动态代理的两种方式,以及区别(静态代理、JDK与CGLIB动态代理、AOP+IoC)
Spring学习总结(二)——静态代理、JDK与CGLIB动态代理、AOP+IoC
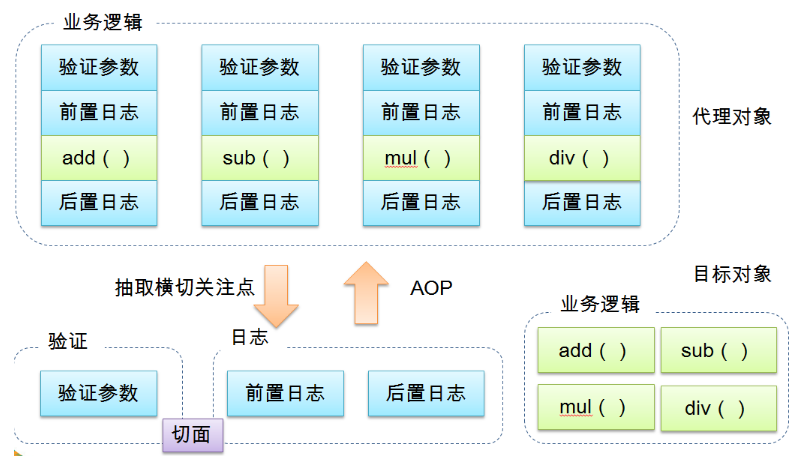
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
一、为什么需要代理模式
假设需实现一个计算的类Math、完成加、减、乘、除功能,如下所示:
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop01;
2
3 public class Math {
4 //加
5 public int add(int n1,int n2){
6 int result=n1+n2;
7 System.out.println(n1+"+"+n2+"="+result);
8 return result;
9 }
10
11
12 //减
13 public int sub(int n1,int n2){
14 int result=n1-n2;
15 System.out.println(n1+"-"+n2+"="+result);
16 return result;
17 }
18
19 //乘
20 public int mut(int n1,int n2){
21 int result=n1*n2;
22 System.out.println(n1+"X"+n2+"="+result);
23 return result;
24 }
25
26 //除
27 public int div(int n1,int n2){
28 int result=n1/n2;
29 System.out.println(n1+"/"+n2+"="+result);
30 return result;
31 }
32 }
现在需求发生了变化,要求项目中所有的类在执行方法时输出执行耗时。最直接的办法是修改源代码,如下所示:
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop01;
2
3 import java.util.Random;
4
5 public class Math {
6 //加
7 public int add(int n1,int n2){
8 //开始时间
9 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
10 lazy();
11 int result=n1+n2;
12 System.out.println(n1+"+"+n2+"="+result);
13 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
14 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
15 return result;
16 }
17
18 //减
19 public int sub(int n1,int n2){
20 //开始时间
21 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
22 lazy();
23 int result=n1-n2;
24 System.out.println(n1+"-"+n2+"="+result);
25 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
26 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
27 return result;
28 }
29
30 //乘
31 public int mut(int n1,int n2){
32 //开始时间
33 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
34 lazy();
35 int result=n1*n2;
36 System.out.println(n1+"X"+n2+"="+result);
37 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
38 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
39 return result;
40 }
41
42 //除
43 public int div(int n1,int n2){
44 //开始时间
45 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
46 lazy();
47 int result=n1/n2;
48 System.out.println(n1+"/"+n2+"="+result);
49 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
50 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
51 return result;
52 }
53
54 //模拟延时
55 public void lazy()
56 {
57 try {
58 int n=(int)new Random().nextInt(500);
59 Thread.sleep(n);
60 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
61 e.printStackTrace();
62 }
63 }
64 }
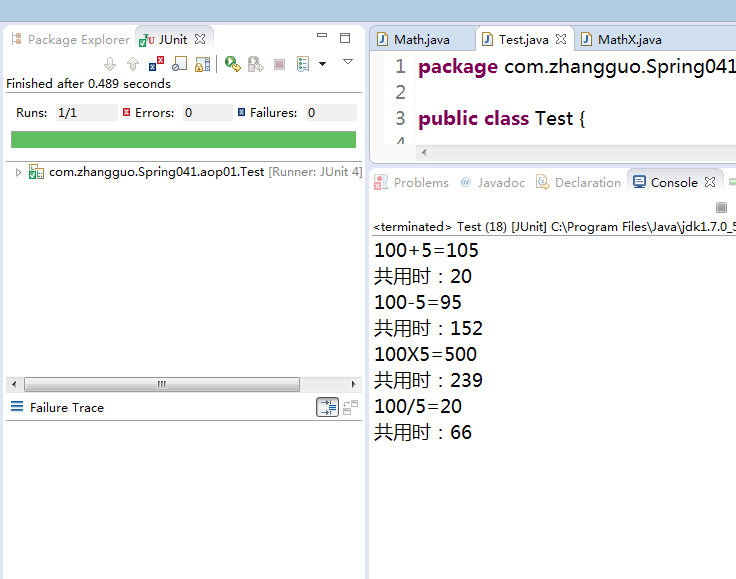
测试运行:
package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop01;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test01()
{
Math math=new Math();
int n1=100,n2=5;
math.add(n1, n2);
math.sub(n1, n2);
math.mut(n1, n2);
math.div(n1, n2);
}
}
运行结果:
缺点:
1、工作量特别大,如果项目中有多个类,多个方法,则要修改多次。
2、违背了设计原则:开闭原则(OCP),对扩展开放,对修改关闭,而为了增加功能把每个方法都修改了,也不便于维护。
3、违背了设计原则:单一职责(SRP),每个方法除了要完成自己本身的功能,还要计算耗时、延时;每一个方法引起它变化的原因就有多种。
4、违背了设计原则:依赖倒转(DIP),抽象不应该依赖细节,两者都应该依赖抽象。而在Test类中,Test与Math都是细节。
使用静态代理可以解决部分问题。
二、静态代理
1、定义抽象主题接口。
package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop02;
/**
* 接口
* 抽象主题
*/
public interface IMath {
//加
int add(int n1, int n2);
//减
int sub(int n1, int n2);
//乘
int mut(int n1, int n2);
//除
int div(int n1, int n2);
}
2、主题类,算术类,实现抽象接口。
package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop02;
/**
* 被代理的目标对象
*真实主题
*/
public class Math implements IMath {
//加
public int add(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1+n2;
System.out.println(n1+"+"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
}
//减
public int sub(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1-n2;
System.out.println(n1+"-"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
}
//乘
public int mut(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1*n2;
System.out.println(n1+"X"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
