Semaphore原理以及使用总结
一、Semaphore是什么
Semaphore 通常我们叫它信号量,可以用来控制同时访问特定资源的线程数量,通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用资源。可以把它简单的理解成我们停车场入口立着的那个显示屏,每有一辆车进入停车场显示屏就会显示剩余车位减1,每有一辆车从停车场出去,显示屏上显示的剩余车辆就会加1,当显示屏上的剩余车位为0时,停车场入口的栏杆就不会再打开,车辆就无法进入停车场了,直到有一辆车从停车场出去为止。相当于是一个计数信号量,用于控制共享资源的访问,比如实例化时可以用N表示访问共享资源的计数器。每访问一次,都会将访问的剩余次数进行减一。也是通过AQS来实现此功能的。
二、使用场景
通常用于那些资源有明确访问数量限制的场景,常用于限流。
比如:数据库连接池,同时进行连接的线程有数量限制,连接不能超过一定的数量,当连接达到了限制数量后,后面的线程只能排队等前面的线程释放了数据库连接才能获得数据库连接。
比如:停车场场景,车位数量有限,同时只能容纳多少台车,车位满了之后只有等里面的车离开停车场外面的车才可以进入。
三、Semaphore常用方法说明
acquire() 获取一个令牌,在获取到令牌、或者被其他线程调用中断之前线程一直处于阻塞状态。 acquire(int permits) 获取一个令牌,在获取到令牌、或者被其他线程调用中断、或超时之前线程一直处于阻塞状态。 acquireUninterruptibly() 获取一个令牌,在获取到令牌之前线程一直处于阻塞状态(忽略中断)。 tryAcquire() 尝试获得令牌,返回获取令牌成功或失败,不阻塞线程。 tryAcquire(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 尝试获得令牌,在超时时间内循环尝试获取,直到尝试获取成功或超时返回,不阻塞线程。 release() 释放一个令牌,唤醒一个获取令牌不成功的阻塞线程。 hasQueuedThreads() 等待队列里是否还存在等待线程。 getQueueLength() 获取等待队列里阻塞的线程数。 drainPermits() 清空令牌把可用令牌数置为0,返回清空令牌的数量。 availablePermits() 返回可用的令牌数量。
四、用semaphore 实现停车场提示牌功能。
每个停车场入口都有一个提示牌,上面显示着停车场的剩余车位还有多少,当剩余车位为0时,不允许车辆进入停车场,直到停车场里面有车离开停车场,这时提示牌上会显示新的剩余车位数。
业务场景 :
1、停车场容纳总停车量10。
2、当一辆车进入停车场后,显示牌的剩余车位数响应的减1.
3、每有一辆车驶出停车场后,显示牌的剩余车位数响应的加1。
4、停车场剩余车位不足时,车辆只能在外面等待。
代码:
public class TestCar { //停车场同时容纳的车辆10 public static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(10); public static void main(String[] args) { //模拟100辆车进入停车场 for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){ Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println("===="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"来到停车场"); if(semaphore.availablePermits() == 0){ System.out.println("车位不足,请耐心等待"); } //获取令牌尝试进入停车场 semaphore.acquire(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"成功进入停车场"); //模拟车辆在停车场停留的时间 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10000)); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"驶出停车场"); //释放令牌,腾出停车场车位 semaphore.release(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } },i+"号车"); thread.start(); } } }
