Java集合框架(一)
集合框架的概述
1 集合、数组都是对多个数据进行存储操作的结构,简称Java容器。
说明:此时的存储,主要指的是内存层面的存储,不涉及到持久化的存储(.txt,.jpg,.avi,数据库中)
2.1 数组在存储多个数据方面的特点:
一旦初始化以后,其长度就确定了。
数组一旦定义好,其元素的类型也就确定了。我们也就只能操作指定类型的数据了。
比如:String[] arr;int[] arr1;Object[] arr2;
2.2 数组在存储多个数据方面的缺点:
一旦初始化以后,其长度就不可修改。
数组中提供的方法非常有限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不便,同时效率不高。
获取数组中实际元素的个数的需求,数组没有现成的属性或方法可用
数组存储数据的特点:有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足。
集合框架的结构
|----Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象
|----List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。 -->“动态”数组
|----ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
|----Set接口:存储无序的、不可重复的数据 -->高中讲的“集合”
|----HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
|----Map接口:双列集合,用来存储一对(key - value)一对的数据 -->高中函数:y = f(x)
|----HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable、Properties
Collection常用方法
- 以ArrayList类为例
@Test
public void test2(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
//add(Object e):将元素e添加到集合coll中
coll.add("AA");
coll.add("BB");
coll.add(123);//自动装箱
coll.add(new Date());
//size():获取添加的元素的个数
System.out.println(coll.size());//4
//addAll(Collection coll1):将coll1集合中的元素添加到当前的集合中
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(456);
coll1.add("CC");
coll.addAll(coll1);
System.out.println(coll.size());//6
System.out.println(coll);
//clear():清空集合元素
coll.clear();
//isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空
System.out.println(coll.isEmpty());
contain或containsAll当中的相等比较是,调用集合中每个对象的equals,如果对某个类的比较有要求,需要在类中重写equal()
@Test
public void test1(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
// Person p = new Person("Jerry",20);
// coll.add(p);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry",20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//1.contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否包含obj
//我们在判断时会调用obj对象所在类的equals()。
boolean contains = coll.contains(123);
System.out.println(contains);
System.out.println(coll.contains(new String("Tom")));
// System.out.println(coll.contains(p));//true
System.out.println(coll.contains(new Person("Jerry",20)));//false -->true,重写equals
//2.containsAll(Collection coll1):判断形参coll1中的所有元素是否都存在于当前集合中。
Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,4567);
System.out.println(coll.containsAll(coll1));
}
@Test
public void test2(){
//3.remove(Object obj):从当前集合中移除obj元素。
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry",20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
coll.remove(1234); //如果是添加内容,也需要进行搜索与equal()
System.out.println(coll);
coll.remove(new Person("Jerry",20));
System.out.println(coll);
//4. removeAll(Collection coll1):差集:从当前集合中移除coll1中所有的元素。
Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456);
coll.removeAll(coll1);
System.out.println(coll);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry",20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//5.retainAll(Collection coll1):交集:获取当前集合和coll1集合的交集,并返回给当前集合
// Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456,789);
// coll.retainAll(coll1);
// System.out.println(coll);
//6.equals(Object obj):要想返回true,需要当前集合和形参集合的元素都相同(ArrayList有序)。
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(456);
coll1.add(123);
coll1.add(new Person("Jerry",20));
coll1.add(new String("Tom"));
coll1.add(false);
System.out.println(coll.equals(coll1));
}
@Test
public void test4(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry",20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//7.hashCode():返回当前对象的哈希值
System.out.println(coll.hashCode());
//8.集合 --->数组:toArray()
Object[] arr = coll.toArray();
for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
//拓展:数组 --->集合:调用Arrays类的静态方法asList()
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"AA", "BB", "CC"});
System.out.println(list);
List arr1 = Arrays.asList(new int[]{123, 456});
System.out.println(arr1.size());//1
List arr2 = Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{123, 456});
System.out.println(arr2.size());//2
}
}
Iterator迭代器
集合元素的遍历操作,使用迭代器Iterator接口
1.内部的方法:hasNext() 和 next()
2.集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,
默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前。
3.内部定义了remove(),可以在遍历的时候,删除集合中的元素。此方法不同于集合直接调用remove()
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry",20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
//next():①指针下移 ②将下移以后集合位置上的元素返回
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
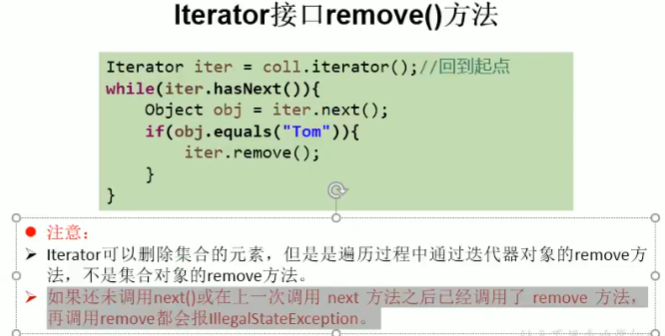
foreach迭代器:遍历数组、Collection集合
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
for(Object obj : coll){
System.out.println(obj);
}
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6};
//for(数组元素的类型 局部变量 : 数组对象)
for(int i : arr){
System.out.println(i);
}
ArrayList的源码分析
2.1 jdk 7情况下
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();//底层创建了长度是10的Object[]数组elementData
list.add(123);//elementData[0] = new Integer(123);
...
list.add(11);//如果此次的添加导致底层elementData数组容量不够,则扩容。
默认情况下,扩容为原来的容量的1.5倍,同时需要将原有数组中的数据复制到新的数组中。
结论:建议开发中使用带参的构造器:ArrayList list = new ArrayList(int capacity)
2.2 jdk 8中ArrayList的变化:
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();//底层Object[] elementData初始化为{}.并没有创建长度为10的数组
list.add(123);//第一次调用add()时,底层才创建了长度10的数组,并将数据123添加到elementData[0]
...
后续的添加和扩容操作与jdk7无异。
2.3 小结:jdk7中的ArrayList的对象的创建类似于单例的饿汉式,而jdk8中的ArrayList的对象的创建类似于单例的懒汉式,延迟了数组的创建,节省内存。
LinkedList的源码分析
LinkedList的源码分析:
LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); 内部声明了Node类型的first和last属性,默认值为null
list.add(123);//将123封装到Node中,创建了Node对象。其中,Node定义为:体现了LinkedList的双向链表的说法
Vector的源码分析
Vector的源码分析:jdk7和jdk8中通过Vector()构造器创建对象时,底层都创建了长度为10的数组。
在扩容方面,默认扩容为原来的数组长度的2倍。
List接口下的方法(根据有序特性)
void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置插入ele元素
boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的所有元素添加进来
Object get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素
int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置
int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置
Object remove(int index):移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素
Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为ele
List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合
ps:remove(10)默认是索引,如果要找数的对象就转换remove(new Integer(10))





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现