trie树(字典树)的部分简单实现
什么是trie树(字典树)?
trie树是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构。 和二叉查找树不同,在trie树中,每个结点上并非存储一个元素。
trie树把要查找的关键词看作一个字符序列。并根据构成关键词字符的先后顺序构造用于检索的树结构。 在trie树上进行检索类似于查阅英语词典。 一棵m度的trie树或者为空,或者由m
棵m度的trie树构成。 例如,电子英文词典,为了方便用户快速检索英语单词,可以建立一棵trie树。例如词典由下面的单词构成:a、b、c、aa、ab、ac、ba、ca、aba、abc、baa
bab、bac、cab、abba、baba、caba、abaca、caaba.
下图形象的展示下trie树:
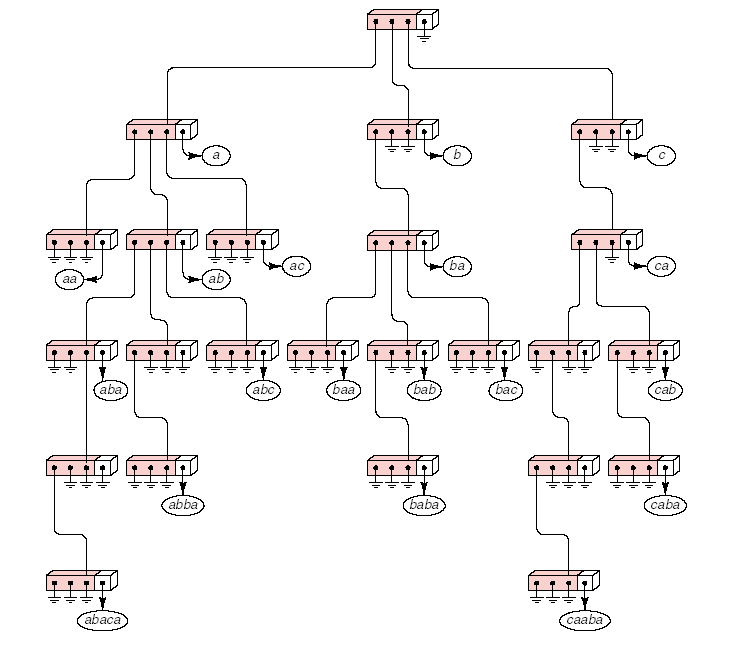
例如在上面图中的trie树中查找单词 aba的流程:
(1)在trie树上进行检索总是始于根结点。
(2)取得要查找关键词的第一个字母(例如 a ),并根据该字母选择对应的子树并转到该子树继续进行检索。
(3)在相应的子树上,取得要查找关键词的第二个字母(例如 b),并进一步选择对应的子树进行检索。
(4) ...
(5)在某个结点处,关键词的所有字母已被取出,则读取附在该结点上的信息,即完成查找。
我的实现代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 5 #define null NULL 6 const int num_chars = 26; 7 8 /*普通的树结点*/ 9 template <typename Entry> 10 class tree_node 11 { 12 public: 13 Entry data; 14 tree_node* first_child; 15 tree_node* next_sibling; 16 tree_node():first_child(null),next_sibling(null){} 17 tree_node(const Entry& x):data(x),first_child(null),next_sibling(null){} 18 }; 19 20 21 22 /*trie树,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构。*/ 23 24 25 //trie树的实现 26 class trie 27 { 28 protected: 29 class trie_node //定义trie树的结点 30 { 31 char* data; 32 trie_node* branch[num_chars]; //常量num_chars = 26 33 trie_node(); 34 }; 35 trie_node* root; //根节点 36 public: 37 trie(); //无参数构造函数 38 trie(trie& tr); //复制构造函数 39 virtual ~trie(); //析构函数 40 int trie_search(const char* word,char* entry) const; //查找操作 41 int insert(const char* word,const char* entry); //插入操作 42 int remove(const char* word,char* entry); //删除操作 43 44 }; 45 46 //trie_node的构造函数 47 trie::trie_node::trie_node() 48 { 49 data = null; 50 for(int i=0;i<num_chars;i++) 51 branch[i] = null; 52 } 53 54 //trie的构造函数 55 trie::trie() 56 { 57 root = null; 58 } 59 60 //trie的检索,查找在某个字符路径结点上的存放的值,并将其放在entry中。比如找对应"abc"的结点上的值并且存放在entry中。 61 int trie::trie_search(const char* word,char* entry) const 62 { 63 int position = 0; 64 char char_code; 65 trie_node* loaction = root; 66 while(location != null && *word != null) 67 { 68 if(*word >= 'A' && *word < 'Z') char_code = *word - 'A'; 69 else if(*word >= 'a' && *word <= 'z') char_code = *word - 'a'; 70 else return 0; 71 location = location->branch[char_code]; 72 position++; 73 word++; 74 } 75 if(location != null && location->data != null) 76 { 77 strcpy(entry,location->data); 78 return 1; 79 } 80 else return 0; 81 } 82 83 //插入操作,此时是往指定的字符串的结点上存放指定的字符串。比如在"abc"位置上防"jeaven"。 84 int trie::insert(const char* word,const char* entry) 85 { 86 int result = 1; 87 int position = 0; 88 if(root == NULL) root = new tire_node(); 89 char char_code; 90 tire_node* location = root; 91 while(location != null && *word != null) 92 { 93 if(*word >= 'a' && *word <= 'z') char_code = *word - 'a'; 94 else if(*word >= 'A' && *word <= 'Z') char_code = *word - 'A'; 95 else return 0; 96 if(location->branch[char_code] == null) 97 location->branch[char_code] = new trie_node(); 98 location = location->branch[char_code]; 99 position++; 100 word++; 101 } 102 103 if(location->branch[char_code] != null) result = 0; 104 else 105 { 106 location->data = new char[strlen(entry)+1]; 107 strcpy(location->data,entry); 108 } 109 return result; 110 } 111 112 113 //删除操作,删除在某字符串路径上的结点存放的值,并且将其放到entry中 114 int trie::remove(const char* word,char* entry) 115 { 116 if(root == null) return 0; 117 trie_node* cur = root; 118 char char_code; 119 while(*word != null) 120 { 121 if(*word >= 'a' && *word <= 'z') char_code = *word - 'a'; 122 else if(*word >= 'A' && *word <= 'Z') char_code = *word - 'A'; 123 else return 0; 124 if(cur->branch[char_code] != null) cur = cur->branch[char_code]; 125 } 126 *entry = cur->data; 127 delete cur; 128 return 1; 129 }
参考:[1] https://www.cnblogs.com/konrad/p/7746030.html
[2] http://blog.csdn.net/guin_guo/article/details/48858339
少一些功利主义的追求,多一些不为什么的坚持!

