“无限极”分类数据表设计的简单再总结
前言:项目中又要用到一个四级分类数据表,之前我曾经在这方面按步就班玩过不少CRUD的操作,感觉工作内容有不少重复,有必要再总结一下,对新手可能会有点帮助,同时以备自己日后再用。
1、数据表设计
开门见山,Category表设计如下:
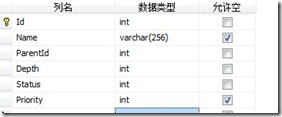
数据表字段简单说明:
| 列名 | 数据类型 | 默认值 | 备注 |
| Id | int | 自增主键 | |
| Name | varchar(256) | 分类类别名称 | |
| ParentId | int | 0 | 父母分类Id |
| Depth | int | 1 | 深度,从1递增 |
| Status | int | 0 | 状态:0禁用,1启用 |
| Priority | int | 0 | 优先级,越大,同级显示的时候越靠前 |
说明:在设计实现这个数据表之前,我搜索参考并比较了一下其他无限层级设计方案,比如这一篇和这一篇,虽然本文最终使用了最常见的层级设计而没有采纳另外的几种方法,但是不可否认它们对开阔设计思路是很有启发的。
2、简单查询
(1)通常,在实际应用中简单查询某一级别可用(Status等于1)的分类非常简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | SELECT [Id] ,[Name] ,[ParentId] ,[Depth] ,[Status] ,[Priority] FROM [Category](NOLOCK) WHERE Status=1 AND Depth=n --n>=1 |
最后按照优先级(Priority)字段逆序即可。
(2)当需要按照某一个Id查找它及它的所有子级或者父级成员,避开递归,直接写sql查询会比较难以下手,而且Sql Server2005之前的版本还需要用到临时表,处理起来不是那么直观。自从Sql Server2005/2008横空出世,利用With语句可用非常轻松地写出查询,下面贴两个开发中经常用到的查询存储过程(Sql Server2005/2008支持):
a、按照某一个Id查询它及它的所有子级成员存储过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_GetChildCategories] (@Id int)ASBEGINWITH Record AS( SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) WHERE Id=@Id UNION ALL SELECT a.Id Id, a.Name Name, a.ParentId ParentId, a.Depth Depth, a.Status Status, a.Priority PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) a JOIN Record b ON a.ParentId=b.Id)SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Record WHERE Status=1 ORDER BY Priority DESC END |
b、按照某一个Id查询它及它的所有父级成员存储过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_GetParentCategories] (@Id int)ASBEGINWITH Record AS( SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) WHERE Id=@Id UNION ALL SELECT a.Id Id, a.Name Name, a.ParentId ParentId, a.Depth Depth, a.Status Status, a.Priority PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) a JOIN Record b ON a.Id=b.ParentId)SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Record WHERE Status=1 ORDER BY Priority DESC END |
分析上面两个存储过程,实际上,您也可以提取出下面的两段sql语句直接代替上面的查询存储过程:
c、按照某一个Id查询它及它的所有子级成员sql语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | WITH Record AS( SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) WHERE Id=@Id --@Id是外部传入的参数 UNION ALL SELECT a.Id Id, a.Name Name, a.ParentId ParentId, a.Depth Depth, a.Status Status, a.Priority PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) a JOIN Record b ON a.ParentId=b.Id)SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Record WHERE Status=1 ORDER BY Priority DESC |
d、按照某一个Id查询它及它的所有父级成员sql语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | WITH Record AS( SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) WHERE Id=@Id --@Id是外部传入的参数 UNION ALL SELECT a.Id Id, a.Name Name, a.ParentId ParentId, a.Depth Depth, a.Status Status, a.Priority PriorityFROM Category(NOLOCK) a JOIN Record b ON a.Id=b.ParentId --匹配关系)SELECT Id, Name, ParentId, Depth, Status, PriorityFROM Record WHERE Status=1 ORDER BY Priority DESC |
参数@Id毫无疑问,是你需要在外部程序里传入的参数。选择存储过程或者直接使用sql语句看自己的喜好(个人倾向于写sql语句)。
3、项目实践经验之谈
在实际项目中,对于分类表,通常都会做相应的缓存(这种类型的数据通常说多也不多,说少也不少,但是相对比较稳定),总结一下我在web项目中的使用经验(经验之谈,请务必小心甄别取舍):
(1)、一次性取出数据库中所有可用分类类别数据;
(2)、数据(Category表数据)转换成对应实体Category;
a、Category实体类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | using System;/// <summary>/// 分类实体/// </summary>[Serializable]public class Category : BaseCategory//继承自BaseCategory{ public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int ParentId { get; set; } public int Depth { get; set; } public int Status { get; set; } public int Priority { get; set; }} |