}
//除
public int div(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1/n2;
System.out.println(n1+"/"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
}
}
3、代理类
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop02;
2
3 import java.util.Random;
4
5 /**
6 * 静态代理类
7 */
8 public class MathProxy implements IMath {
9
10 //被代理的对象
11 IMath math=new Math();
12
13 //加
14 public int add(int n1, int n2) {
15 //开始时间
16 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
17 lazy();
18 int result=math.add(n1, n2);
19 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
20 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
21 return result;
22 }
23
24 //减法
25 public int sub(int n1, int n2) {
26 //开始时间
27 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
28 lazy();
29 int result=math.sub(n1, n2);
30 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
31 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
32 return result;
33 }
34
35 //乘
36 public int mut(int n1, int n2) {
37 //开始时间
38 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
39 lazy();
40 int result=math.mut(n1, n2);
41 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
42 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
43 return result;
44 }
45
46 //除
47 public int div(int n1, int n2) {
48 //开始时间
49 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
50 lazy();
51 int result=math.div(n1, n2);
52 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
53 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
54 return result;
55 }
56
57 //模拟延时
58 public void lazy()
59 {
60 try {
61 int n=(int)new Random().nextInt(500);
62 Thread.sleep(n);
63 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
64 e.printStackTrace();
65 }
66 }
67 }
4、测试运行
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop02;
2
3 public class Test {
4
5 IMath math=new MathProxy();
6 @org.junit.Test
7 public void test01()
8 {
9 int n1=100,n2=5;
10 math.add(n1, n2);
11 math.sub(n1, n2);
12 math.mut(n1, n2);
13 math.div(n1, n2);
14 }
15 }
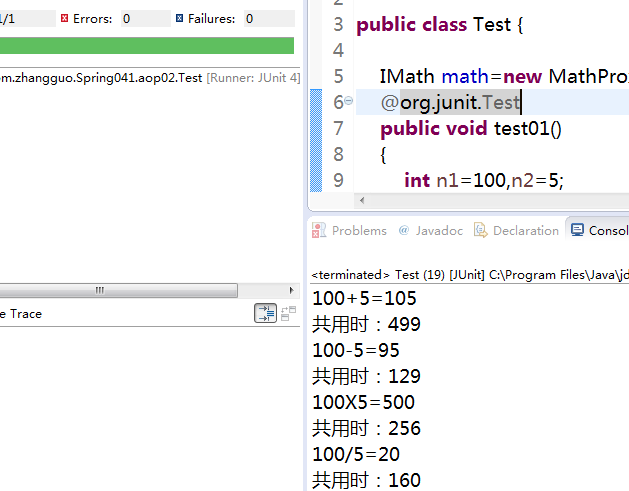
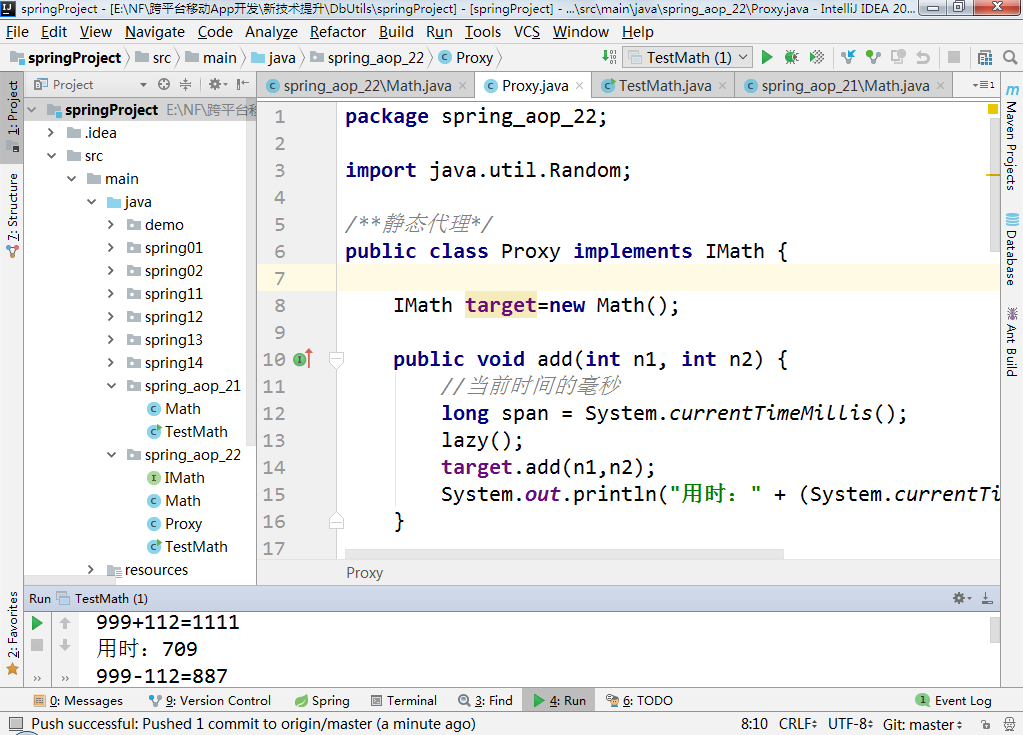
5、小结
通过静态代理,是否完全解决了上述的4个问题:
已解决:
5.1、解决了“开闭原则(OCP)”的问题,因为并没有修改Math类,而扩展出了MathProxy类。
5.2、解决了“依赖倒转(DIP)”的问题,通过引入接口。
5.3、解决了“单一职责(SRP)”的问题,Math类不再需要去计算耗时与延时操作,但从某些方面讲MathProxy还是存在该问题。
未解决:
5.4、如果项目中有多个类,则需要编写多个代理类,工作量大,不好修改,不好维护,不能应对变化。
如果要解决上面的问题,可以使用动态代理。
三、动态代理,使用JDK内置的Proxy实现
只需要一个代理类,而不是针对每个类编写代理类。
在上一个示例中修改代理类MathProxy如下:
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop03;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
4 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
5 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
6 import java.util.Random;
7
8 /**
9 * 动态代理类
10 */
11 public class DynamicProxy implements InvocationHandler {
12
13 //被代理的对象
14 Object targetObject;
15
16 /**
17 * 获得被代理后的对象
18 * @param object 被代理的对象
19 * @return 代理后的对象
20 */
21 public Object getProxyObject(Object object){
22 this.targetObject=object;
23 return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
24 targetObject.getClass().getClassLoader(), //类加载器
25 targetObject.getClass().getInterfaces(), //获得被代理对象的所有接口
26 this); //InvocationHandler对象
27 //loader:一个ClassLoader对象,定义了由哪个ClassLoader对象来生成代理对象进行加载
28 //interfaces:一个Interface对象的数组,表示的是我将要给我需要代理的对象提供一组什么接口,如果我提供了一组接口给它,那么这个代理对象就宣称实现了该接口(多态),这样我就能调用这组接口中的方法了
29 //h:一个InvocationHandler对象,表示的是当我这个动态代理对象在调用方法的时候,会关联到哪一个InvocationHandler对象上,间接通过invoke来执行
30 }
31
32
33 /**
34 * 当用户调用对象中的每个方法时都通过下面的方法执行,方法必须在接口
35 * proxy 被代理后的对象
36 * method 将要被执行的方法信息(反射)
37 * args 执行方法时需要的参数
38 */
39 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
40 //被织入的内容,开始时间
41 long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
42 lazy();
43
44 //使用反射在目标对象上调用方法并传入参数
45 Object result=method.invoke(targetObject, args);
46
47 //被织入的内容,结束时间
48 Long span= System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
