HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 最小生成树+DFS
Minimal Ratio Tree
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
【Problem Description】
For a tree, which nodes and edges are all weighted, the ratio of it is calculated according to the following equation.![]()
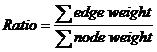
【Input】
Input contains multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains two integers n (2<=n<=15) and m (2<=m<=n), which stands for the number of nodes in the graph and the number of nodes in the minimal ratio tree. Two zeros end the input. The next line contains n numbers which stand for the weight of each node. The following n lines contain a diagonally symmetrical n×n connectivity matrix with each element shows the weight of the edge connecting one node with another. Of course, the diagonal will be all 0, since there is no edge connecting a node with itself.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
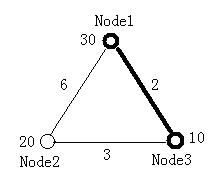
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.![]()
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.
【Output】
For each test case output one line contains a sequence of the m nodes which constructs the minimal ratio tree. Nodes should be arranged in ascending order. If there are several such sequences, pick the one which has the smallest node number; if there's a tie, look at the second smallest node number, etc. Please note that the nodes are numbered from 1 .
【Sample Input】
3 2 30 20 10 0 6 2 6 0 3 2 3 0 2 2 1 1 0 2 2 0 0 0
【Sample Output】
1 3 1 2
【题意】
给出一张n个点的图,图中的每一个结点以及每一条边都有其权值,要求从中选出m个点,找到m-1条边将其连接,使得边权值与点权值的比值达到最小。
【分析】
要使得比值最小,则点权值和尽可能地大同时边权值和尽可能地小。直接上考虑,边权值和尽可能小即对这m个点作最小生成树。
而题目给定的n不大,故可以用DFS搜出需要的m个点,然后对m个点进行最小生成树,中间注意判断和保存即可。
我用了一个dijkstra+优先队列的prim去找MST,这也是我第一次尝试使用STL的优先队列。

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<queue> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 bool flag[16],outp[16]; 9 int n,m,node[16]; 10 int ma[16][16]; 11 double mi; 12 13 typedef struct heaptyp 14 { 15 int num,key; 16 friend bool operator < (heaptyp a,heaptyp b) 17 { 18 return a.num>b.num; 19 } 20 } heaptype; 21 22 void prim(int s,int tot) 23 { 24 int i,j,now,ans; 25 bool fla[16]; 26 priority_queue<heaptype>heap; 27 heaptype aaa; 28 29 memset(fla,0,sizeof(fla)); 30 fla[s]=true; 31 ans=0; 32 for (i=1;i<=n;i++) 33 if (flag[i]&&ma[s][i]) 34 { 35 heaptype temp; 36 temp.num=ma[s][i]; 37 temp.key=i; 38 heap.push(temp); 39 aaa=heap.top(); 40 } 41 42 for (j=1;j<m;j++) 43 { 44 heaptype h=heap.top(); 45 heap.pop(); 46 aaa=heap.top(); 47 while (fla[h.key]) 48 { 49 h=heap.top(); 50 heap.pop(); 51 } 52 now=h.key; 53 fla[now]=true; 54 ans+=h.num; 55 for (i=1;i<=n;i++) 56 if (flag[i]&&ma[now][i]) 57 if (!fla[i]) 58 { 59 heaptype temp; 60 temp.num=ma[now][i]; 61 temp.key=i; 62 heap.push(temp); 63 aaa=heap.top(); 64 } 65 } 66 double rat=(double)ans/tot; 67 if (mi-rat>0.0000001) 68 { 69 mi=rat; 70 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) outp[i]=fla[i]; 71 } 72 } 73 74 void dfs(int now,int last,int tot) 75 { 76 if (now==m) 77 { 78 int i; 79 for (i=1;i<=n;i++) 80 if (flag[i]) break; 81 prim(i,tot); 82 } 83 else 84 { 85 now++; 86 for (int i=last+1;i<=n-m+now;i++) 87 { 88 flag[i]=true; 89 dfs(now,i,tot+node[i]); 90 flag[i]=false; 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 95 int main() 96 { 97 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 98 while (!(n==0&&m==0)) 99 { 100 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&node[i]); 101 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 102 for (int j=1;j<=n;j++) scanf("%d",&ma[i][j]); 103 104 mi=2147483647; 105 memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag)); 106 for (int i=1;i<=n-m+1;i++) 107 { 108 flag[i]=true; 109 dfs(1,i,node[i]); 110 flag[i]=false; 111 } 112 113 int i; 114 for (i=1;i<=n;i++) 115 if (outp[i]) 116 { 117 printf("%d",i); 118 break; 119 } 120 for (int j=i+1;j<=n;j++) 121 if (outp[j]) printf(" %d",j); 122 printf("\n"); 123 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 124 } 125 126 return 0; 127 }
Do Cool Things That Matter!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号