【JDK】JDK源码分析-Map
Map 接口
Map 是一个接口,它表示一种“键-值(key-value)”映射的对象(Entry),其中键是不重复的(值可以重复),且最多映射到一个值(可以理解为“映射”或者“字典”)。
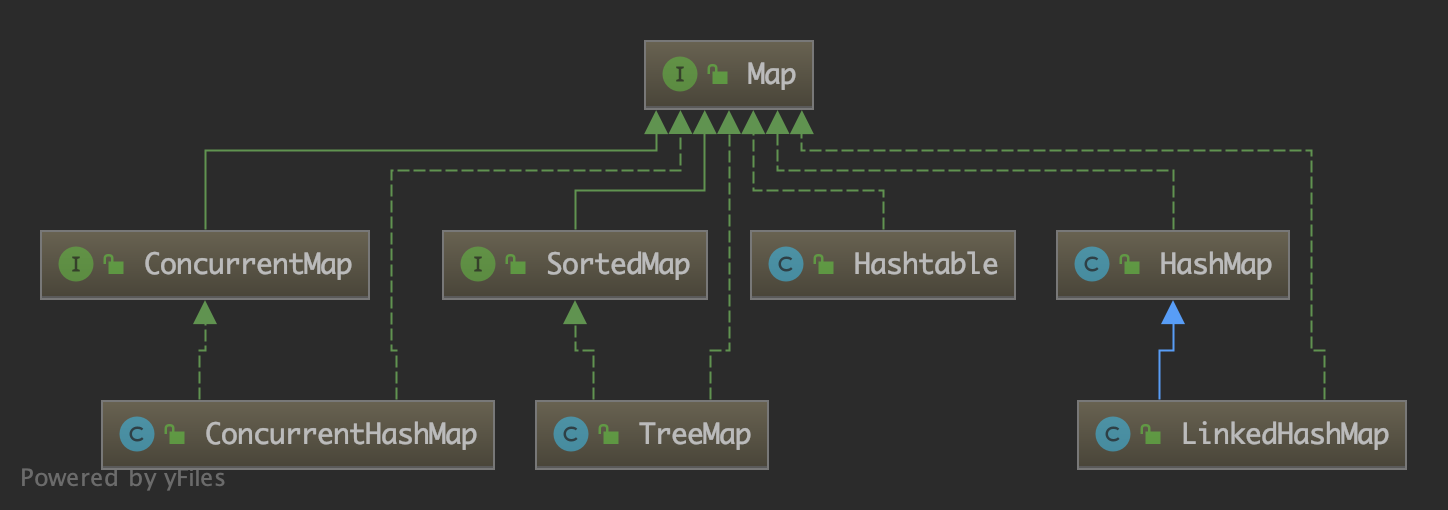
Map 常用的实现类有 HashMap、TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap、LinkedHashMap 等,它们的继承结构如下:
Map 的方法列表如下:
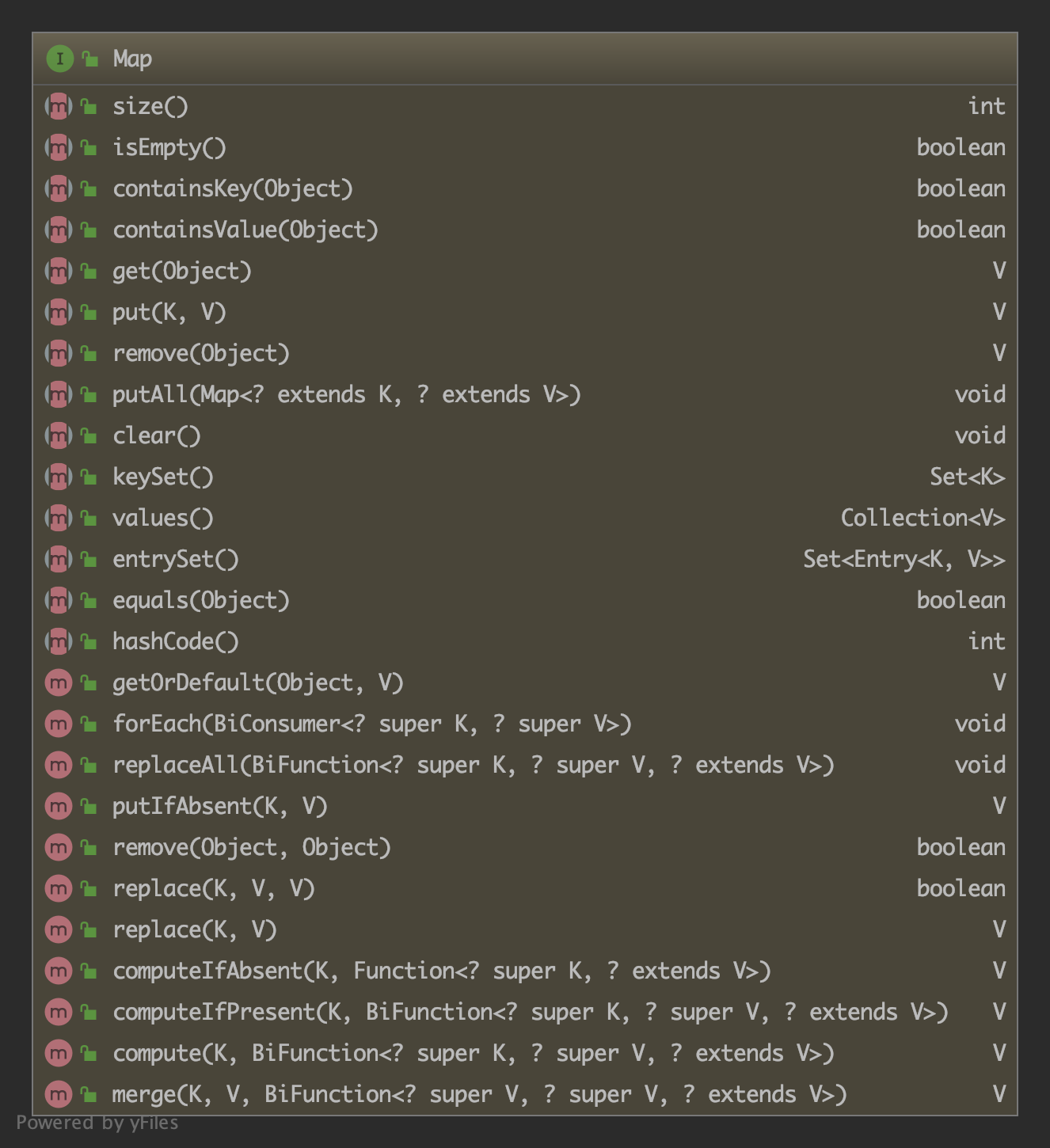
一些常用方法:
// 将键-值对存入 Map,若 key 对应的 value 已存在,则将其替换 // 返回原先 key 对应的 value(若不存在,返回 null) V put(K key, V value); // 将指定 Map 中的所有元素拷贝到本 Map 中 void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m); // 返回本 Map 中所有 key 的 Set 视图 Set<K> keySet(); // 返回本 Map 中所有 value 的 Collection 视图 Collection<V> values(); // 返回本 Map 中所有 Entry 的 Set 视图 // 其中 Entry 是 Map 内部的一个接口,可以理解为 Map 的“元数据” Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
此外,JDK 1.8 又增加了不少方法,如下:
// 获取 key 对应的 value,若 value 为 null,则返回 defaultValue default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) { V v; return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) ? v : defaultValue; } // 遍历 Map 中的元素 default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) { K k; V v; try { k = entry.getKey(); v = entry.getValue(); } catch(IllegalStateException ise) { // this usually means the entry is no longer in the map. throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise); } action.accept(k, v); } } // 通过给定的函数计算出新的 Entry 替换所有旧的 Entry default void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) { Objects.requireNonNull(function); for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) { K k; V v; try { k = entry.getKey(); v = entry.getValue(); } catch(IllegalStateException ise) { // this usually means the entry is no longer in the map. throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise); } // ise thrown from function is not a cme. v = function.apply(k, v); try { entry.setValue(v); } catch(IllegalStateException ise) { // this usually means the entry is no longer in the map. throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise); } } } // 若 key 对应的 value 不存在,则把 key-value 存入 Map,否则无操作 