49 System.out.println("共用时:"+span);
50
51 return result;
52 }
53
54 //模拟延时
55 public void lazy()
56 {
57 try {
58 int n=(int)new Random().nextInt(500);
59 Thread.sleep(n);
60 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
61 e.printStackTrace();
62 }
63 }
64
65 }
测试运行:
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop03;
2
3 public class Test {
4
5 //实例化一个MathProxy代理对象
6 //通过getProxyObject方法获得被代理后的对象
7 IMath math=(IMath)new DynamicProxy().getProxyObject(new Math());
8 @org.junit.Test
9 public void test01()
10 {
11 int n1=100,n2=5;
12 math.add(n1, n2);
13 math.sub(n1, n2);
14 math.mut(n1, n2);
15 math.div(n1, n2);
16 }
17
18 IMessage message=(IMessage) new DynamicProxy().getProxyObject(new Message());
19 @org.junit.Test
20 public void test02()
21 {
22 message.message();
23 }
24 }
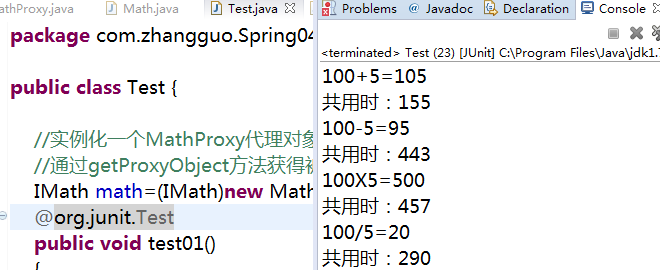
小结:
JDK内置的Proxy动态代理可以在运行时动态生成字节码,而没必要针对每个类编写代理类。中间主要使用到了一个接口InvocationHandler与Proxy.newProxyInstance静态方法,参数说明如下:
使用内置的Proxy实现动态代理有一个问题:被代理的类必须实现接口,未实现接口则没办法完成动态代理。
如果项目中有些类没有实现接口,则不应该为了实现动态代理而刻意去抽出一些没有实例意义的接口,通过cglib可以解决该问题。
四、动态代理,使用cglib实现
CGLIB(Code Generation Library)是一个开源项目,是一个强大的,高性能,高质量的Code生成类库,它可以在运行期扩展Java类与实现Java接口,通俗说cglib可以在运行时动态生成字节码。
4.1、引用cglib,通过maven
修改pom.xml文件,添加依赖
保存pom.xml配置文件,将自动从共享资源库下载cglib所依赖的jar包,主要有如下几个:

4.2、使用cglib完成动态代理,大概的原理是:cglib继承被代理的类,重写方法,织入通知,动态生成字节码并运行,因为是继承所以final类是没有办法动态代理的。具体实现如下:
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop04;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
4 import java.util.Random;
5
6 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
7 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
8 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
9
10 /*
11 * 动态代理类
12 * 实现了一个方法拦截器接口
13 */
14 public class DynamicProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
15
16 // 被代理对象
17 Object targetObject;
18
19 //Generate a new class if necessary and uses the specified callbacks (if any) to create a new object instance.
20 //Uses the no-arg constructor of the superclass.
21 //动态生成一个新的类,使用父类的无参构造方法创建一个指定了特定回调的代理实例
22 public Object getProxyObject(Object object) {
23 this.targetObject = object;
24 //增强器,动态代码生成器
25 Enhancer enhancer=new Enhancer();
26 //回调方法
27 enhancer.setCallback(this);
28 //设置生成类的父类类型
29 enhancer.setSuperclass(targetObject.getClass());
30 //动态生成字节码并返回代理对象
31 return enhancer.create();
32 }
33
34 // 拦截方法
35 public Object intercept(Object object, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
36 // 被织入的横切内容,开始时间 before
37 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
38 lazy();
39
40 // 调用方法
41 Object result = methodProxy.invoke(targetObject, args);
42
43 // 被织入的横切内容,结束时间
44 Long span = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
45 System.out.println("共用时:" + span);
46
47 return result;
48 }
49
50 // 模拟延时
51 public void lazy() {
52 try {
53 int n = (int) new Random().nextInt(500);
54 Thread.sleep(n);
55 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
56 e.printStackTrace();
57 }
58 }
59
60 }
参数:Object为由CGLib动态生成的代理类实例,Method为上文中实体类所调用的被代理的方法引用,Object[]为参数值列表,MethodProxy为生成的代理类对方法的代理引用。
返回:从代理实例的方法调用返回的值。
测试运行:
package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop04;
public class Test {
//实例化一个DynamicProxy代理对象
//通过getProxyObject方法获得被代理后的对象
Math math=(Math)new DynamicProxy().getProxyObject(new Math());
@org.junit.Test
public void test01()
{
int n1=100,n2=5;
math.add(n1, n2);
math.sub(n1, n2);
math.mut(n1, n2);
math.div(n1, n2);
}
//另一个被代理的对象,不再需要重新编辑代理代码
Message message=(Message) new DynamicProxy().getProxyObject(new Message());
@org.junit.Test
public void test02()
{
message.message();
}
}
运行结果:

4.3、小结
使用cglib可以实现动态代理,即使被代理的类没有实现接口,但被代理的类必须不是final类。
五、使用Spring实现AOP
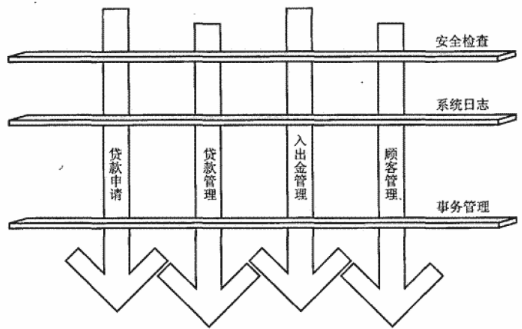
横切关注点:跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能。(软件系统,可以看做由一组关注点即业务或功能或方法组成。其中,直接的业务关注点是直切关注点,而为直切关注点服务的,就是横切关注点。)即是,与我们业务逻辑无关的,但是我们需要关注的部分,就是横切关注点。
