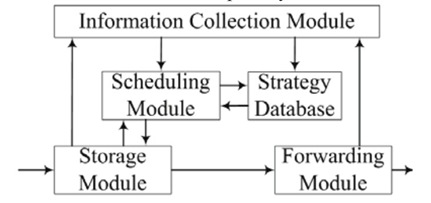
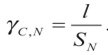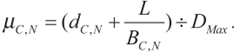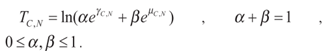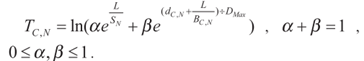A DTN Congestion Mechanism Based on Distributed Storage
Author:Daowen Hua, Xuehui Du, Guoyu Xu, Lifeng Cao, Huan Chen
Year:2010
Bundle Selection:
The bundle seleciton considers three factors:left TTL, size of bundle,priority of bundle.
Ajacent Nodes Selection:
Take the Migration Value ![]() as the evaluation metric of the node selection which includes 3 aspects:node storage,link delay and link bandwidth.
as the evaluation metric of the node selection which includes 3 aspects:node storage,link delay and link bandwidth.
General hypothesis:
- the length of bundle is L
- the storage of neighbour N adjacent to custodian C is
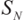 .
. - Storage value is
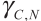 .
. - Delay from C to N is
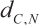 .
. - corresponding link bandwidth is
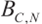 .
. - maximum delivery delay is
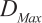
- Delivery value is
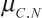
When congestion appears at a custodian, it calculates the migration value for its adjacent neighbours and selects the minimum one.
Bundle Retrieval:
If the adjacent node (holding the migrated bundles) finds new forwarding path for these migrated bundles, these bundles will be forwarded rather than migrating back to previous custodian, and a notification will be sent to the previous custodian.Or it will wait until the previous custodian resolves congestion.
The retrieval algorithm is opposite to the previous migration from congestion custodian to neighbours.
If the previous custodian knows the locaiton of the bundles it previously migrated,it sends a single request to the specified neighbour otherwise it will send a group request.
There are two points:the contact should be established to take the bundles back;the bundles with high priority and less size should be preferred.
Simulation:
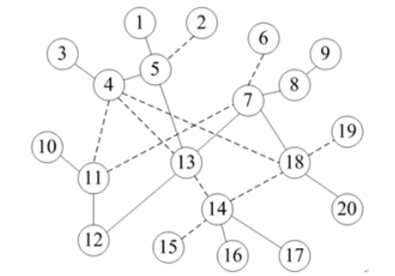
Simulation enviroment:OPENET
Network topology: