代码随想录算法训练营第十八天| 513. 找树左下角的值 112. 路径总和 113. 路径总和 II 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
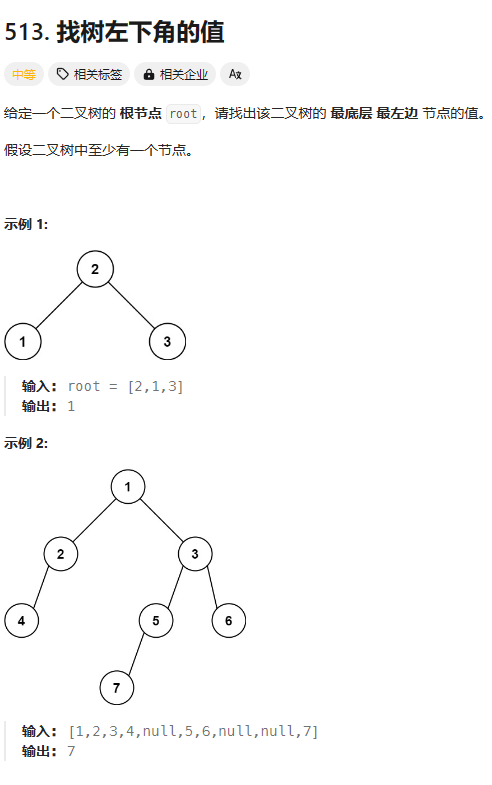
513. 找树左下角的值
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/description/
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
int val = 0;
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.offer(root);
while (!deque.isEmpty()){
int len = deque.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
if (i == 0) val = node.val;
if (node.left != null) deque.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) deque.offer(node.right);
}
}
return val;
}
总结:层序遍历
112. 路径总和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/description/

public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) return false;
boolean sum = sum(root, targetSum);
return sum;
}
public boolean sum(TreeNode node,int sum){
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return sum - node.val == 0; // 到达叶子节点时判断路径和是否等于目标和
}
boolean sumLeft = false;
boolean sumRight = false;
if (node.left != null) {
sumLeft = sum(node.left, sum - node.val);
}
if (node.right != null){
sumRight = sum(node.right, sum - node.val);
}
return sumLeft || sumRight;
}
总结:递归到叶子节点,判断是否合理
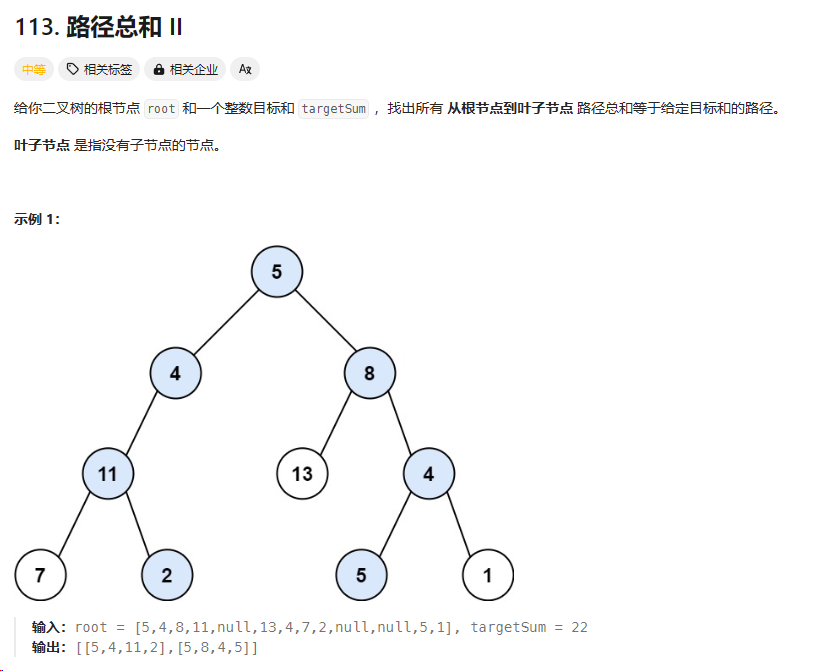
113. 路径总和 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/description/
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return resList;
pathSSum(root,targetSum,resList,path);
return resList;
}
public void pathSSum(TreeNode node,int targetSum,List<List<Integer>> resList,List<Integer> path){
if (node.left == null && node.right == null){
if (targetSum - node.val == 0){
path.add(node.val);
resList.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
path.remove(path.size() - 1); //回溯
}
return;
}
if (node.left != null){
path.add(node.val);
pathSSum(node.left,targetSum - node.val,resList,path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); //回溯
}
if (node.right != null){