切面(ASPECT):横切关注点被模块化的特殊对象。即,它是一个类。
通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作。即,它是类中的一个方法。
目标(Target):被通知对象。
代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
切入点(PointCut):切面通知执行的“地点”的定义。
连接点(JointPoint):与切入点匹配的执行点。
下面示意图:
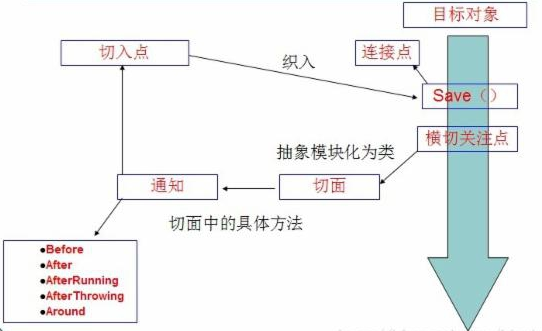
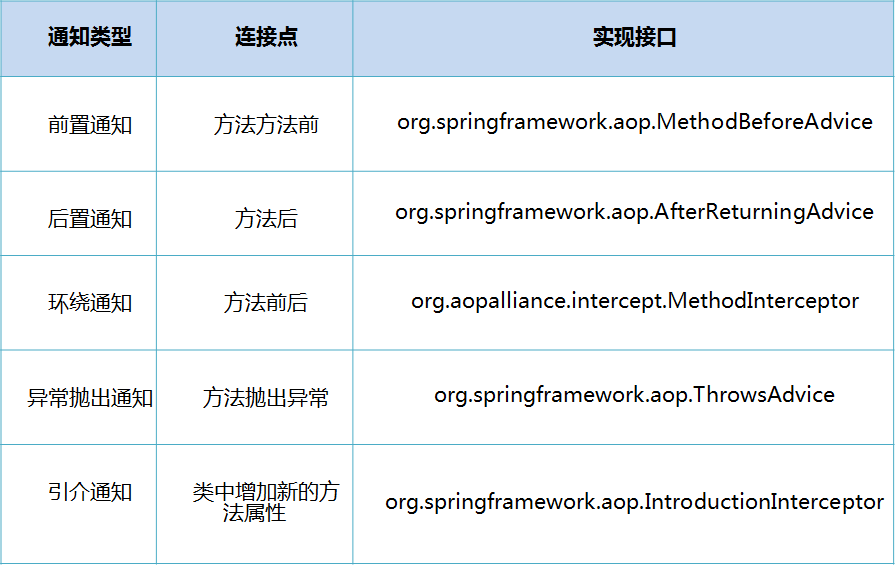
SpringAOP中,通过Advice定义横切逻辑,Spring中支持5种类型的Advice:
5.1、新建 一个Maven项目,在项目中引入Spring核心库与AOP,修改pom.xml文件,在dependencies中增加如下节点:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.3.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
当保存pom.xml文件时会从远程共享库自动将需要引入的jar包下载到本地并引入项目中:
5.2、定义通知(Advice)
前置通知
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop05;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
4
5 import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
6
7 /**
8 * 前置通知
9 */
10 public class BeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
11
12 /**
13 * method 方法信息
14 * args 参数
15 * target 被代理的目标对象
16 */
17 public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
18 System.out.println("-----------------前置通知-----------------");
19 }
20 }
后置通知
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop05;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
4
5 import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
6
7 /**
8 * 后置通知
9 *
10 */
11 public class AfterAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
12
13 /*
14 * returnValue 返回值
15 * method 被调用的方法
16 * args 方法参数
17 * target 被代理对象
18 */
19 public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
20 System.out.println("-----------------后置通知-----------------");
21 }
22
23 }
环绕通知
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop05;
2
3 import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
4 import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
5
6 /**
7 * 环绕通知
8 * 方法拦截器
9 *
10 */
11 public class SurroundAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
12
13 public Object invoke(MethodInvocation i) throws Throwable {
14 //前置横切逻辑
15 System.out.println("方法" + i.getMethod() + " 被调用在对象" + i.getThis() + "上,参数 " + i.getArguments());
16 //方法调用
17 Object ret = i.proceed();
18 //后置横切逻辑
19 System.out.println("返回值:"+ ret);
20 return ret;
21 }
22 }
5.3、创建代理工厂、设置被代理对象、添加通知。
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop05;
2
3 import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
4
5 public class Test {
6
7 @org.junit.Test
8 public void test01()
9 {
10 //实例化Spring代理工厂
11 ProxyFactory factory=new ProxyFactory();
12 //设置被代理的对象
13 factory.setTarget(new Math());
14 //添加通知,横切逻辑
15 factory.addAdvice(new BeforeAdvice());
16 factory.addAdvice(new AfterAdvice());
17 factory.addAdvice(new SurroundAdvice());
18 //从代理工厂中获得代理对象
19 IMath math=(IMath) factory.getProxy();
20 int n1=100,n2=5;
21 math.add(n1, n2);
22 math.sub(n1, n2);
23 math.mut(n1, n2);
24 math.div(n1, n2);
25 }
26 @org.junit.Test
27 public void test02()
28 {
29 //message.message();
30 }
31 }
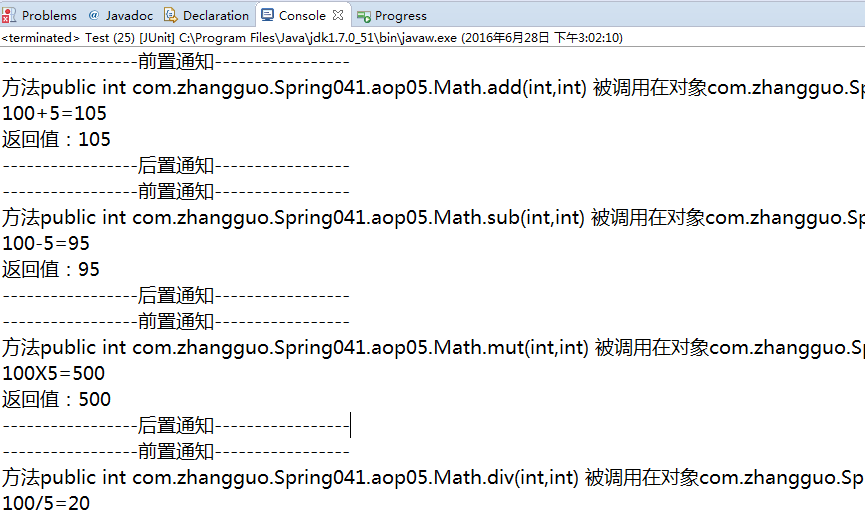
运行结果:
5.4、封装代理创建逻辑
在上面的示例中如果要代理不同的对象需要反复创建ProxyFactory对象,代码会冗余。同样以实现方法耗时为示例代码如下:
5.4.1、创建一个环绕通知:
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop05;
2
3 import java.util.Random;
4
5 import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
6 import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
7
8 /**
9 * 用于完成计算方法执行时长的环绕通知
10 */
11 public class TimeSpanAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
12
13 public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
14 // 被织入的横切内容,开始时间 before
15 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
16 lazy();
17
18 //方法调用
19 Object result = invocation.proceed();
20
21 // 被织入的横切内容,结束时间
22 Long span = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
23 System.out.println("共用时:" + span);
24
25 return result;
26 }
27
28 // 模拟延时
29 public void lazy() {
30 try {
31 int n = (int) new Random().nextInt(500);