我们看到,Category实体继承自BaseCategory类,这个类我们定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | public abstract class BaseCategory : DotNet.Common.Model.PagerBase //PagerBase 分页基类{ /// <summary> /// 一级分类id /// </summary> public int FirstCategoryId { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 一级分类名 /// </summary> public string FirstCategoryName { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 二级分类id /// </summary> public int SecondCategoryId { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 二级分类名 /// </summary> public string SecondCategoryName { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 三级分类id /// </summary> public int ThirdCategoryId { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 三级分类名 /// </summary> public string ThirdCategoryName { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 四级分类id /// </summary> public int ForthCategoryId { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 四级分类名 /// </summary> public string ForthCategoryName { get; set; }} |
b、接着通过一定的方法或函数,对Category实体类再做一些处理,完善它的层级关系。比如通过递归函数,初始化一次,准备好这些有层级的数据实体:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 | /// <summary>/// 分类实用帮助类/// </summary>public class CategoryUtil{ /// <summary> /// 分层级的数据实体字典 key: Id value:分类实体 /// </summary> public static IDictionary<int, Category> DictCategories { get; set; } static CategoryUtil() { Init(); } /// <summary> /// 根据品类类别构造一个适合查找的dictionary(1~4级品类ID和对应名称) /// </summary> private static void Init() { //DictProductTypes=//查库,一次取出所有可用分类数据 to do foreach (KeyValuePair<int, Category> kv in DictCategories) { Category model = kv.Value; switch (model.Depth) { default: break; case 1: model.FirstCategoryId = model.Id; model.FirstCategoryName = model.Name; break; case 2: model.SecondCategoryId = model.Id; model.SecondCategoryName = model.Name; break; case 3: model.ThirdCategoryId = model.Id; model.ThirdCategoryName = model.Name; break; case 4: model.ForthCategoryId = model.Id; model.ForthCategoryName = model.Name; break; } InitCascadeCategory(model, model.ParentId, model.Depth); } } /// <summary> /// 初始化层级 /// </summary> /// <param name="query"></param> /// <param name="parentId"></param> /// <param name="depth"></param> private static void InitCascadeCategory(Category query, int parentId, int depth) { if (depth < 2) { return; } foreach (KeyValuePair<int, Category> kv in DictCategories) { Category model = kv.Value; if (parentId == model.Id && model.Depth == depth - 1) { switch (depth) { default: break; case 2: query.FirstCategoryId = model.Id; query.FirstCategoryName = model.Name; break; case 3: query.SecondCategoryId = model.Id; query.SecondCategoryName = model.Name; break; case 4: query.ThirdCategoryId = model.Id; query.ThirdCategoryName = model.Name; break; } InitCascadeCategory(query, model.ParentId, --depth);//递归 break; } } }} |
然后进行第(3)步,进行缓存。
需要特别说明的是,BaseCategory类我们只多设计了8个属性,四个层级(目前为止开发中超过四个层级的我还没有遇到过),当然你可能会问,如果超过4个层级怎么办?曾经看到过有一种通用设计的思路,就是通过一个集合对象(或嵌套的集合对象)进行层级类别的存取,比如泛型Dictionary,LinkedList等等,我还没有尝试实现过,但是设计实现思路确实可以借鉴。
(3)、按照某种策略缓存数据,如每天或者每个月更新一次数据,等等。
(4)、直接查询操作缓存中的分类数据。
4、思考
(1)、数据表中Depth字段是不是必要的,是否多余?
(2)、查询时如何避免递归?
(3)、层级过多(比如超过20层级),有没有更好的设计和解决方法?
… … … …
越想越感到问题多多,期待您的建议和意见。
===============================分割线分割线==============================
update:根据心海巨澜在本文下面的留言,个人感觉是一个非常不错的解决方案,同时想到了一个和它关联紧密的附加问题。举例来说,一个产品表Product,假设产品信息基本字段包括自增长主键Id,产品名称Name,价格Price,生产日期CreateDate,还有就是产品所对应的分类信息,这个分类信息到底应该如何设计才能快速查询出某一分类下的产品(该分类及其子级分类所对应的所有产品),而且利于后台进行修改维护不至于轻易产生“脏”数据?我个人的经验是直接在数据表Product上面设置几个字段,如FirstCategoryId…ForthCategoryId等等,它们具体什么意思看名称就可以猜到了吧?! 简单来说,就是适当冗余,查询非常直接,而且利于创建索引,不知您是怎么看待这个问题的。
数据表脚本下载:Category表
作者:Jeff Wong
出处:http://jeffwongishandsome.cnblogs.com/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎围观转载。转载时请您务必在文章明显位置给出原文链接,谢谢您的合作。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
2009-10-26 iBATIS.net直接执行sql语句
2008-10-26 javascript:面向对象编程基础:继承