例方法
17: public void ThreadMain()
18: {
19: Console.WriteLine("running in a thread,data:{0}",data);
20: }
21: }
22: }
Program.cs:
1: using System;
2: using System.Collections.Generic;
3: using System.Linq;
4: using System.Text;
5: using System.Threading;
6:
7: namespace Threading
8: {
9: class Program
10: {
11: static void Main(string[] args)
12: { //创建自定义类的实例
13: var obj = new MyThead("info");
14: //在Thread类的构造方法里面调用自定义类的实例方法
15: var t3 = new Thread(obj.ThreadMain);
16: t3.Start();
17: }
18: }
19: }
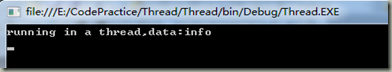
运行结果如下所示:
3、后台线程
在默认情况下,用Thread类创建的线程是前台线程。线程池中的线程总是后台线程。在用Thread类创建线程时,可以设置IsBackground属性,以确认该线程是前台线程还是后台线程。Main()方法中将线程t1的IsBackground设置为false(默认值)。在启动新线程后,主线程就把结束消息写入控制台。新线程会写入启动消息和结束消息,在这个过程中它要休眠3秒,在这个过程中它要睡眠3秒,在新线程会完成其工作前,这3秒钟有利于主线程结束。
1: using System;
2: using System.Collections.Generic;
3: using System.Linq;
4: using System.Text;
5: using System.Threading;
6:
7: namespace Threading
8: {
9: class Program
10: {
11: static void Main(string[] args)
12: {
13: var t1 = new Thread(ThreadMain)
14: {Name="MyNewThread",IsBackground=true };
15: t1.Start();
16: Console.ReadKey();
17: }
18: static void ThreadMain()
19: {
20: Console.WriteLine("Thread {0} started", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
21: Thread.Sleep(3000);
22: Console.WriteLine("Thread {0} completed", Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
23: }
24: }
25: }
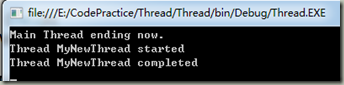
运行结果如下所示:
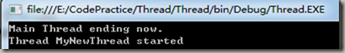
如果将用来启动新线程的IsBackground属性改为true,显示在控制台上的结果就会不同。在控制台上,可以看到相同的结果-新线程的启动消息,但没有结束消息。如果线程没有正常结束,就也有可能看不到启动消息。原因是前台进程在主线程运行完毕后任然会运行,而后台在主线程运行完毕后会结束运行。