LeetCodeHot100 链表 160. 相交链表 206. 反转链表 234. 回文链表 141. 环形链表 142. 环形链表 II 21. 合并两个有序链表 2. 两数相加 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 25. K 个一组翻转链表 138. 随机链表的复制 148. 排序链表 23. 合并 K 个升序链表
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
ListNode p = headA;
while (p != null){
lenA++;
p = p.next;
}
p = headB;
while (p != null){
lenB++;
p = p.next;
}
if (lenA > lenB){
for (int i = 0; i < lenA - lenB; i++) {
headA = headA.next;
}
}else if (lenA < lenB){
for (int i = 0; i < lenB - lenA; i++) {
headB = headB.next;
}
}
while (headA != null){
if (headA == headB){
break;
}else {
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
}
return headA;
}
总结:关键点就是消除长度差
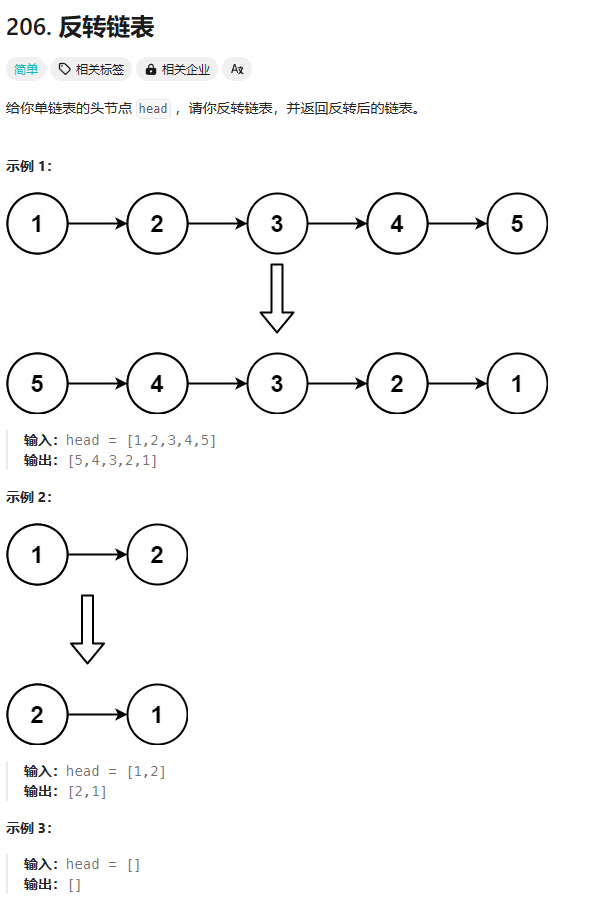
206. 反转链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
总结:三指针,每次两个指针cur指向pre 就完成了反转。
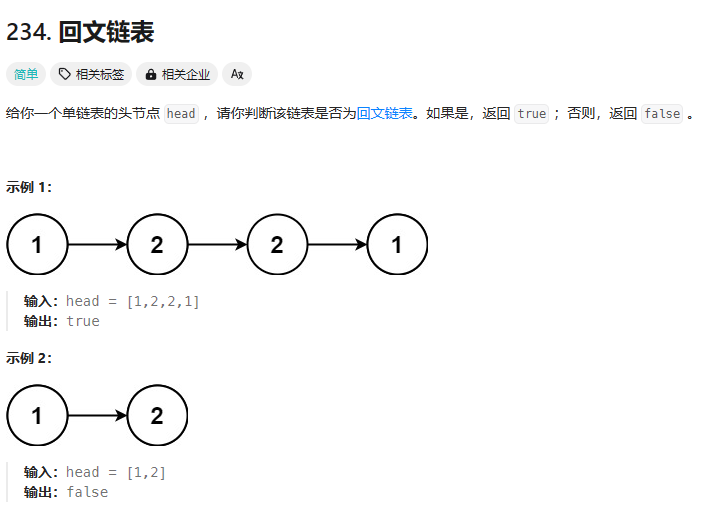
234. 回文链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Deque<ListNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null){
stack.addLast(node);
node = node.next;
}
while (head != null){
ListNode node1 = stack.pollLast();
if (head.val == node1.val){
head = head.next;
}else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
总结:用栈很方便,也可以快慢指针,快的一次两个格,慢的一次一格,去找中点,再反转后半段,再去比较。
141. 环形链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked

public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast){
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return false;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