32 Thread.sleep(n);
33 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
34 e.printStackTrace();
35 }
36 }
37 }
5.4.2、封装动态代理类
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop05;
2
3 import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
4
5 /**
6 * 动态代理类
7 *
8 */
9 public abstract class DynamicProxy {
10 /**
11 * 获得代理对象
12 * @param object 被代理的对象
13 * @return 代理对象
14 */
15 public static Object getProxy(Object object){
16 //实例化Spring代理工厂
17 ProxyFactory factory=new ProxyFactory();
18 //设置被代理的对象
19 factory.setTarget(object);
20 //添加通知,横切逻辑
21 factory.addAdvice(new TimeSpanAdvice());
22 return factory.getProxy();
23 }
24 }
5.4.3、测试运行
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop05;
2
3 import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
4
5 public class Test {
6
7 @org.junit.Test
8 public void test01()
9 {
10 //从代理工厂中获得代理对象
11 IMath math=(IMath) DynamicProxy.getProxy(new Math());
12 int n1=100,n2=5;
13 math.add(n1, n2);
14 math.sub(n1, n2);
15 math.mut(n1, n2);
16 math.div(n1, n2);
17 }
18 @org.junit.Test
19 public void test02()
20 {
21 IMessage message=(IMessage) DynamicProxy.getProxy(new Message());
22 message.message();
23 }
24 }
运行结果:
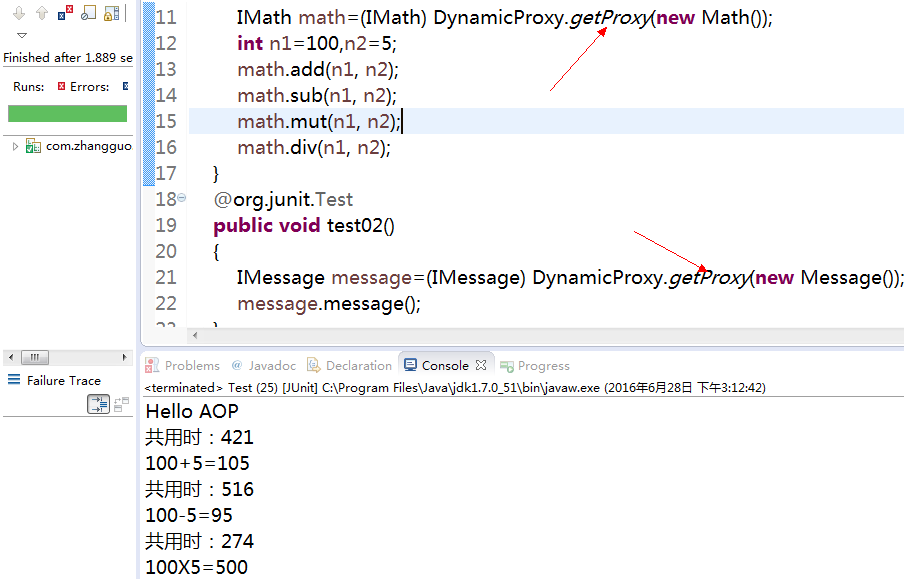
封装动态代理类:
package spring_aop_26;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
public class SpringProxy<T> implements MethodInterceptor {
/**获得代理后的对象*/
public T getProxyObject(Object target){
//代理工厂
ProxyFactory proxy=new ProxyFactory();
//添加被代理的对象
proxy.setTarget(target);
//添加环绕通知
proxy.addAdvice(this);
//获得代理后的对象
return (T) proxy.getProxy();
}
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
before();
//调用方法获得结果
Object result=methodInvocation.proceed();
after(result);
return result;
}
public void before(){
System.out.println("调用方法前");
}
public void after(Object result){
System.out.println("调用方法后"+result);
}
}
运行结果:
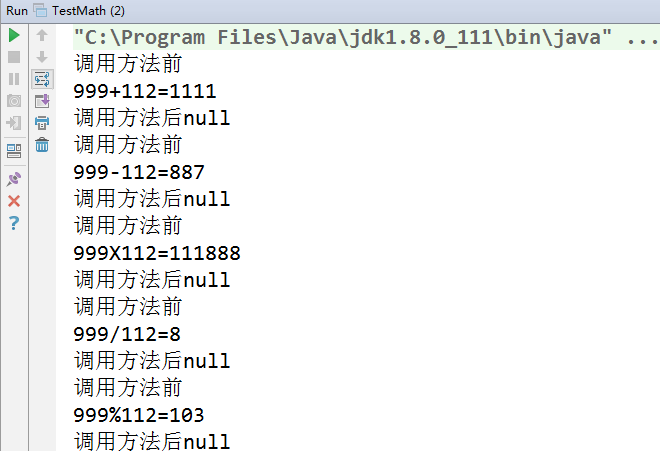
通过反射创建对象:
Class<T> entityClass = (Class<T>) ((ParameterizedType) getClass().getGenericSuperclass()).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
T entity = entityClass.newInstance();
六、使用IOC配置的方式实现AOP
6.1、引入Spring IOC的核心jar包,方法与前面相同。
6.2、创建IOC的配置文件beans.xml,内容如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 6 <!-- 被代理的目标对象 --> 7 <bean id="target" class="com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop06.Math"></bean> 8 <!--通知、横切逻辑--> 9 <bean id="advice" class="com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop06.AfterAdvice"></bean> 10 <!--代理对象 --> 11 <!--interceptorNames 通知数组 --> 12 <!--p:target-ref 被代理的对象--> 13 <!--p:proxyTargetClass 被代理对象是否为一个类,如果是则使用cglib,否则使用jdk动态代理 --> 14 <bean id="proxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean" 15 p:interceptorNames="advice" 16 p:target-ref="target" 17 p:proxyTargetClass="true"></bean> 18 </beans>
6.3、获得代理类的实例并测试运行
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop06;
2
3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
5
6 public class Test {
7
8 @org.junit.Test
9 public void test01()
10 {
11 //容器
12 ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
13 //从代理工厂中获得代理对象
14 IMath math=(IMath)ctx.getBean("proxy");
15 int n1=100,n2=5;
16 math.add(n1, n2);
17 math.sub(n1, n2);
18 math.mut(n1, n2);
19 math.div(n1, n2);
20 }
21 }

6.4、小结
这里有个值得注意的问题:从容器中获得proxy对象时应该是org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean类型的对象(如下代码所示),但这里直接就转换成IMath类型了,这是因为:ProxyFactoryBean本质上是一个用来生产Proxy的FactoryBean。如果容器中的某个对象持有某个FactoryBean的引用它取得的不是FactoryBean本身而是 FactoryBean的getObject()方法所返回的对象。所以如果容器中某个对象依赖于ProxyFactoryBean那么它将会使用到 ProxyFactoryBean的getObject()方法所返回的代理对象这就是ProxyFactryBean得以在容器中使用的原因。
1 ProxyFactoryBean message=new ProxyFactoryBean(); 2 message.setTarget(new Message()); 3 message.addAdvice(new SurroundAdvice()); 4 ((IMessage)message.getObject()).message();
七、使用XML配置Spring AOP切面
7.1、添加引用,需要引用一个新的jar包:aspectjweaver,该包是AspectJ的组成部分。可以去http://search.maven.org搜索后下载或直接在maven项目中添加依赖。
