ThreadLocal内存泄露总结
ThreadLoacal为每个线程都提供了变量的副本,使得每个线程在某个时间访问到,这样对线程间的数据进行了隔离。如下图所以:

ThreadLocal的使用
ThreadLocal类接口很简单,只有4个方法。
1 1:public void set(T value) ;
2 2:public T get() ;
3 3:public void remove() ;
4 4:protected Object initialValue()
1:设置当前线程的线程局部变量的值。
2:该方法返回当前线程所对应的线程局部变量。
3:将当前线程局部变量的值删除,目的是为了减少内存的占用,该方法是JDK 5.0新增的方法。需要指出的是,当线程结束后,对应该线程的局部变量将自动被垃圾回收,所以显式调用该方法清除线程的局部变量并不是必须的操作,但它可以加快内存回收的速度。
4:返回该线程局部变量的初始值,该方法是一个protected的方法,显然是为了让子类覆盖而设计的。这个方法是一个延迟调用方法,在线程第1次调用get()或set(Object)时才执行,并且仅执行1次。ThreadLocal中的缺省实现直接返回一个null。
ThreadLocal解析
1 /**
2 * Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
3 * thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
4 * current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
5 * by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
6 *
7 * @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
8 */
9 public T get() {
10 Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
11 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
12 if (map != null) {
13 ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
14 if (e != null) {
15 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
16 T result = (T)e.value;
17 return result;
18 }
19 }
20 return setInitialValue();
21 }
1 /**
2 * Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
3 * to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
4 * override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
5 * method to set the values of thread-locals.
6 *
7 * @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
8 * this thread-local.
9 */
10 public void set(T value) {
11 Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
12 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
13 if (map != null)
14 map.set(this, value);
15 else
16 createMap(t, value);
17 }
1 /**
2 * Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
3 * InheritableThreadLocal.
4 *
5 * @param t the current thread
6 * @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
7 */
8 void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
9 t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
10 }
1 static class ThreadLocalMap { 2 3 /** 4 * The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using 5 * its main ref field as the key (which is always a 6 * ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get() 7 * == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the 8 * entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to 9 * as "stale entries" in the code that follows. 10 */ 11 static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { 12 /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ 13 Object value; 14 15 Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { 16 super(k); 17 value = v; 18 } 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two. 23 */ 24 private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; 25 26 /** 27 * The table, resized as necessary. 28 * table.length MUST always be a power of two. 29 */ 30 private Entry[] table; 31 32 ......
可以看到有个Entry内部静态类,它继承了WeakReference,总之它记录了两个信息,一个是ThreadLocal<?>类型,一个是Object类型的值。getEntry方法则是获取某个ThreadLocal对应的值,set方法就是更新或赋值相应的ThreadLocal对应的值。
1 private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) { 2 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1); 3 Entry e = table[i]; 4 if (e != null && e.get() == key) 5 return e; 6 else 7 return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e); 8 }
1 private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) { 2 Entry[] tab = table; 3 int len = tab.length; 4 5 while (e != null) { 6 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 7 if (k == key) 8 return e; 9 if (k == null) 10 expungeStaleEntry(i); 11 else 12 i = nextIndex(i, len); 13 e = tab[i]; 14 } 15 return null; 16 }
