Java自学-I/O 控制台输入流System.in
Java 控制台输入流 System.in和Scanner
System.out 是常用的在控制台输出数据的
System.in 可以从控制台输入数据
步骤 1 : System.in
package stream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 控制台输入
try (InputStream is = System.in;) {
while (true) {
// 敲入a,然后敲回车可以看到
// 97 13 10
// 97是a的ASCII码
// 13 10分别对应回车换行
int i = is.read();
System.out.println(i);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
步骤 2 : Scanner读取字符串
使用System.in.read虽然可以读取数据,但是很不方便
使用Scanner就可以逐行读取了
package stream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
String line = s.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}
步骤 3 : Scanner从控制台读取整数
使用Scanner从控制台读取整数
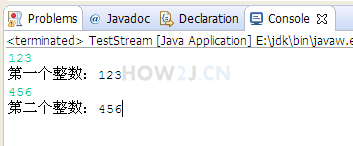
package stream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("第一个整数:"+a);
int b = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("第二个整数:"+b);
}
}
练习: 自动创建类
自动创建有一个属性的类文件。
通过控制台,获取类名,属性名称,属性类型,根据一个模板文件,自动创建这个类文件,并且为属性提供setter和getter

public class @class@ {
public @type@ @property@;
public @class@() {
}
public void set@Uproperty@(@type@ @property@){
this.@property@ = @property@;
}
public @type@ get@Uproperty@(){
return this.@property@;
}
}
答案:
package stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 接受客户输入
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入类的名称:");
String className = s.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入属性的类型:");
String type = s.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入属性的名称:");
String property = s.nextLine();
String Uproperty = toUpperFirstLetter(property);
// 读取模版文件
File modelFile = new File("E:\\project\\j2se\\src\\Model.txt");
String modelContent = null;
try (FileReader fr = new FileReader(modelFile)) {
char cs[] = new char[(int) modelFile.length()];
fr.read(cs);
modelContent = new String(cs);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//替换
String fileContent = modelContent.replaceAll("@class@", className);
fileContent = fileContent.replaceAll("@type@", type);
fileContent = fileContent.replaceAll("@property@", property);
fileContent = fileContent.replaceAll("@Uproperty@", Uproperty);
String fileName = className+".java";
//替换后的内容
System.out.println("替换后的内容:");
System.out.println(fileContent);
File file = new File("E:\\project\\j2se\\src",fileName);
try(FileWriter fw =new FileWriter(file);){
fw.write(fileContent);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("文件保存在:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
}
public static String toUpperFirstLetter(String str){
char upperCaseFirst =Character.toUpperCase(str.charAt(0));
String rest = str.substring(1);
return upperCaseFirst + rest;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号