示例中使用pom.xml文件如下所示:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zhangguo</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring041</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Spring041</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.version>4.3.0.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<version>4.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
7.2、定义通知
该通知不再需要实现任何接口或继承抽象类,一个普通的bean即可,方法可以带一个JoinPoint连接点参数,用于获得连接点信息,如方法名,参数,代理对象等。
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08;
2
3 import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
4
5 /**
6 * 通知
7 */
8 public class Advices {
9 //前置通知
10 public void before(JoinPoint jp)
11 {
12 System.out.println("--------------------bofore--------------------");
13 System.out.println("方法名:"+jp.getSignature()+",参数:"+jp.getArgs().length+",代理对象:"+jp.getTarget());
14 }
15 //后置通知
16 public void after(JoinPoint jp){
17 System.out.println("--------------------after--------------------");
18 }
19 }
通知的类型有多种,有些参数会不一样,特别是环绕通知,通知类型如下:
1 //前置通知 2 public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) 3 4 //后置通知 5 public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) 6 7 //返回值通知 8 public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) 9 10 //抛出异常通知 11 //在方法出现异常时会执行的代码可以访问到异常对象,可以指定在出现特定异常时在执行通知代码 12 public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) 13 14 //环绕通知 15 //环绕通知需要携带ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数 16 //环绕通知类似于动态代理的全过程:ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数可以决定是否执行目标方法。 17 //而且环绕通知必须有返回值,返回值即为目标方法的返回值 18 public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd)
7.3、配置IOC容器依赖的XML文件beansOfAOP.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 6 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd"> 10 11 <!--被代理的目标对象 --> 12 <bean id="math" class="com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math"></bean> 13 <!-- 通知 --> 14 <bean id="advice" class="com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Advices"></bean> 15 <!-- AOP配置 --> 16 <!-- proxy-target-class属性表示被代理的类是否为一个没有实现接口的类,Spring会依据实现了接口则使用JDK内置的动态代理,如果未实现接口则使用cblib --> 17 <aop:config proxy-target-class="true"> 18 <!-- 切面配置 --> 19 <!--ref表示通知对象的引用 --> 20 <aop:aspect ref="advice"> 21 <!-- 配置切入点(横切逻辑将注入的精确位置) --> 22 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.*(..))" id="pointcut1"/> 23 <!--声明通知,method指定通知类型,pointcut指定切点,就是该通知应该注入那些方法中 --> 24 <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/> 25 <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/> 26 </aop:aspect> 27 </aop:config> 28 </beans>
加粗部分的内容是在原IOC内容中新增的,主要是为AOP服务,如果引入失败则没有智能提示。xmlns:是xml namespace的简写。xmlns:xsi:其xsd文件是xml需要遵守的规范,通过URL可以看到,是w3的统一规范,后面通过xsi:schemaLocation来定位所有的解析文件,这里只能成偶数对出现。
<bean id="advice" class="com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Advices"></bean>表示通知bean,也就是横切逻辑bean。<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">用于AOP配置,proxy-target-class属性表示被代理的类是否为一个没有实现接口的类,Spring会依据实现了接口则使用JDK内置的动态代理,如果未实现接口则使用cblib;在Bean配置文件中,所有的Spring AOP配置都必须定义在<aop:config>元素内部。对于每个切面而言,都要创建一个<aop:aspect>元素来为具体的切面实现引用后端Bean实例。因此,切面Bean必须有一个标识符,供<aop:aspect>元素引用。
aop:aspect表示切面配置, ref表示通知对象的引用;aop:pointcut是配置切入点,就是横切逻辑将注入的精确位置,那些包,类,方法需要拦截注入横切逻辑。
aop:before用于声明通知,method指定通知类型,pointcut指定切点,就是该通知应该注入那些方法中。在aop Schema中,每种通知类型都对应一个特定地XML元素。通知元素需要pointcut-ref属性来引用切入点,或者用pointcut属性直接嵌入切入点表达式。method属性指定切面类中通知方法的名称。有如下几种:
<!-- 前置通知 --> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/> <!-- 后置通知 --> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/> <!--环绕通知 --> <aop:around method="around" pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.s*(..))"/> <!--异常通知 --> <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.d*(..))" throwing="exp"/> <!-- 返回值通知 --> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.m*(..))" returning="result"/>
参数解释:
7.3.1 表达式类型