五、Semaphore实现原理
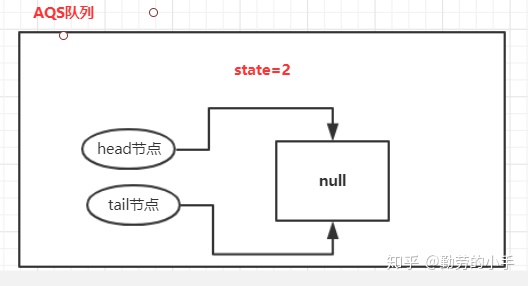
(1)、Semaphore初始化。
Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(2);
1、当调用new Semaphore(2) 方法时,默认会创建一个非公平的锁的同步阻塞队列。
2、把初始令牌数量赋值给同步队列的state状态,state的值就代表当前所剩余的令牌数量。
初始化完成后同步队列信息如下图:
(2)获取令牌
semaphore.acquire();
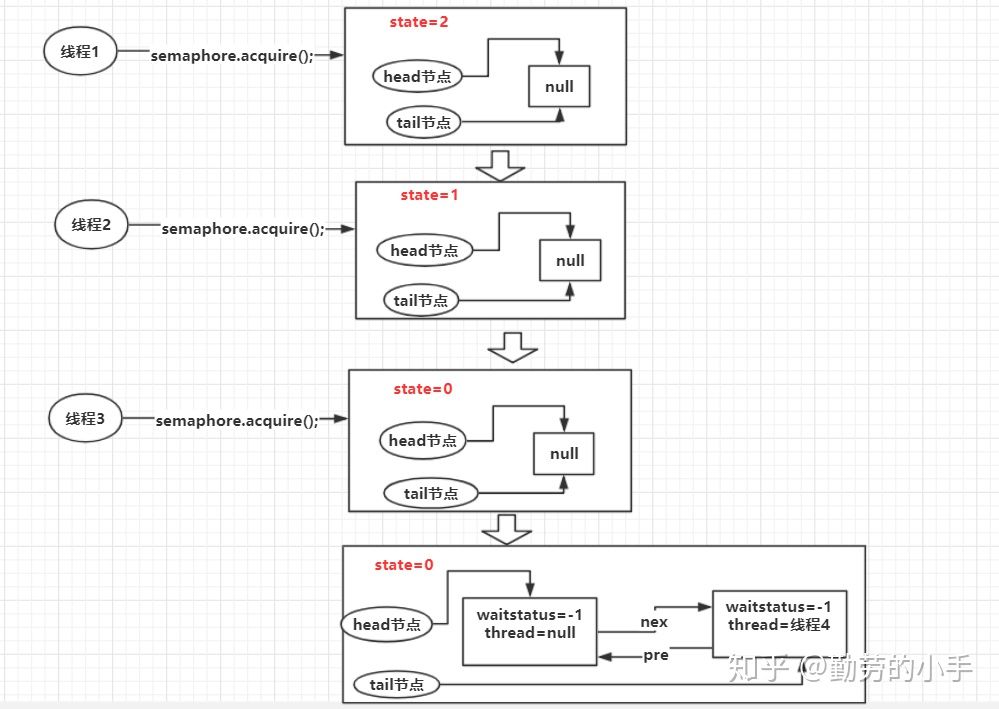
1、当前线程会尝试去同步队列获取一个令牌,获取令牌的过程也就是使用原子的操作去修改同步队列的state ,获取一个令牌则修改为state=state-1。
2、当计算出来的state<0,则代表令牌数量不足,此时会创建一个Node节点加入阻塞队列,挂起当前线程。
3、当计算出来的state>=0,则代表获取令牌成功。
源码:
/** * 获取1个令牌 */ public void acquire() throws InterruptedException { sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1); }
/** * 共享模式下获取令牌,获取成功则返回,失败则加入阻塞队列,挂起线程 * @param arg * @throws InterruptedException */ public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException(); //尝试获取令牌,arg为获取令牌个数,当可用令牌数减当前令牌数结果小于0,则创建一个节点加入阻塞队列,挂起当前线程。 if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg); }
/** * 1、创建节点,加入阻塞队列, * 2、重双向链表的head,tail节点关系,清空无效节点 * 3、挂起当前节点线程 * @param arg * @throws InterruptedException */ private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { //创建节点加入阻塞队列 final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); boolean failed = true; try { for (;;) { //获得当前节点pre节点 final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head) { int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);//返回锁的state if (r >= 0) { setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return; } } //重组双向链表,清空无效节点,挂起当前线程 if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) throw new InterruptedException(); } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
线程1、线程2、线程3、分别调用semaphore.acquire(),整个过程队列信息变化如下图:
(3)、释放令牌
semaphore.release();
当调用semaphore.release() 方法时
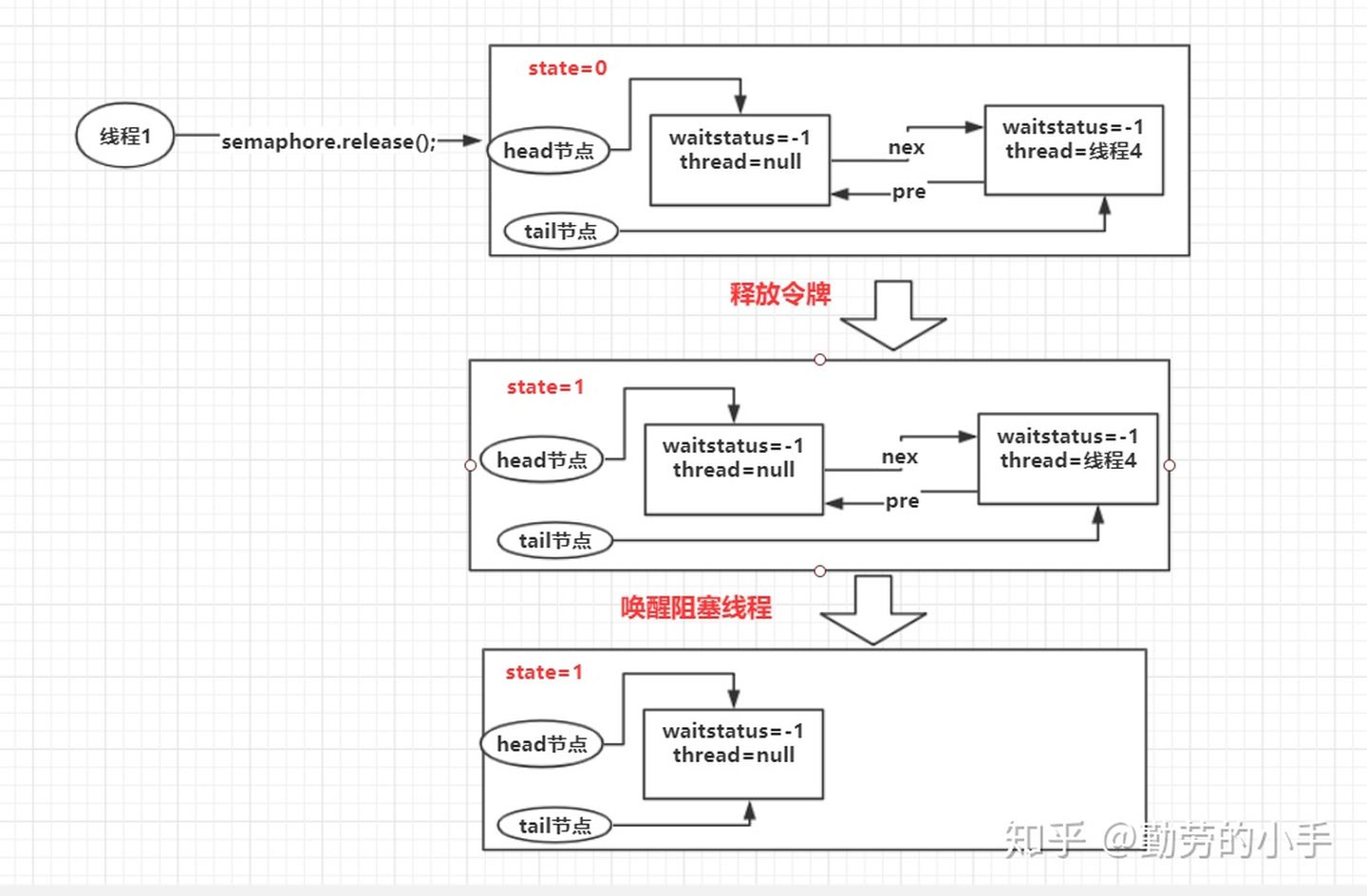
1、线程会尝试释放一个令牌,释放令牌的过程也就是把同步队列的state修改为state=state+1的过程
2、释放令牌成功之后,同时会唤醒同步队列中的一个线程。
3、被唤醒的节点会重新尝试去修改state=state-1 的操作,如果state>=0则获取令牌成功,否则重新进入阻塞队列,挂起线程。
源码:
/** * 释放令牌 */ public void release() { sync.releaseShared(1); }