总结:快慢指针,快的走两个格,慢的走一个格,如果有环,则一定fast和slow能够碰上。
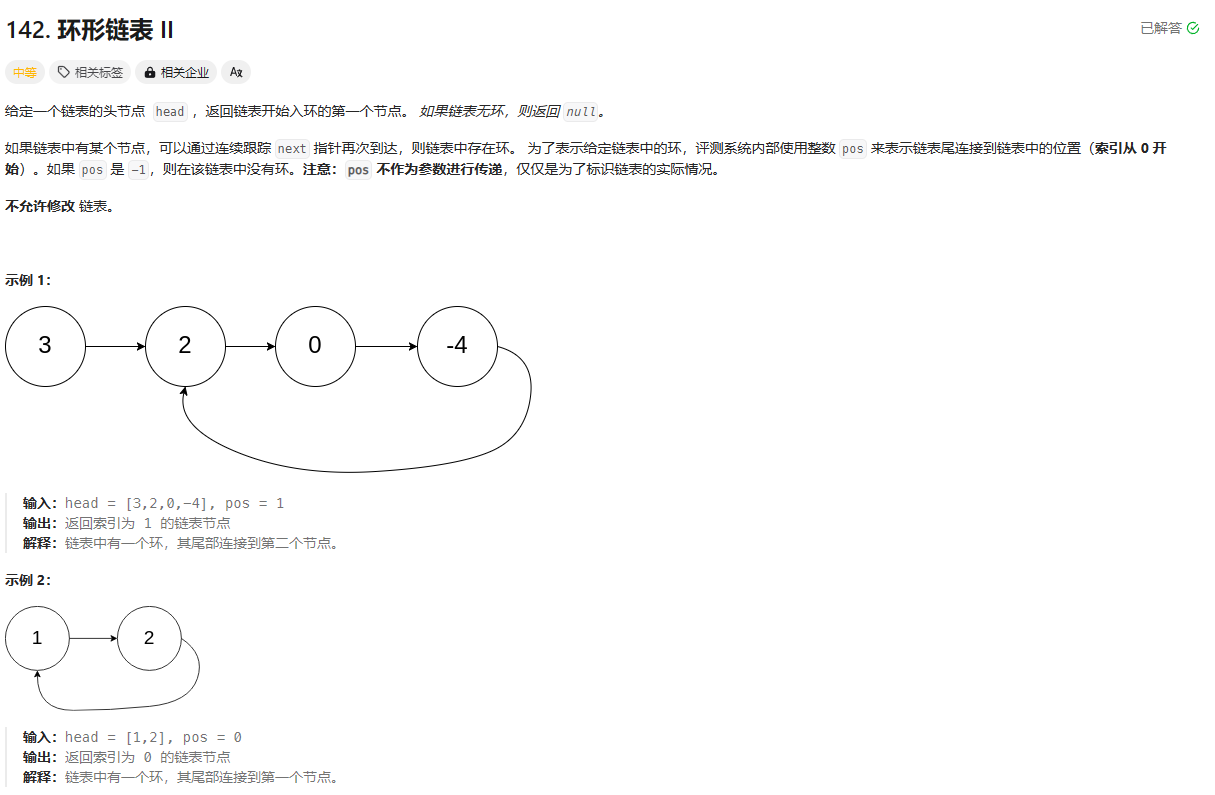
142. 环形链表 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null){
if (set.contains(head)) return head;
set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
总结:hash
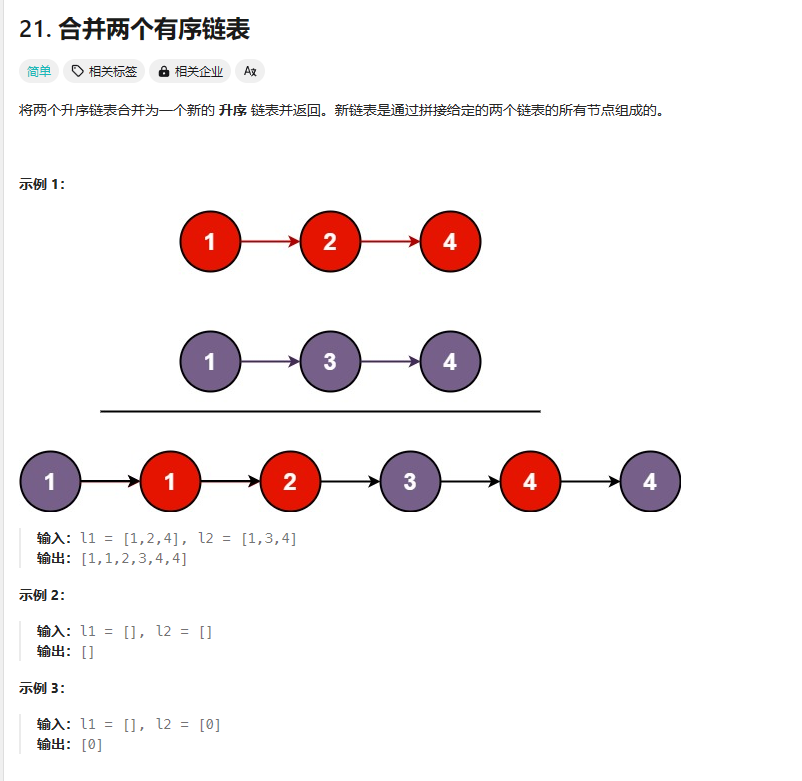
21. 合并两个有序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null){
return list1;
}
if (list1.val < list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}else {
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
总结:合并两个链表用递归很方便
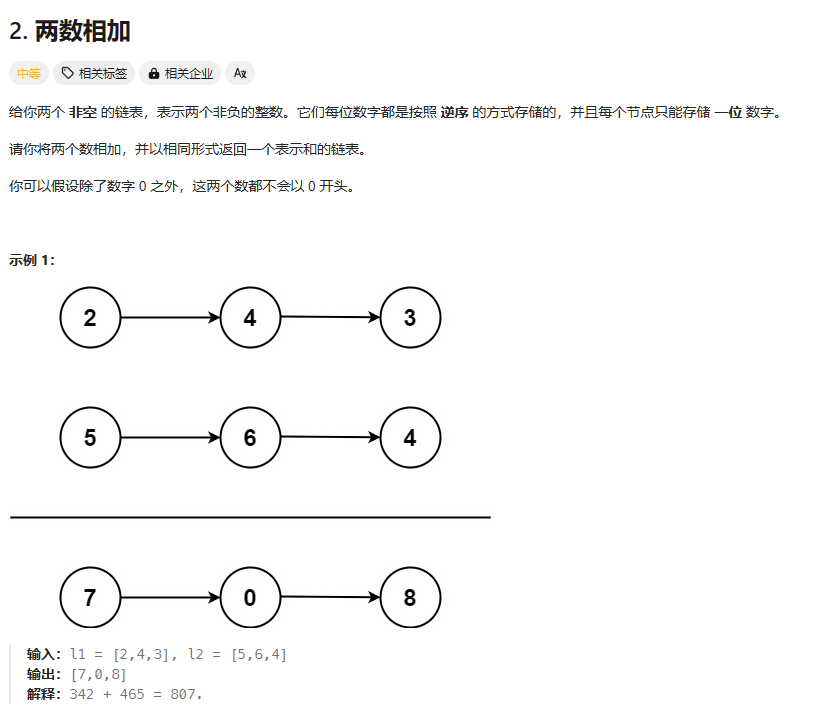
2. 两数相加
https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-two-numbers/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = pre;
int flag = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null){
int x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = x + y + flag;
flag = sum / 10;
int newSum = sum % 10 ;
cur.next = new ListNode(newSum);
cur = cur.next;
if(l1 != null)
l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null)
l2 = l2.next;
}
if (flag == 1){
cur.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return pre.next;
}
总结:每次同时遍历两个链表,取值,有空的就认为是0, 每次构造的新节点的值是 取的两个值+flag 再余10,记得每次更新flag,添加的是newSum。
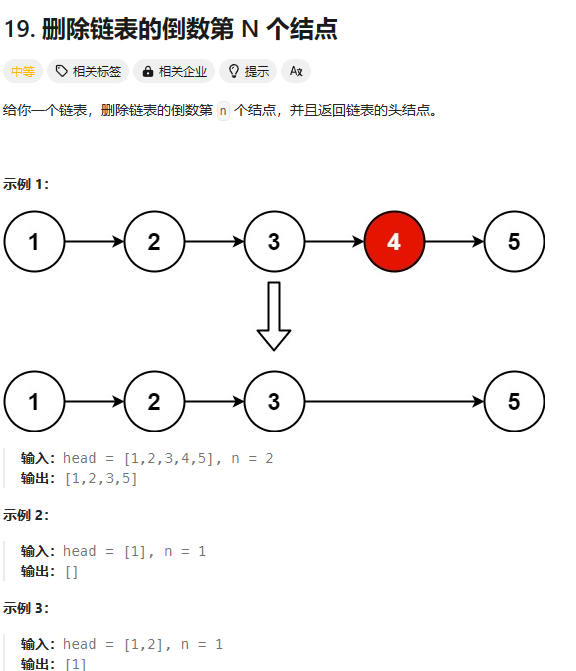
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if (head == null) return head;
int len = 0;
ListNode p = head;
while (p != null){
len++;
p = p.next;
}