标准的Aspectj Aop的pointcut的表达式类型是很丰富的,但是Spring Aop只支持其中的9种,外加Spring Aop自己扩充的一种一共是10种类型的表达式,分别如下。
- execution:一般用于指定方法的执行,用的最多。
- within:指定某些类型的全部方法执行,也可用来指定一个包。
- this:Spring Aop是基于代理的,生成的bean也是一个代理对象,this就是这个代理对象,当这个对象可以转换为指定的类型时,对应的切入点就是它了,Spring Aop将生效。
- target:当被代理的对象可以转换为指定的类型时,对应的切入点就是它了,Spring Aop将生效。
- args:当执行的方法的参数是指定类型时生效。
- @target:当代理的目标对象上拥有指定的注解时生效。
- @args:当执行的方法参数类型上拥有指定的注解时生效。
- @within:与@target类似,看官方文档和网上的说法都是@within只需要目标对象的类或者父类上有指定的注解,则@within会生效,而@target则是必须是目标对象的类上有指定的注解。而根据笔者的测试这两者都是只要目标类或父类上有指定的注解即可。
- @annotation:当执行的方法上拥有指定的注解时生效。
- bean:当调用的方法是指定的bean的方法时生效。
7.3.2 使用示例
(1) execution
execution是使用的最多的一种Pointcut表达式,表示某个方法的执行,其标准语法如下。
execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern? name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
modifiers-pattern表示方法的访问类型,public等;
ret-type-pattern表示方法的返回值类型,如String表示返回类型是String,“*”表示所有的返回类型;
declaring-type-pattern表示方法的声明类,如“com.elim..*”表示com.elim包及其子包下面的所有类型;
name-pattern表示方法的名称,如“add*”表示所有以add开头的方法名;
param-pattern表示方法参数的类型,name-pattern(param-pattern)其实是一起的表示的方法集对应的参数类型,如“add()”表示不带参数的add方法,“add(*)”表示带一个任意类型的参数的add方法,“add(*,String)”则表示带两个参数,且第二个参数是String类型的add方法;
throws-pattern表示异常类型;其中以问号结束的部分都是可以省略的。
- 1、“execution(* add())”匹配所有的不带参数的add()方法。
- 2、“execution(public * com..*.add*(..))”匹配所有com包及其子包下所有类的以add开头的所有public方法。
- 3、“execution(* *(..) throws Exception)”匹配所有抛出Exception的方法。
(2) within
within是用来指定类型的,指定类型中的所有方法将被拦截。
- 1、“within(com.spring.aop.service.UserServiceImpl)”匹配UserServiceImpl类对应对象的所有方法外部调用,而且这个对象只能是UserServiceImpl类型,不能是其子类型。
- 2、“within(com.elim..*)”匹配com.elim包及其子包下面所有的类的所有方法的外部调用。
(3) this
Spring Aop是基于代理的,this就表示代理对象。this类型的Pointcut表达式的语法是this(type),当生成的代理对象可以转换为type指定的类型时则表示匹配。基于JDK接口的代理和基于CGLIB的代理生成的代理对象是不一样的。
- 1、“this(com.spring.aop.service.IUserService)”匹配生成的代理对象是IUserService类型的所有方法的外部调用。
(4) target
Spring Aop是基于代理的,target则表示被代理的目标对象。当被代理的目标对象可以被转换为指定的类型时则表示匹配。
- 1、“target(com.spring.aop.service.IUserService)”则匹配所有被代理的目标对象能够转换为IUserService类型的所有方法的外部调用。
(5) args
args用来匹配方法参数的。
- 1、“args()”匹配任何不带参数的方法。
- 2、“args(java.lang.String)”匹配任何只带一个参数,而且这个参数的类型是String的方法。
- 3、“args(..)”带任意参数的方法。
- 4、“args(java.lang.String,..)”匹配带任意个参数,但是第一个参数的类型是String的方法。
- 5、“args(..,java.lang.String)”匹配带任意个参数,但是最后一个参数的类型是String的方法。
(6) @target
@target匹配当被代理的目标对象对应的类型及其父类型上拥有指定的注解时。
- 1、“@target(com.spring.support.MyAnnotation)”匹配被代理的目标对象对应的类型上拥有MyAnnotation注解时。
(7) @args
@args匹配被调用的方法上含有参数,且对应的参数类型上拥有指定的注解的情况。
- 1、“@args(com.spring.support.MyAnnotation)”匹配方法参数类型上拥有MyAnnotation注解的方法调用。如我们有一个方法add(MyParam param)接收一个MyParam类型的参数,而MyParam这个类是拥有注解MyAnnotation的,则它可以被Pointcut表达式“@args(com.elim.spring.support.MyAnnotation)”匹配上。
(8) @within
@within用于匹配被代理的目标对象对应的类型或其父类型拥有指定的注解的情况,但只有在调用拥有指定注解的类上的方法时才匹配。
- 1、“@within(com.spring.support.MyAnnotation)”匹配被调用的方法声明的类上拥有MyAnnotation注解的情况。比如有一个ClassA上使用了注解MyAnnotation标注,并且定义了一个方法a(),那么在调用ClassA.a()方法时将匹配该Pointcut;如果有一个ClassB上没有MyAnnotation注解,但是它继承自ClassA,同时它上面定义了一个方法b(),那么在调用ClassB().b()方法时不会匹配该Pointcut,但是在调用ClassB().a()时将匹配该方法调用,因为a()是定义在父类型ClassA上的,且ClassA上使用了MyAnnotation注解。但是如果子类ClassB覆写了父类ClassA的a()方法,则调用ClassB.a()方法时也不匹配该Pointcut。
(9) @annotation
@annotation用于匹配方法上拥有指定注解的情况。
- 1、“@annotation(com.spring.support.MyAnnotation)”匹配所有的方法上拥有MyAnnotation注解的方法外部调用。
(10) bean
bean用于匹配当调用的是指定的Spring的某个bean的方法时。
- 1、“bean(abc)”匹配Spring Bean容器中id或name为abc的bean的方法调用。
- 2、“bean(user*)”匹配所有id或name为以user开头的bean的方法调用。
7.3.4 表达式组合
表达式的组合其实就是对应的表达式的逻辑运算,与、或、非。可以通过它们把多个表达式组合在一起。
- 1、“bean(userService) && args()”匹配id或name为userService的bean的所有无参方法。
- 2、“bean(userService) || @annotation(MyAnnotation)”匹配id或name为userService的bean的方法调用,或者是方法上使用了MyAnnotation注解的方法调用。
- 3、“bean(userService) && !args()”匹配id或name为userService的bean的所有有参方法调用。
7.3.5 基于Aspectj注解的Pointcut表达式应用
在使用基于Aspectj注解的Spring Aop时,我们可以把通过@Pointcut注解定义Pointcut,指定其表达式,然后在需要使用Pointcut表达式的时候直接指定Pointcut。
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* add(..))")
