ImportSelector与DeferredImportSelector的区别
在使用@Import注解来注册bean的时候,Import注解的值可以是ImportSelector或者DeferredImportSelector的实现类,spring容器会实例化这个实现类,并执行其selectImports方法,那么问题来了:ImportSelector和DeferredImportSelector的区别在哪里,我们自定义Imort逻辑的时候该选择哪个呢?本文通过分析相关的spring源码来查找答案;
全文概览
本文由以下几部分组成:
1. 看官方文档;
2. 分析spring源码中对这两个接口的处理;
3. 实战验证;
看官方文档
先看官方文档看起,我选择了4.3.9版本在线文档(这是个Release版),地址:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/4.3.19.RELEASE/javadoc-api/
原文:
A variation of ImportSelector that runs after all @Configuration beans have been processed. This type of selector can be particularly useful when the selected imports are @Conditional.
Implementations can also extend the Ordered interface or use the Order annotation to indicate a precedence against other DeferredImportSelectors.
我的理解:
1. DeferredImportSelector是ImportSelector的一个扩展;
2. ImportSelector实例的selectImports方法的执行时机,是在@Configguration注解中的其他逻辑被处理之前,所谓的其他逻辑,包括对@ImportResource、@Bean这些注解的处理(注意,这里只是对@Bean修饰的方法的处理,并不是立即调用@Bean修饰的方法,这个区别很重要!);
3. DeferredImportSelector实例的selectImports方法的执行时机,是在@Configguration注解中的其他逻辑被处理完毕之后,所谓的其他逻辑,包括对@ImportResource、@Bean这些注解的处理;
4. DeferredImportSelector的实现类可以用Order注解,或者实现Ordered接口来对selectImports的执行顺序排序;
分析spring源码中对这两个接口的处理
接下来看看源码:
1. 在spring-framework-4.1.8.RELEASE工程中找到类ConfigurationClassParser.java,这里面有处理配置类的主要逻辑;
2. 找到方法parse(Set configCandidates):
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) { this.deferredImportSelectors = new LinkedList<DeferredImportSelectorHolder>(); //检查每个bean的定义 for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) { BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition(); try { if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { //对于每个有注解的类,都执行方法parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName()); } else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) { parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName()); } else { parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex); } } //最后再处理DeferredImportSelector的实现类 processDeferredImportSelectors(); }
由以上代码可以大致看出DeferredImportSelector的实现类被最后放在processDeferredImportSelectors方法中处理,那么前面的parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName)做了些什么呢?继续看;
3. 展开方法parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName)里面,是执行processConfigurationClass方法;
4. 再展开processConfigurationClass方法,看到核心逻辑是调用doProcessConfigurationClass方法,展开看看:
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException { //为了聚焦Import相关处理,此处略去部分不相关代码,不在这里展示了 ... ... // 处理@Import注解 processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true); // 处理@ImportResource注解 if (sourceClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(ImportResource.class.getName())) { AnnotationAttributes importResource = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class); String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("value"); Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader"); for (String resource : resources) { String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource); configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass); } } // 处理@Bean注解,注意是处理注解,不是执行@Bean修饰的方法 Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = sourceClass.getMetadata().getAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName()); for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) { configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass)); } // 处理Configuration类的父类,外面在调用doProcessConfigurationClass方法的时有迭代处理,确保所有父类的注解都会被处理 if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) { String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName(); if (!superclass.startsWith("java") && !this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) { this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass); // Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse return sourceClass.getSuperClass(); } } // 再也没有父类了,返回null表示当前Configuration处理完毕 return null; }
