List的两种子类LinkedList, ArrayList的选择
List的两种子类LinkedList, ArrayList的选择
背景:LeetCode的一道回溯题目
分析
题目意思是枚举所有的子集,必然想到回溯算法,本人使用回溯习惯使用一个成员变量链表和一个答案列表
配合回溯算法
List<List<Integer>> ans;
List<Integer> track;
在选择使用哪种List的实现时,本人经常使用LinkedList,今天提交答案时发现,使用LinkedList的耗时为:
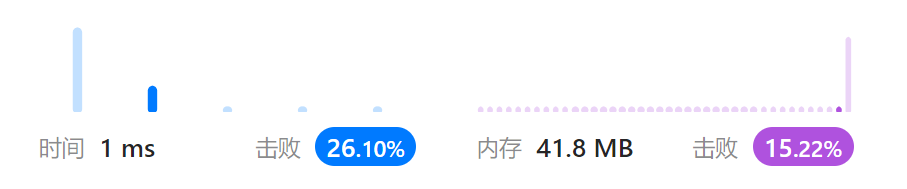
转头发现,这道题中,track的最大容量是固定的,是题目给出的数组nums.length,于是替换为 ArrayList:
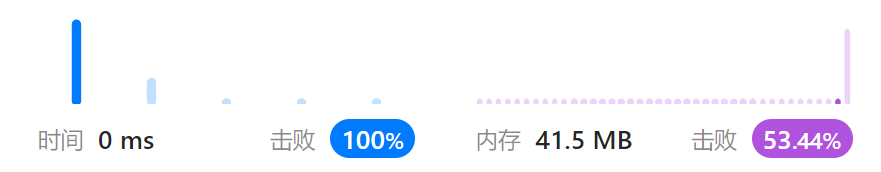
附上代码(ArrayList版本)
class Solution {
// 不必要频繁创建节点对象, ArrayList 底层操作数组
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> track;
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
// ArrayList 提前分配空间 (取决于数组nums的长度)
this.track = new ArrayList<>(nums.length);
backtrack(nums, 0);
return ans;
}
private void backtrack(int[] nums, int start) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(track));
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 做决策
track.add(nums[i]);
// backtrack
backtrack(nums, i+1);
// 取消决策
track.remove(track.size()-1);
}
}
}
ArrayList源码
特性总结:
- Object[] 存储,连续性好
- 无参构造时
new ArrayList<>()默认容量为10 - 容量满时
size+1 > elementData.length时扩容,新容量为1.5倍, - 线程不安全 --
size++
属性
/**
* Default initial capacity.
* 无参构造时, 默认的容量 DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*
* 无参构造时, 默认空Object[]数组,共享的
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*
* 无参构造时, 添加第一个元素时用于计算膨胀
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*
* 底层Object[]数组的引用指针,无参时=DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,
* 添加第一个元素时将会膨胀
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* 实际 ArrayList 中的元素数量(线程不安全的元凶)
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
构造器
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
常用方法
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will
* be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
线程不安全分析
以add()方法为例
- add时,检查是否已满,满则扩容为1.5倍,否则将
elementData[size++] = e
size++ 这条语句导致了线程不安全
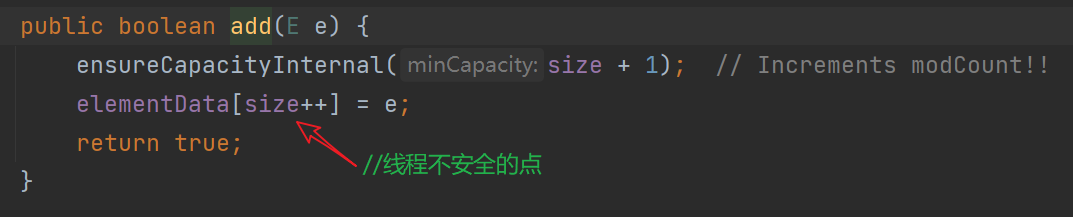
- ensureCapacityInternal -> ensureExplicitCapacity -> calculateCapacity
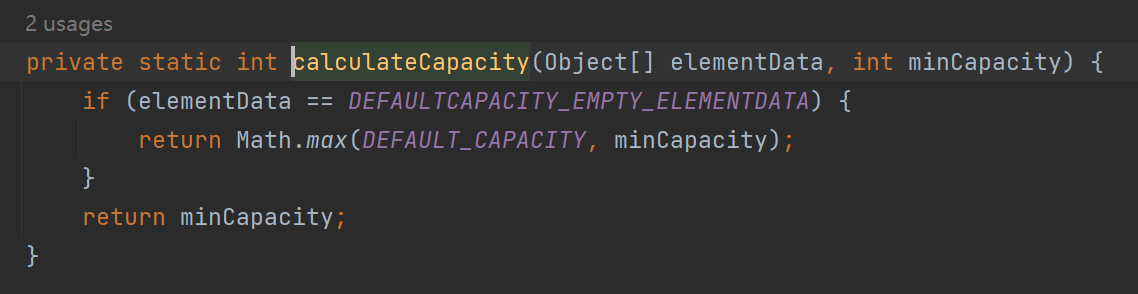
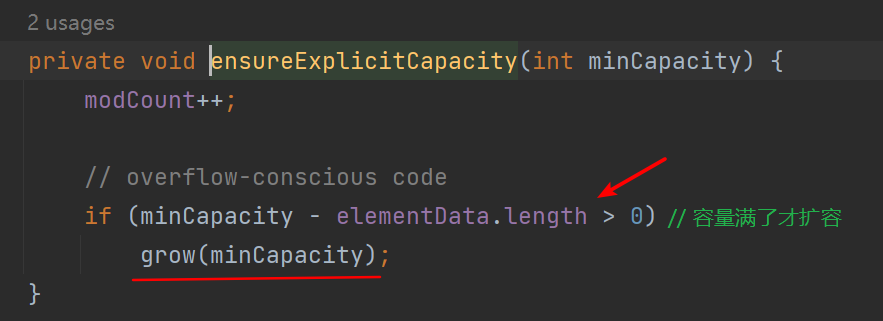
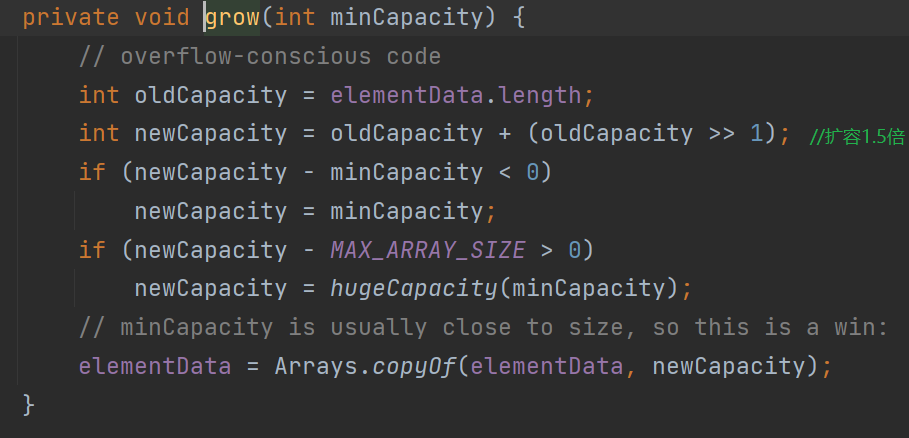
- 扩容
grow()
总结