利用getEntryAfterMiss方法找到Entry或者调用expungeStaleEntry方法处理key为null。这里nextIndex去处理当前hash冲突。
Hash冲突怎么解决
与Hashmap不同,ThreadLocal用的是一种线性探测的方式处理,根据hashcode值确定元素在table数组中的位置,如果发现这个位置已经有其他元素和位置冲突就存放下一个为空的位置。
1 private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { 2 3 // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at 4 // least as common to use set() to create new entries as 5 // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast 6 // path would fail more often than not. 7 8 Entry[] tab = table; 9 int len = tab.length; 10 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); 11 12 for (Entry e = tab[i]; 13 e != null; 14 e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { 15 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 16 17 if (k == key) { 18 e.value = value; 19 return; 20 } 21 22 if (k == null) { 23 replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); 24 return; 25 } 26 } 27 28 tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); 29 int sz = ++size; 30 if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) 31 rehash(); 32 }
1 /** 2 * Increment i modulo len. 3 */ 4 private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) { 5 return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0); 6 } 7 8 /** 9 * Decrement i modulo len. 10 */ 11 private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) { 12 return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1); 13 }
扩容操作
1 /** 2 * Re-pack and/or re-size the table. First scan the entire 3 * table removing stale entries. If this doesn't sufficiently 4 * shrink the size of the table, double the table size. 5 */ 6 private void rehash() { 7 expungeStaleEntries(); 8 9 // Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis 10 if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4) 11 resize(); 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * Double the capacity of the table. 16 */ 17 private void resize() { 18 Entry[] oldTab = table; 19 int oldLen = oldTab.length; 20 int newLen = oldLen * 2; 21 Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen]; 22 int count = 0; 23 24 for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) { 25 Entry e = oldTab[j]; 26 if (e != null) { 27 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 28 if (k == null) { 29 e.value = null; // Help the GC 30 } else { 31 int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1); 32 while (newTab[h] != null) 33 h = nextIndex(h, newLen); 34 newTab[h] = e; 35 count++; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 40 setThreshold(newLen); 41 size = count; 42 table = newTab; 43 }
当数据超过阈值的四分之三时,扩容2倍,阈值设置为长度的三分之二。
引发的内存泄漏分析
我们可以知道每个Thread 维护一个ThreadLocalMap,这个映射表的key是ThreadLocal实例本身,value是真正需要存储的Object,也就是说ThreadLocal本身并不存储值,它只是作为一个key来让线程从ThreadLocalMap获取value。
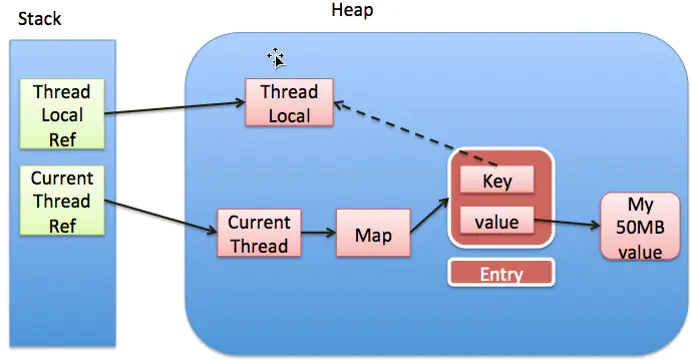
图中的虚线表示弱引用。
这样,当把threadlocal变量置为null以后,没有任何强引用指向threadlocal实例,所以threadlocal将会被gc回收。这样一来,ThreadLocalMap中就会出现key为null的Entry,就没有办法访问这些key为null的Entry的value,如果当前线程再迟迟不结束的话,这些key为null的Entry的value就会一直存在一条强引用链:Thread Ref -> Thread -> ThreaLocalMap -> Entry -> value,而这块value永远不会被访问到了,所以存在着内存泄露。
只有当前thread结束以后,current thread就不会存在栈中,强引用断开,Current Thread、Map value将全部被GC回收。最好的做法是不在需要使用ThreadLocal变量后,都调用它的remove()方法,清除数据。调用remove()方法最佳时机是线程运行结束之前的finally代码块中调用,这样能完全避免操作不当导致的内存泄漏,这种主动清理的方式比惰性删除有效。