/** *释放共享锁,同时会唤醒同步队列中的一个线程。 * @param arg * @return */ public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) { //释放共享锁 if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { //唤醒所有共享节点线程 doReleaseShared(); return true; } return false; }
/** * 唤醒同步队列中的一个线程 */ private void doReleaseShared() { for (;;) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h != tail) { int ws = h.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {//是否需要唤醒后继节点 if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))//修改状态为初始0 continue; unparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒h.nex节点线程 } else if (ws == 0 && !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)); } if (h == head) // loop if head changed break; } }
继上面的图,当我们线程1调用semaphore.release(); 时候整个流程如下图:
六、源码解读
看一下Semaphore的两个构造函数:
/** * Creates a {@code Semaphore} with the given number of * permits and nonfair fairness setting. * * @param permits the initial number of permits available. * This value may be negative, in which case releases * must occur before any acquires will be granted. */ public Semaphore(int permits) { sync = new NonfairSync(permits); } /** * Creates a {@code Semaphore} with the given number of * permits and the given fairness setting. * * @param permits the initial number of permits available. * This value may be negative, in which case releases * must occur before any acquires will be granted. * @param fair {@code true} if this semaphore will guarantee * first-in first-out granting of permits under contention, * else {@code false} */ public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) { sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits); }
默认是非公平锁。两个构造方法都必须传int permits值。
这个int值在实例化内部类时,被设置为AQS中的state。
Sync(int permits) { setState(permits); }
(1)、acquire()获取信号
内部类Sync调用AQS中的acquireSharedInterruptibly()方法
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException(); if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg); }