ListNode realHead = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode pre = realHead;
for (int i = 0; i < len - n; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = pre.next.next;
return realHead.next;
}
总结:关键点就在于构建虚拟头结点
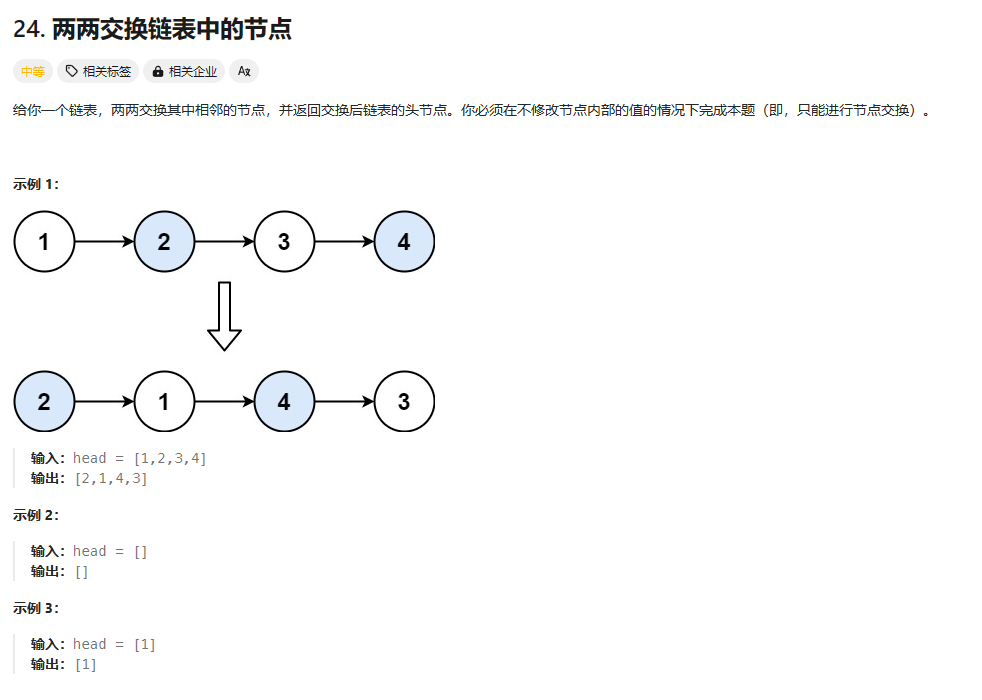
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode pre = newHead;
ListNode node1 = newHead.next;
ListNode node2 = newHead.next.next;
while (node1 != null && node2 != null){
ListNode temp = node2.next;
pre.next = node2;
node2.next = node1;
node1.next = temp;
pre = node1;
node1 = temp;
node2 = temp == null ? null : temp.next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
总结:注意细节
25. K 个一组翻转链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked

public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode hair = new ListNode(0);
hair.next = head;
ListNode pre = hair;
while (head != null) {
ListNode tail = pre;
// 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 k
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
tail = tail.next;
if (tail == null) {
return hair.next;
}
}
ListNode nex = tail.next;
ListNode[] reverse = myReverse(head, tail);
head = reverse[0];
tail = reverse[1];
// 把子链表重新接回原链表
pre.next = head;
tail.next = nex;
pre = tail;
head = tail.next;
}
return hair.next;
}
public ListNode[] myReverse(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
ListNode prev = tail.next;
ListNode p = head;
while (prev != tail) {
ListNode nex = p.next;
p.next = prev;
prev = p;
p = nex;
}