1 /** 2 * Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries 3 * lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges 4 * any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null. See 5 * Knuth, Section 6.4 6 * 7 * @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key 8 * @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot 9 * (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked 10 * for expunging). 11 */ 12 private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) { 13 Entry[] tab = table; 14 int len = tab.length; 15 16 // expunge entry at staleSlot 17 tab[staleSlot].value = null; 18 tab[staleSlot] = null; 19 size--; 20 21 // Rehash until we encounter null 22 Entry e; 23 int i; 24 for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); 25 (e = tab[i]) != null; 26 i = nextIndex(i, len)) { 27 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 28 if (k == null) { 29 e.value = null; 30 tab[i] = null; 31 size--; 32 } else { 33 int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); 34 if (h != i) { 35 tab[i] = null; 36 37 // Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until 38 // null because multiple entries could have been stale. 39 while (tab[h] != null) 40 h = nextIndex(h, len); 41 tab[h] = e; 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 return i; 46 }
这个方法在ThreadLocal的set、get、remove时都会被调用,从上面代码中,可以看出先清理指定的Entry,再遍历,如果发现有Entry的key为null,就清理。Key == null,也就是ThreadLocal对象是null。所以当程序中,将ThreadLocal对象设置为null,在该线程继续执行时,如果执行另一个ThreadLocal时,就会触发该方法。就有可能清理掉Key是null的那个ThreadLocal对应的值。所以说expungStaleEntry()方法清除线程ThreadLocalMap里面所有key为null的value。
1 /** 2 * Remove the entry for key. 3 */ 4 private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) { 5 Entry[] tab = table; 6 int len = tab.length; 7 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); 8 for (Entry e = tab[i]; 9 e != null; 10 e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { 11 if (e.get() == key) { 12 e.clear(); 13 expungeStaleEntry(i); 14 return; 15 } 16 } 17 }
在ThreadLocal的实现,我们可以看见,无论是get()、set()在某些时候,调用了expungeStaleEntry方法用来清除Entry中Key为null的Value,但是这是不及时的,也不是每次都会执行的,所以一些情况下还是会发生内存泄露。只有remove()方法中显式调用了expungeStaleEntry方法。
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal>
由于ThreadLocalMap持有ThreadLocal的弱引用,即使没有手动删除,ThreadLocal的对象实例也会被回收。value在下一次ThreadLocalMap调用set,get,remove都有机会被回收。所以说jvm利用弱引用来避免内存泄露,通过remove方法回收弱引用。
小结
key使用强引用:引用ThreadLocal的对象被回收了,但是ThreadLocalMap还持有ThreadLocal的强引用,如果没有手动删除,ThreadLocal的对象实例不会被回收,导致Entry内存泄漏。
key使用弱引用:引用的ThreadLocal的对象被回收了,由于ThreadLocalMap持有ThreadLocal的弱引用,即使没有手动删除,ThreadLocal的对象实例也会被回收。value在下一次ThreadLocalMap调用set,get,remove都有机会被回收
1 public void remove() { 2 ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); 3 if (m != null) 4 m.remove(this); 5 }
使用线程池 + ThreadLocal时要小心,因为这种情况下,线程是一直在不断的重复运行的,如果没有及时的清理,那么之前对该线程的使用,就会影响到后面的线程了,从而也就造成了value可能造成累积的情况,所以要调用remove()方法及时清除来解决。
错误使用ThreadLocal导致线程不安全
1 public class ThreadLocalUnsafe implements Runnable { 2 3 public static Number number = new Number(0); 4 5 public void run() { 6 //每个线程计数加一 7 number.setNum(number.getNum() + 1); 8 //将其存储到ThreadLocal中 9 value.set(number); 10 //输出num值 11 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=" + value.get().getNum()); 12 } 13 14 public static ThreadLocal<Number> value = new ThreadLocal<Number>() { 15 }; 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 19 new Thread(new ThreadLocalUnsafe()).start(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 26 @Data 27 public class Number { 28 29 private int num; 30 31 }
代码中的数据会发生线程不安全的现象(输出的全是5),static修饰的类在JVM中只保存一个实例对象,ThreadLocalMap中保存的其实是对象的一个引用,这样的话,当有其他线程对这个引用指向的对象实例做修改时,其实也同时影响了所有的线程持有的对象引用所指向的同一个对象实例,这样的话会导致每个线程输出的内容一致,而上面的程序要正常的工作,应该的用法是让每个线程中的ThreadLocal都应该持有一个新的Number对象。
总结
ThreadLocal是解决线程安全的一个很好的思路,它通过为每个线程提供了一个独立的变量副本解决了额变量并发访问的冲突问题。在很多情况下,ThreadLocal比直接使用synchronized同步机制解决线程安全问题更简单,更方便,且结果程序拥有更高的并发性。ThreadLocal和synchronize用一句话总结就是一个用存储拷贝进行空间换时间,一个是用锁机制进行时间换空间。