5. 根据上述代码分析,可以梳理出下图中的逻辑:
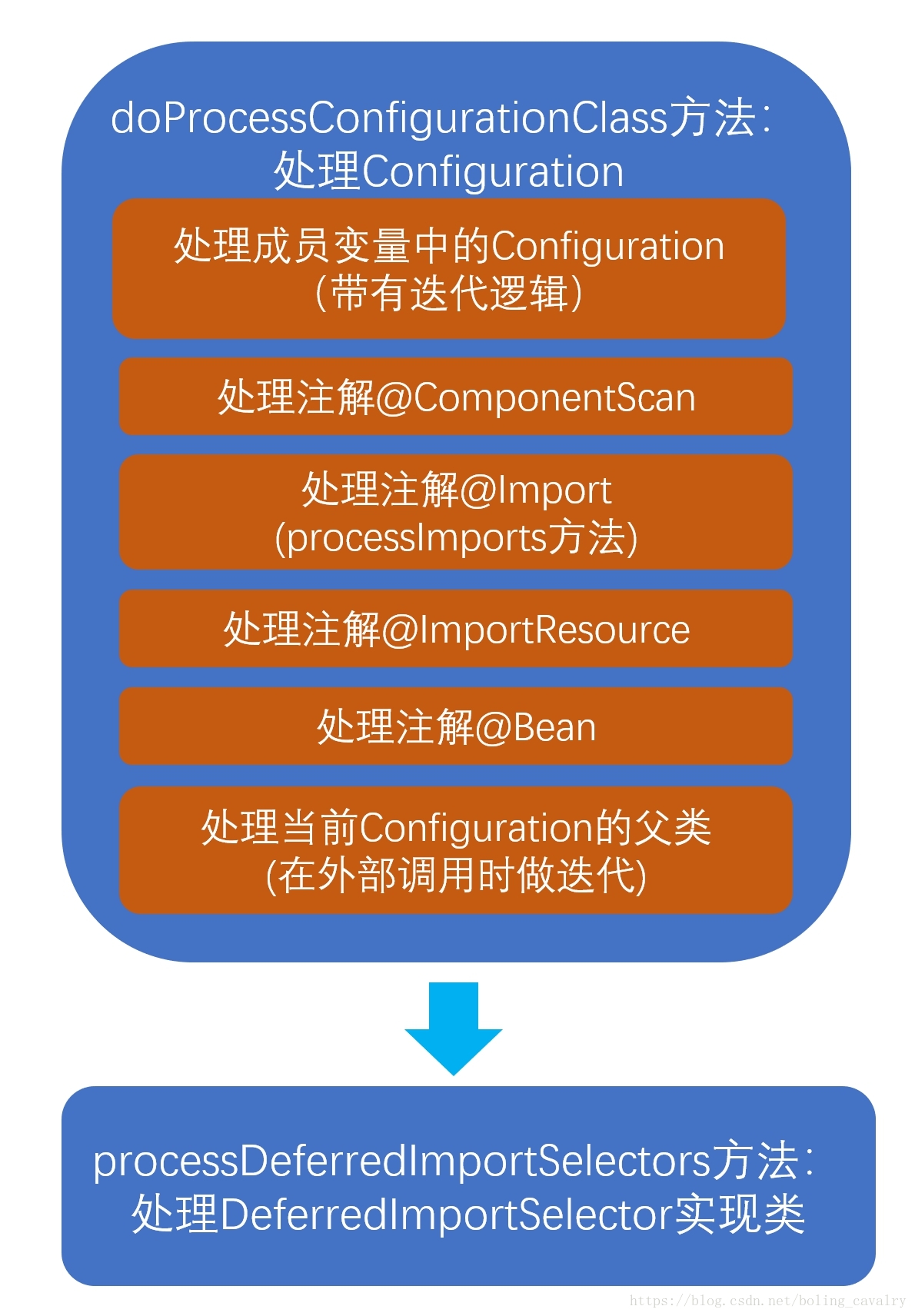
现在需要再看看processImports和processDeferredImportSelectors这两个方法的具体代码;
6. 先看processImports方法:
private void processImports(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass, Collection<SourceClass> importCandidates, boolean checkForCircularImports) throws IOException { if (importCandidates.isEmpty()) { return; } if (checkForCircularImports && this.importStack.contains(configClass)) { this.problemReporter.error(new CircularImportProblem(configClass, this.importStack)); } else { this.importStack.push(configClass); try { for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) { //如果是ImportSelector接口的实现类,就在此处理 if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) { // Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass(); //实例化这些ImportSelector的实现类 ImportSelector selector = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class); //如果这实现类还实现了BeanFactoryAware、EnvironmentAware这些接口,就要先执行这些接口中声明的方法 invokeAwareMethods(selector); //如果这个实现类也实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,就被加入到集合deferredImportSelectors中 if (this.deferredImportSelectors != null && selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) { this.deferredImportSelectors.add( new DeferredImportSelectorHolder(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector)); } else { //注意,这一行是关键代码!!!执行实现类的selectImports方法 String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata()); Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames); processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, false); } } //此处略去的和ImportSelector不相关的逻辑代码 ... ... ... } } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" + configClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex); } finally { this.importStack.pop(); } } }
以上代码有两个关键点:
第一、当前被处理的类,如果实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,就被加入到集合deferredImportSelectors中;
第二、当前被处理的类,如果没有实现DeferredImportSelector接口,但是实现了ImportSelector接口,就被执行selectImports方法;
7. 接下来看看processDeferredImportSelectors方法的源码,提前推测应该是处理集合deferredImportSelectors中的所有类,这些类都实现了DeferredImportSelector接口:
private void processDeferredImportSelectors() { List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors; this.deferredImportSelectors = null; //按照Order注解或者Ordered接口进行排序 Collections.sort(deferredImports, DEFERRED_IMPORT_COMPARATOR); for (DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport : deferredImports) { ConfigurationClass configClass = deferredImport.getConfigurationClass(); try { //此处是关键代码,执行DeferredImportSelector实现类的selectImports方法 String[] imports = deferredImport.getImportSelector().selectImports(configClass.getMetadata()); processImports(configClass, asSourceClass(configClass), asSourceClasses(imports), false); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" + configClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex); } } }
至此,源码分析完毕了,从代码可以很清晰的看出ImportSelector与DeferredImportSelector的区别,就是selectImports方法执行时机有差别,这个差别期间,spring容器对此Configguration类做了些其他的逻辑:包括对@ImportResource、@Bean这些注解的处理(注意,这里只是对@Bean修饰的方法的处理,并不是立即调用@Bean修饰的方法,这个区别很重要!);
实例代码见:https://gitee.com/gd1234/springboot-study/tree/master/src/main/java/com/springboot/study