调用tryAcquireShared()方法尝试获取信号。如果没有可用信号,将当前线程加入等待队列并挂起。tryAcquireShared()方法被Semaphore的内部类NonfairSync和FairSync重写,实现有一些区别。
NonfairSync.tryAcquireShared()
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) { for (;;) { int available = getState(); int remaining = available - acquires; if (remaining < 0 || compareAndSetState(available, remaining)) return remaining; } }
可以看到,非公平锁对于信号的获取是直接使用CAS进行尝试的。
FairSync.tryAcquireShared()
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) { for (;;) { if (hasQueuedPredecessors()) return -1; int available = getState(); int remaining = available - acquires; if (remaining < 0 || compareAndSetState(available, remaining)) return remaining; } }
先调用hasQueuedPredecessors()方法,判断队列中是否有等待线程。如果有,直接返回-1,表示没有可用信号。队列中没有等待线程,再使用CAS尝试更新state,获取信号。再看看acquireSharedInterruptibly()方法中,如果没有可用信号加入队列的方法doAcquireSharedInterruptibly()。
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); // 1 boolean failed = true; try { for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head) { // 2 int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); if (r >= 0) { setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return; } } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && // 3 parkAndCheckInterrupt()) throw new InterruptedException(); } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
- 封装一个Node节点,加入队列尾部
- 在无限循环中,如果当前节点是头节点,就尝试获取信号
- 不是头节点,在经过节点状态判断后,挂起当前线程
(2)、release()释放信号
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) { if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { // 1 doReleaseShared(); // 2 return true; } return false; }
- 更新state加一
- 唤醒等待队列头节点线程
tryReleaseShared()方法在内部类Sync中被重写
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) { for (;;) { int current = getState(); int next = current + releases; if (next < current) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded"); if (compareAndSetState(current, next)) return true; } }
这里也就是直接使用CAS算法,将state也就是可用信号,加1。