path.add(node.val);
pathSSum(node.right,targetSum - node.val,resList,path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); //回溯
}
}
总结:带了点回溯
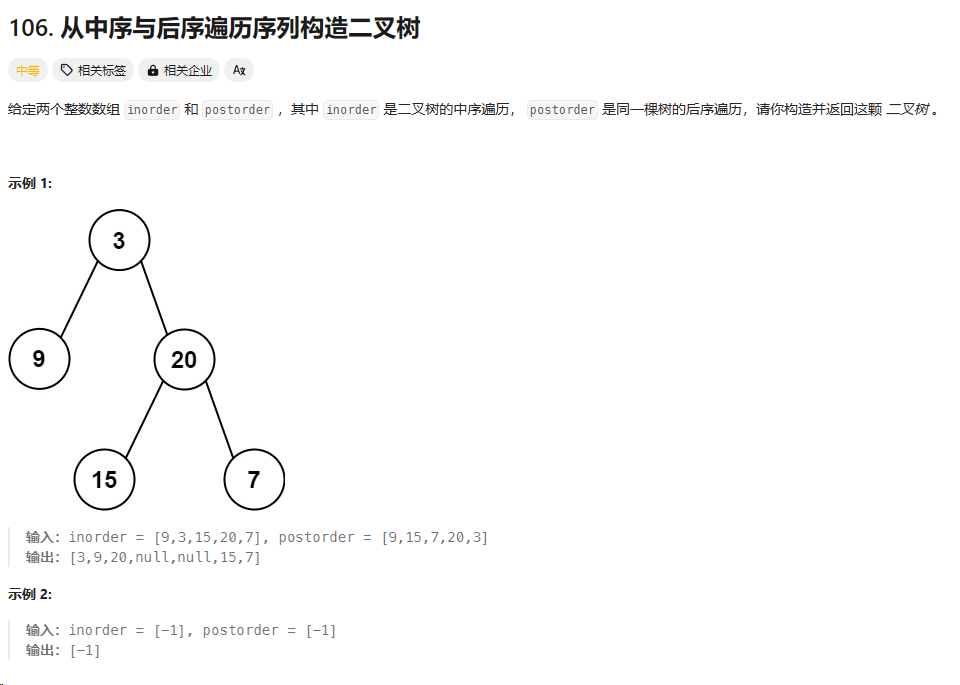
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/description/
int post_idx;
int[] postorder;
int[] inorder;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
this.postorder = postorder;
this.inorder = inorder;
// 从后序遍历的最后一个元素开始
post_idx = postorder.length - 1;
// 建立(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return helper(0, inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int in_left, int in_right) {
// 如果这里没有节点构造二叉树了,就结束
if (in_left > in_right) {
return null;
}
// 选择 post_idx 位置的元素作为当前子树根节点
int root_val = postorder[post_idx];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(root_val);
// 根据 root 所在位置分成左右两棵子树
int index = map.get(root_val);
// 下标减一
post_idx--;
// 构造右子树
root.right = helper(index + 1, in_right);
// 构造左子树
root.left = helper(in_left, index - 1);
return root;
}
总结:力扣官方的代码,递归中每次传中序数组的左右边界,每次递归把当前的root拿出来去给他构造left,right。返回当前root,注意这里要先构造右子树,再左子树,因为后序数组的遍历是先右再左的。
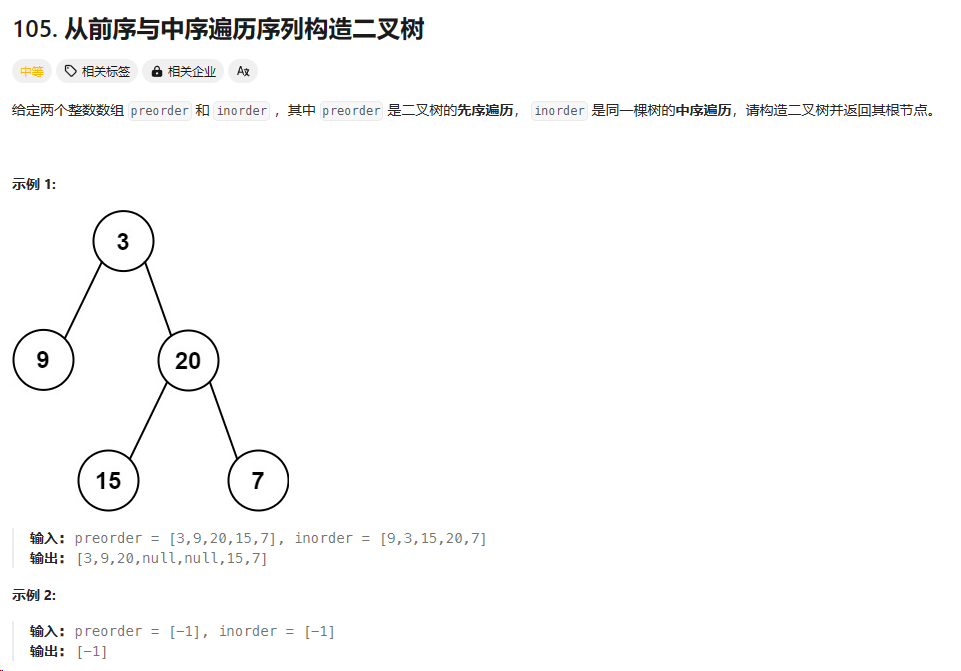
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/description/
int[] preorder;
int[] inorder;
int pre_index;
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.preorder = preorder;
this.inorder = inorder;
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
pre_index = 0;
return helper(0,inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int left,int right){
if (left > right) return null;
int concurrentRootVal = preorder[pre_index];
pre_index++;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(concurrentRootVal);
int index = map.get(concurrentRootVal);
node.left = helper(left,index - 1);
node.right = helper(index + 1 ,right);
return node;
}
总结:力扣官方的代码,递归中每次传中序数组的左右边界,每次递归把当前的root拿出来去给他构造left,right。返回当前root,注意这里要先构造左子树,再右子树,因为前序数组的遍历是先左再右的。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号