在回溯算法中,或其他的列表容量上限可以确定的场景中,使用定容量的 ArrayList性能是远高于 LinkedList的,同时ArrayList底层使用数组,连续性更好,通常建议使用ArrayList,不建议为了空间而妥协使用LinkedList
LinkedList源码
内部类 - Node
一个简单的双向链表节点
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
属性
/**
* LinkedList 的实际存储的容量
*
*/
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
*
* 指向链表的头节点
*
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
*
* 指向链表的尾节点
*
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
构造器
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
//////////////// 有参构造器的 addAll(c) ///////////////////////
//////////////// 仅供参考,不需要记忆,就是简单的遍历 ///////////////////////
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in
* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is
* this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
常用方法
- 读
-
getFirst() -
getLast() -
get(int index) -
peek()↑Deque -
peekFirst()↑Deque -
peekLast()↑Deque
- 写
-
add(E) -
add(int,E) -
set(int, E)根据给定的index,确定从first查找还是从last查找 -
offer(E)↑Deque -
offerFirst(E)↑Deque -
offerLast(E)↑Deque -
push(E)↑Deque
- 删
-
remove(Object) -
remove(int) -
removeFirst()↑Deque -
removeLast()↑Deque -
remove()<==>removeFirst()↑Deque -
pop()↑Deque -
poll()↑Deque -
pollFirst()↑Deque -
pollLast()↑Deque
线程不安全分析
结论:线程不安全
以add(E)为例
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//////////////////// linkLast(e) /////////////////////
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
可见当两个线程同时调用 linkLast(E)方法时
l=last两次指向的都是同一个尾节点last
那么这两次插入操作,必定有一次插入失效
栈、队列的操作
不推荐使用 Stack实现栈,推荐使用 Deque 的 LinkedList 实现
栈 - Stack
-
入栈
-
push(E)↑Deque等价于
addFirst(e)
-
-
出栈
-
pop()↑Deque等价于
removeFirst()
-
-
peek
-
peek()↑Deque等价于
return first
-
队列 - Queue
-
入队
-
offer(E)↑Deque相当于
add(E)队列尾部添加元素
-
-
出队
-
poll()↑Deque相当于
removeFirst()删除链表头的元素
-
-
看队首
-
peek()↑Deque等价于
return first
-
双端队列 - Deque
这里的左右是一种常用的叫法,认为队的首处于左侧,队尾处于右侧
-
左入队
offerFirst(E)↑Deque
-
右入队
offerLast(E)↑Deque
-
左出队
pollFirst()↑Deque
-
右出队
pollLast()↑Deque
-
左peek
peekFirst()↑Deque
-
右peek
peekLast()↑Deque
总结
- 当业务中使用栈Stack、队列Queue、双端队列Deque时,选择使用LinkedList
- 当业务中其他场景,只有严格要求内存时,使用LinkedList,否选择ArrayList


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号