利用sklearn对多分类的每个类别进行指标评价
今天晚上,笔者接到客户的一个需要,那就是:对多分类结果的每个类别进行指标评价,也就是需要输出每个类型的精确率(precision),召回率(recall)以及F1值(F1-score)。
对于这个需求,我们可以用sklearn来解决,方法并没有难,笔者在此仅做记录,供自己以后以及读者参考。
我们模拟的数据如下:
y_true = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '北京', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
y_pred = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
其中y_true为真实数据,y_pred为多分类后的模拟数据。使用sklearn.metrics中的classification_report即可实现对多分类的每个类别进行指标评价。
示例的Python代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
y_true = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '北京', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
y_pred = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
t = classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=['北京', '上海', '成都'])
print(t)
输出结果如下:
precision recall f1-score support
北京 0.75 0.75 0.75 4
上海 1.00 0.67 0.80 3
成都 0.50 0.67 0.57 3
accuracy 0.70 10
macro avg 0.75 0.69 0.71 10
weighted avg 0.75 0.70 0.71 10
需要注意的是,输出的结果数据类型为str,如果需要使用该输出结果,则可将该方法中的output_dict参数设置为True,此时输出的结果如下:
{'北京': {'precision': 0.75, 'recall': 0.75, 'f1-score': 0.75, 'support': 4},
'上海': {'precision': 1.0, 'recall': 0.6666666666666666, 'f1-score': 0.8, 'support': 3},
'成都': {'precision': 0.5, 'recall': 0.6666666666666666, 'f1-score': 0.5714285714285715, 'support': 3},
'accuracy': 0.7,
'macro avg': {'precision': 0.75, 'recall': 0.6944444444444443, 'f1-score': 0.7071428571428572, 'support': 10},
'weighted avg': {'precision': 0.75, 'recall': 0.7, 'f1-score': 0.7114285714285715, 'support': 10}}
使用confusion_matrix方法可以输出该多分类问题的混淆矩阵,代码如下:
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
y_true = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '北京', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
y_pred = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
print(confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, labels = ['北京', '上海', '成都']))
输出结果如下:
[[2 0 1]
[0 3 1]
[0 1 2]]
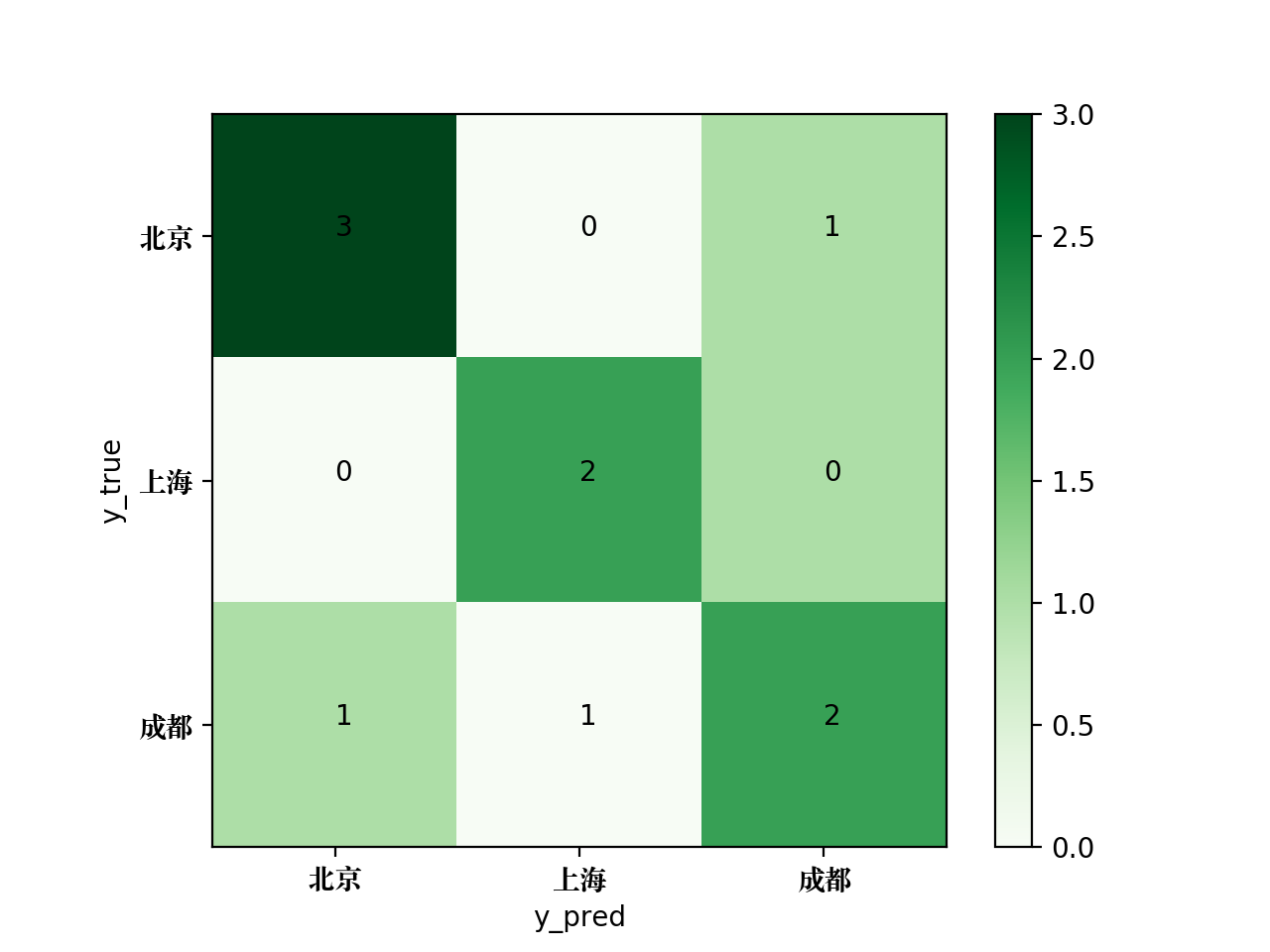
为了将该混淆矩阵绘制成图片,可使用如下的Python代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# author: Jclian91
# place: Daxing Beijing
# time: 2019-11-14 21:52
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
# 支持中文字体显示, 使用于Mac系统
zhfont=mpl.font_manager.FontProperties(fname="/Library/Fonts/Songti.ttc")
y_true = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '北京', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
y_pred = ['北京', '上海', '成都', '上海', '成都', '成都', '上海', '成都', '北京', '上海']
classes = ['北京', '上海', '成都']
confusion = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
# 绘制热度图
plt.imshow(confusion, cmap=plt.cm.Greens)
indices = range(len(confusion))
plt.xticks(indices, classes, fontproperties=zhfont)
plt.yticks(indices, classes, fontproperties=zhfont)
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('y_pred')
plt.ylabel('y_true')
# 显示数据
for first_index in range(len(confusion)):
for second_index in range(len(confusion[first_index])):
plt.text(first_index, second_index, confusion[first_index][second_index])
# 显示图片
plt.show()
生成的混淆矩阵图片如下:
本次分享到此结束,感谢大家阅读,也感谢在北京大兴待的这段日子,当然还会再待一阵子~