private void beforeAdd() {}
@Before("beforeAdd()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("-----------before-----------");
}
}
上面的代码中我们就是在@Before()中直接指定使用当前类定义的beforeAdd()方法对应的Pointcut的表达式,如果我们需要指定的Pointcut定义不是在当前类中的,我们需要加上类名称,如下面这个示例中引用的就是定义在MyService中的add()方法上的Pointcut的表达式。
@Before("com.spring.aop.service.MyService.add()")
public void before2() {
System.out.println("-----------before2-----------");
}
当然了,除了通过引用Pointcut定义间接的引用其对应的Pointcut表达式外,我们也可以直接使用Pointcut表达式的,如下面这个示例就直接在@Before中使用了Pointcut表达式。
/**
* 所有的add方法的外部执行时
*/
@Before("execution(* add())")
public void beforeExecution() {
System.out.println("-------------before execution---------------");
}
7.4、获得代理对象
1 package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08;
2
3 import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean;
4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
6
7 public class Test {
8
9 @org.junit.Test
10 public void test01()
11 {
12 //容器
13 ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beansOfAOP.xml");
14 //从代理工厂中获得代理对象
15 IMath math=(IMath)ctx.getBean("math");
16 int n1=100,n2=5;
17 math.add(n1, n2);
18 math.sub(n1, n2);
19 math.mut(n1, n2);
20 math.div(n1, n2);
21 }
22 }
7.5、测试运行
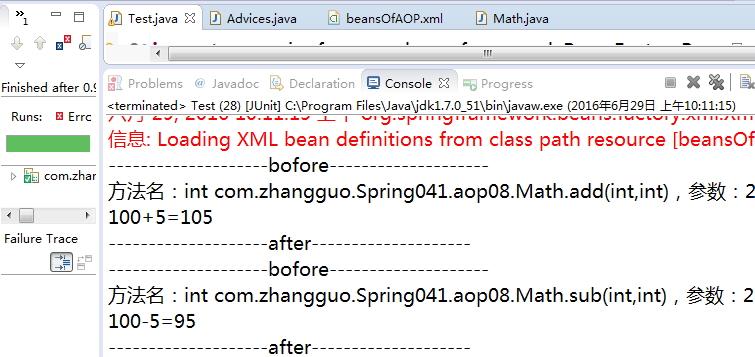
7.6、环绕通知、异常后通知、返回结果后通知
在配置中我们发现共有5种类型的通知,前面我们试过了前置通知与后置通知,另外几种类型的通知如下代码所示:
package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
/**
* 通知
*/
public class Advices {
//前置通知
public void before(JoinPoint jp)
{
System.out.println("--------------------前置通知--------------------");
System.out.println("方法名:"+jp.getSignature().getName()+",参数:"+jp.getArgs().length+",被代理对象:"+jp.getTarget().getClass().getName());
}
//后置通知
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("--------------------后置通知--------------------");
}
//环绕通知
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("--------------------环绕开始--------------------");
Object object=pjd.proceed();
System.out.println("--------------------环绕结束--------------------");
return object;
}
//异常后通知
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint jp,Exception exp)
{
System.out.println("--------------------异常后通知,发生了异常:"+exp.getMessage()+"--------------------");
}
//返回结果后通知
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result)
{
System.out.println("--------------------返回结果后通知--------------------");
System.out.println("结果是:"+result);
}
}
参数说明:
Spring的AOP中before,afterReturning,afterThrowing参数说明:
1、持行方法之前:public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object cObj) throws Throwable;
method:调用的方法;
args:调用方法所传的参数数组;
cObj:调用的类对象;
2、持行方法之后:public void afterReturning(Object rObj, Method method, Object[] args, Object cObj) throws Throwable;
rObj:调用方法返回的对象;
method:调用的方法;
args:调用方法所传的参数数组;
cObj:调用的类对象;
3、有异常抛出时:public void afterThrowing(Method method, Object[] args, Object cObj, Exception e);
method:调用的方法;
args:调用方法所传的参数数组;
cObj:调用的类对象;
e:所抛出的异常类型;
在异常抛出时的Exception必须指定为具体的异常对象,如ClassNotFoundException。
容器配置文件beansOfAOP.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!--被代理的目标对象 -->
<bean id="math" class="com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math"></bean>
<!-- 通知 -->
<bean id="advice" class="com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Advices"></bean>
<!-- AOP配置 -->
<!-- proxy-target-class属性表示被代理的类是否为一个没有实现接口的类,Spring会依据实现了接口则使用JDK内置的动态代理,如果未实现接口则使用cblib -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- 切面配置 -->
<!--ref表示通知对象的引用 -->
<aop:aspect ref="advice">
<!-- 配置切入点(横切逻辑将注入的精确位置) -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.a*(..))" id="pointcut1"/>
<!--声明通知,method指定通知类型,pointcut指定切点,就是该通知应该注入那些方法中 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.s*(..))"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.d*(..))" throwing="exp"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08.Math.m*(..))" returning="result"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
测试代码:
package com.zhangguo.Spring041.aop08;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test01()
{
//容器
ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beansOfAOP.xml");
//从代理工厂中获得代理对象
IMath math=(IMath)ctx.getBean("math");
int n1=100,n2=0;
math.add(n1, n2);
math.sub(n1, n2);
math.mut(n1, n2);
math.div(n1, n2);
}
}
运行结果:

小结:不同类型的通知参数可能不相同;aop:after-throwing需要指定通知中参数的名称throwing="exp",则方法中定义应该是这样:afterThrowing(JoinPoint jp,Exception exp);aop:after-returning同样需要设置returning指定方法参数的名称。通过配置切面的方法使AOP变得更加灵活。
7.6、spring中使用Aspect方式进行AOP如何得到method对象
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
try
{
Object[] arguments = pjp.getArgs();
result = method.invoke(mock, arguments);
s_logger.debug("Mocking " + formatCall(a_joinPoint));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e)
{
s_logger.debug("Failed to delegate to mock: "
+ formatCall(a_joinPoint), e);
throw e.getTargetException();
}
八、示例下载
https://git.coding.net/zhangguo5/Spring.git




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号