default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) { V v = get(key); if (v == null) { v = put(key, value); } return v; } // 若 key 对应的值等于 value,则移除 key;否则无操作 default boolean remove(Object key, Object value) { Object curValue = get(key); if (!Objects.equals(curValue, value) || (curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) { return false; } remove(key); return true; } // 若 key 对应的值等于 oldValue,则将其替换为 newValue;否则无操作 default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) { Object curValue = get(key); if (!Objects.equals(curValue, oldValue) || (curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) { return false; } put(key, newValue); return true; } // Map 中存在 key 时,将 key-value 存入,相当于: /* if (map.containsKey(key)) { return map.put(key, value); } else return null; } */ default V replace(K key, V value) { V curValue; if (((curValue = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) { curValue = put(key, value); } return curValue; } // 当 key 对应的 value 不存在时,使用给定的函数计算得出 newValue // 并将 key-newValue 存入 Map default V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) { Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction); V v; if ((v = get(key)) == null) { V newValue; if ((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) != null) { put(key, newValue); return newValue; } } return v; } // 当 key 对应的 value 存在时,使用给定的函数计算得出 newValue, // 当 newValue 不为 null 时将 key-newValue 存入 Map;否则移除 key default V computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) { Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction); V oldValue; if ((oldValue = get(key)) != null) { V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue); if (newValue != null) { put(key, newValue); return newValue; } else { remove(key); return null; } } else { return null; } } // 根据 key 和其对应的 oldValue,使用给定的函数计算出 newValue // 若 newValue 为 null // 若 oldValue 不为空或 key 存在,则删除 key-oldValue // 否则无操作 // 若 newValue 不为 null,用 newValue 替换 oldValue default V compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) { Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction); V oldValue = get(key); V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue); if (newValue == null) { // delete mapping if (oldValue != null || containsKey(key)) { // something to remove remove(key); return null; } else { // nothing to do. Leave things as they were. return null; } } else { // add or replace old mapping put(key, newValue); return newValue; } } default V merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) { Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction); Objects.requireNonNull(value); V oldValue = get(key); V newValue = (oldValue == null) ? value : remappingFunction.apply(oldValue, value); if(newValue == null) { remove(key); } else { put(key, newValue); } return newValue; }
PS: 1.8 中的几个方法看似比较复杂,但有些方法实质上相当于对一些 if...else 语句的封装,利用 lambda 表达式可以让代码更简洁。
Entry 接口
Map 接口内部还定义了一个 Entry 接口(上面已经出现),它其实相当于 Map 内部存储的「元数据」,也就是 键-值(key-value) 映射。方法列表如下:
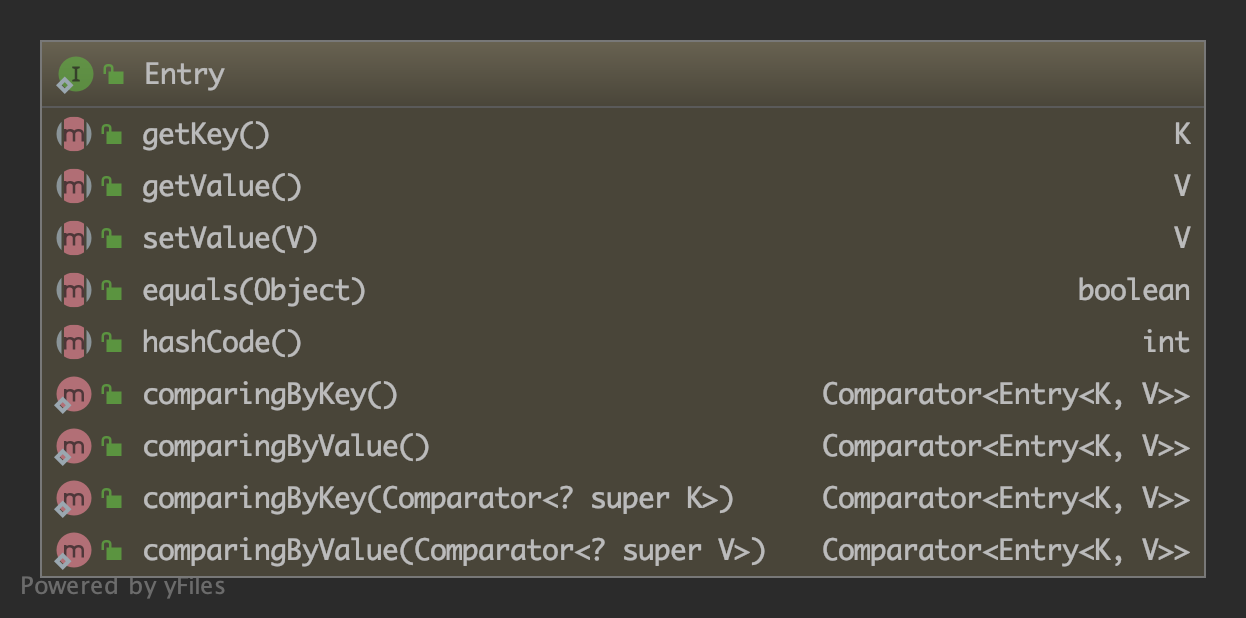
其中前面几个方法都比较简单,这里分析下后面几个 JDK 1.8 引入的方法,如下:
// 返回一个比较器,它以自然顺序比较 Entry 的 key public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() { return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey()); } // 返回一个比较器,它以自然顺序比较 Entry 的 value public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() { return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue()); } // 返回一个比较器,它使用给定的 Comparator 比较 Entry 的 key public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<? super K> cmp) { Objects.requireNonNull(cmp); return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey()); } // 返回一个比较器,它使用给定的 Comparator 比较 Entry 的 value public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<? super V> cmp) { Objects.requireNonNull(cmp); return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue()); }
小结
1. Map 接口虽然没有继承自 Collection 接口,但也是 JCF(Java Collections Framework) 的一部分;
2. Map 存储的是键-值(key-value)映射结构的对象;
3. Entry 接口定义在其内部,它是真正定义键-值映射的结构,相当于 Map 的「元数据」。
Stay hungry, stay foolish.

PS: 本文首发于微信公众号【WriteOnRead】。