return new ListNode[]{tail, head};
}
总结:就是看翻转的范围,去遍历
138. 随机链表的复制
https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked

public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node p = head;
HashMap<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();
while (p != null){
Node node = new Node(p.val);
map.put(p,node);
p = p.next;
}
p = head;
while (p != null){
Node node = map.get(p);
if (p.next != null){
node.next = map.get(p.next);
}
if (p.random != null){
node.random = map.get(p.random);
}
p = p.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
总结:hashmap存的是老节点和新节点的对应 先把对应关系都put进去,再去遍历老节点,一个个塞next,random
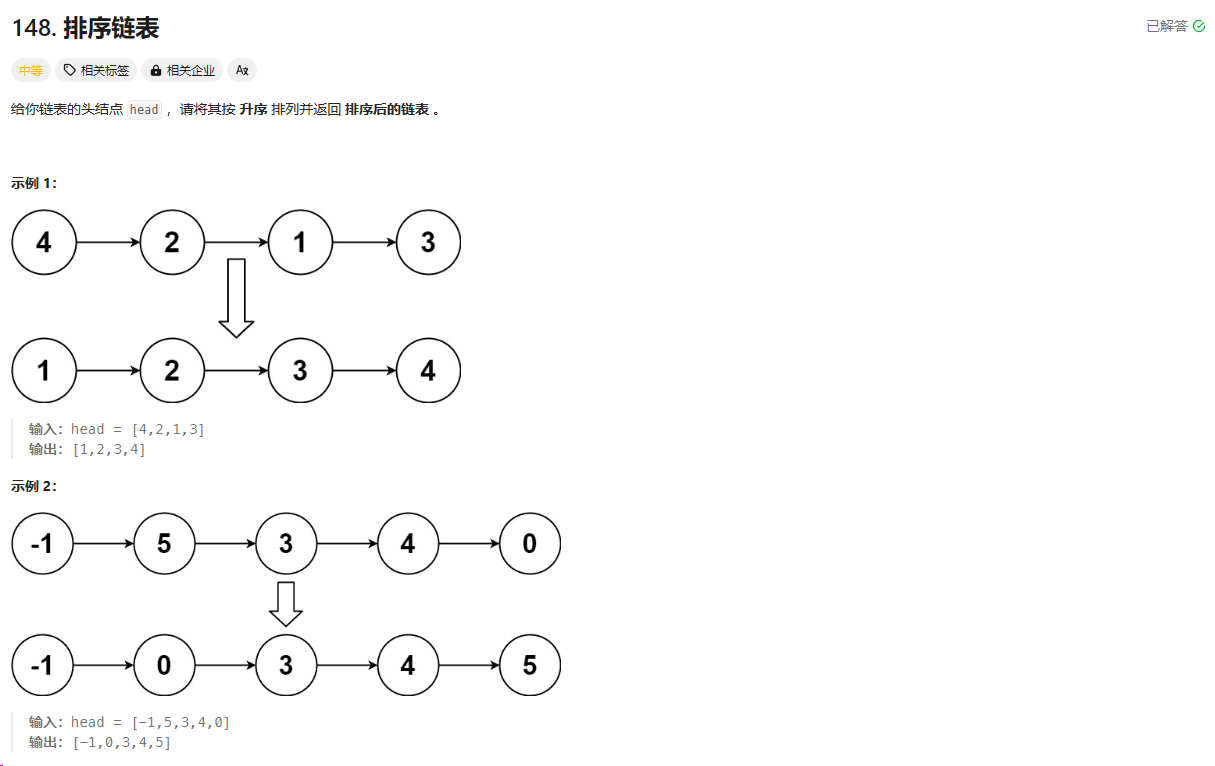
148. 排序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode slowPre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
slowPre = slow;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slowPre.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(slow);
return merge(left,right);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode leftHead,ListNode rightHead){
ListNode realHead = new ListNode();
ListNode pre = realHead;
ListNode p1 = leftHead;
ListNode p2 = rightHead;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null){
if (p1.val < p2.val){
pre.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
}else {
pre.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
if (p1 != null){
pre.next = p1;
}else {
pre.next = p2;
}
return realHead.next;
}
总结:归并排序,每次从中点分割链表,然后两边递归,两边都是有序的,把两边合并成一个有序的再返回。
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked

public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) return null;
return mergrHelper(lists,0, lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode mergrHelper(ListNode[] lists,int start,int end){
if (start == end) return lists[start];
int mid = start + ((end - start) / 2);
ListNode left = mergrHelper(lists, start, mid);
ListNode right = mergrHelper(lists, mid + 1, end);
return merge(left,right);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode leftHead,ListNode rightHead){
ListNode realHead = new ListNode();
ListNode pre = realHead;
ListNode p1 = leftHead;
ListNode p2 = rightHead;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null){
if (p1.val < p2.val){
pre.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
}else {
pre.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
if (p1 != null){
pre.next = p1;
}else {
pre.next = p2;
}
return realHead.next;
}
总结:递归 ,两两合并,分治思想。 也可以用小根堆去做,每次把最小的点插入 小根堆如下,代码很简洁。
//小根堆解法
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.val - o2.val);
for (ListNode list : lists) {
if (list != null) queue.add(list);
}
ListNode realHead = new ListNode();
ListNode pre = realHead;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
ListNode curMin = queue.poll();
pre.next = curMin;
pre = pre.next;
if (curMin.next != null) queue.add(curMin.next);
}
return realHead.next;
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?